Exploring Data Connections Using Spreadsheet Software
Correlation analysis is a statistical method used to examine the strength and direction of a relationship between two or more variables. It helps determine if changes in one variable are associated with changes in another. