Understanding Treasury Bills and Their Appeal
Treasury Bills, commonly known as T-bills, represent short-term debt securities issued by the government. They serve as a fundamental tool for the government to raise funds for various operational needs. These instruments are highly regarded in the investment world, particularly among those with a conservative approach, primarily because they are backed by the full faith and credit of the issuing government. This backing translates to a very low-risk investment option, making them attractive for investors prioritizing capital preservation. How to calculate t bill yield becomes important when comparing it to other investment options.
The appeal of T-bills lies in their simplicity and safety. Investors purchase them at a discount to their face value, and upon maturity, they receive the full face value. The difference between the purchase price and the face value represents the investor’s earnings. It’s important to understand the distinction between the discount rate and the yield. The discount rate is the annualized percentage reduction from the face value, while the yield is the actual return an investor receives, taking into account the time to maturity. For investors wondering how to calculate t bill yield, understanding these differences is vital.
T-bills are favored by risk-averse investors, institutions managing short-term liquidity, and even individual investors looking for a safe haven for their funds. The government regularly auctions T-bills with varying maturities, ranging from a few weeks to a year, offering flexibility to investors with different investment horizons. Knowing how to calculate t bill yield allows investors to make informed decisions about whether T-bills align with their financial goals and risk tolerance, enhancing their portfolio with a secure and predictable investment option. Understanding how to calculate t bill yield also enables comparison against other low-risk, short-term investments, ensuring the best possible return for a given risk profile.
How to Determine the Earnings on Your T-Bill Investment
This section explains how to calculate T-bill yield. It is crucial for understanding the return on investment. Treasury Bills (T-bills) are bought at a discount. The face value is received at maturity. The difference between the purchase price and face value determines the profit. This profit, considered against the initial investment and time to maturity, gives the yield. Knowing how to calculate t bill yield allows investors to compare T-bills with other investments.
Understanding how to calculate t bill yield involves a straightforward process. The process will be broken down into simple steps. Each step clarifies how the yield is derived from the T-bill’s characteristics. This includes its discounted purchase price and maturity date. This section serves as a practical guide. It will provide investors with the knowledge to evaluate the returns on their T-bill investments effectively. By learning how to calculate t bill yield, one can make informed financial decisions.
We will explore the process of how to calculate t bill yield. This will allow you to assess your potential earnings. Understanding the factors that influence T-bill yields is also crucial. The subsequent sections will offer detailed explanations and examples. These will help you grasp the nuances of T-bill investing. Ultimately, the aim is to equip you with the tools to confidently how to calculate t bill yield. This ensures you understand the real return on these low-risk government securities. This empowers you to make sound investment choices.
Key Components for Calculating T-Bill Yield
To understand how to calculate t bill yield effectively, one must first grasp the essential components that influence the calculation. These components are the Face Value, the Purchase Price, and the Time to Maturity. Each plays a crucial role in determining the final yield percentage. Understanding these components is critical before delving into how to calculate t bill yield.
The Face Value, also known as par value, is the amount the investor will receive upon the T-bill’s maturity date. It represents the principal amount the government promises to pay back. The Purchase Price is the discounted price an investor pays to acquire the T-bill. T-bills are sold at a discount, meaning the purchase price is lower than the face value. The difference between the face value and the purchase price is essentially the investor’s profit before considering the time factor. When learning how to calculate t bill yield, remember that a lower purchase price relative to the face value results in a higher yield.
The Time to Maturity refers to the number of days until the T-bill matures and the investor receives the face value. This is expressed in days because T-bills are short-term investments. The shorter the time to maturity, the less time the investor’s money is tied up, influencing the annualized yield calculation. The discount rate is also a vital concept; it is the percentage reduction from the face value. In this context, the discount rate is used by the government to determine the purchase price. Understanding how the discount rate translates into the final yield is key to understanding how to calculate t bill yield and assessing the attractiveness of the investment.
Breaking Down the T-Bill Yield Formula
The formula to understand how to calculate t bill yield might seem daunting at first, but breaking it down makes it manageable. Essentially, it quantifies the return on investment relative to the discounted purchase price and the holding period. The core principle revolves around the difference between the face value (what you receive at maturity) and the purchase price (what you paid), annualized over the term of the T-bill.
The complete formula for calculating the T-Bill yield is: Yield = ((Face Value – Purchase Price) / Purchase Price) * (360 / Days to Maturity). Let’s dissect this: “Face Value – Purchase Price” represents your profit. Dividing this profit by the “Purchase Price” gives you the return on your investment for the holding period. Multiplying by “360 / Days to Maturity” annualizes this return, providing a standardized yield for comparison purposes. The 360-day convention is used in finance for simplification.
For a simplified understanding of how to calculate t bill yield, consider this: it’s the percentage return you earn, adjusted to reflect a full year. It’s important to distinguish between the annual yield and the holding period return. The holding period return is simply the profit divided by the purchase price. The annual yield, as calculated by the formula, allows you to compare T-bill returns with other investments that may have different maturities. Understanding how to calculate t bill yield is crucial for making informed decisions about fixed income investments. Furthermore, be aware that this yield is an annualized figure and does not account for compounding. While the discount rate is used to determine the purchase price of the T-bill, the yield represents the actual return an investor receives, taking into account the time value of money and the discounted purchase.
Step-by-Step Calculation with a Practical Example
To illustrate how to calculate t bill yield, consider a practical example. Imagine an investor purchases a Treasury Bill with a face value of $10,000. The purchase price, reflecting the discount, is $9,800. The T-bill will mature in 180 days. These figures will be used to demonstrate the calculation.
First, determine the discount amount. This is the difference between the face value and the purchase price. In this case, $10,000 (Face Value) – $9,800 (Purchase Price) = $200 (Discount). Next, the holding period return is calculated by dividing the discount by the purchase price: $200 / $9,800 = 0.0204 or 2.04%. This represents the return for the 180-day holding period. To annualize this figure and find out how to calculate t bill yield, the following calculation is performed. Multiply the holding period return by (365 / Time to Maturity). Here is how to calculate t bill yield: 0.0204 * (365 / 180) = 0.0414 or 4.14%. Therefore, the approximate annual yield on this T-bill is 4.14%. Understanding how to calculate t bill yield with a step-by-step approach is crucial for evaluating investment returns.
It’s important to recognize that this annualized yield is an approximation. It assumes that the T-bill could be reinvested at the same rate for the entire year, which may not be the case. Furthermore, factors like compounding are not considered in this simple calculation of how to calculate t bill yield. This example provides a tangible understanding of how the formula works. It also highlights the relationship between the face value, purchase price, time to maturity, and the resulting yield. Investors can adapt this approach to analyze different T-bill offerings and make informed decisions. Mastering how to calculate t bill yield empowers investors to compare investment opportunities effectively.
Factors Influencing T-Bill Yields
Several factors can influence Treasury Bill (T-Bill) yields, impacting the return an investor receives. The overall interest rate environment plays a significant role. When interest rates rise, newly issued T-Bills tend to have higher yields to attract investors. Conversely, when interest rates fall, T-Bill yields typically decrease. Understanding how to calculate T-Bill yield becomes even more crucial in a fluctuating rate environment.
Inflation expectations are another key driver of T-Bill yields. Investors demand higher yields to compensate for the erosion of purchasing power caused by inflation. If inflation is expected to rise, T-Bill yields will likely increase to reflect this anticipated loss. The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy also has a direct impact. Actions taken by the Fed, such as adjusting the federal funds rate or implementing quantitative easing, can significantly influence short-term interest rates, including T-Bill yields. The supply and demand dynamics for T-Bills also affect yields. Increased demand for T-Bills, often driven by a “flight to safety” during times of economic uncertainty, can push prices up and yields down. Conversely, a surplus of T-Bills on the market can lead to lower prices and higher yields. Understanding these dynamics is key to understanding how to calculate T-Bill yield and to predicting potential investment returns.
Furthermore, economic growth prospects influence T-Bill yields. Strong economic growth often leads to higher interest rates as demand for credit increases. This, in turn, can push T-Bill yields upward. Weaker economic growth may result in lower interest rates and lower T-Bill yields. Global economic conditions, including international interest rates and geopolitical events, can also indirectly affect T-Bill yields, making the process of how to calculate T-Bill yield and forecast returns more complex. Monitoring these factors provides a more complete perspective when evaluating T-Bill investments.
Using Online Calculators for Quick T-Bill Yield Estimates
The process of determining how to calculate t bill yield can be simplified by using online calculators. These tools offer a convenient way to estimate potential returns on Treasury Bills. They are particularly helpful for those who prefer not to perform the calculations manually. Many financial websites and brokerage platforms provide these calculators free of charge.
These online tools typically require you to input key information. This includes the face value of the T-bill, the purchase price, and the time to maturity in days. Once you enter these values, the calculator automatically computes the estimated yield. This provides an immediate understanding of the potential return on investment. Using these calculators can save time and reduce the risk of manual calculation errors when determining how to calculate t bill yield.
It’s crucial to understand the limitations of online T-bill yield calculators. The results produced are only as accurate as the data inputted. Ensure that you enter the correct values for the face value, purchase price, and time to maturity. Some calculators may not account for fees or other charges associated with purchasing the T-bill. Always verify the results with a trusted financial professional, especially when making significant investment decisions. Remember that while these tools offer a quick estimate of how to calculate t bill yield, they should not be the sole basis for your investment strategy. Furthermore, understanding the underlying principles of how to calculate t bill yield will help you interpret the calculator’s output more effectively. Being informed about the factors influencing T-bill yields, such as interest rate movements and economic conditions, allows for a more comprehensive assessment of the investment’s potential. These calculators are valuable resources for quickly estimating returns. They work best when used in conjunction with a solid understanding of T-bill investing and sound financial advice.
Understanding the Difference Between Yield and Discount Rate
It is crucial to distinguish between the T-Bill discount rate and the actual T-Bill yield when evaluating short-term investment options. Often, these terms are used interchangeably, leading to potential misunderstandings. While both relate to T-Bill returns, they represent distinct calculations and perspectives. Understanding how to calculate t bill yield requires grasping this difference.
The discount rate is the annualized percentage reduction from the face value of the T-Bill. It’s used to determine the purchase price. For example, a T-Bill with a face value of $1,000 and a discount rate of 5% might be purchased for $950. The discount rate reflects the implied interest on the T-Bill based on its face value. It doesn’t directly represent the investor’s actual return. How to calculate t bill yield accurately involves understanding that the discount rate is just one component.
The T-Bill yield, on the other hand, represents the actual return an investor receives, considering the purchase price and the time to maturity. It takes into account the investor’s cost basis (the purchase price) and calculates the percentage return earned over the holding period, annualized for comparison purposes. The yield provides a more accurate picture of profitability. This is because it reflects the return on the actual investment amount, not just a percentage of the face value. If you want to learn how to calculate t bill yield effectively, focus on the yield calculation for a true reflection of returns. The difference between the face value and the purchase price, factored against the time to maturity, determines the yield. Factors like market demand and prevailing interest rates influence both the discount rate and the ultimately how to calculate t bill yield. Therefore, always consider the yield for making informed investment decisions regarding T-Bills, as it provides a clearer and more precise measure of investment performance. How to calculate t bill yield helps investors assess the true return on their investment beyond just the discount rate.

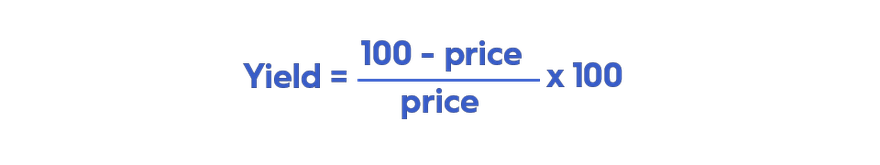

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Treasury-yield-8782292e8ad64d4a9669cbc61f73b06a.jpg)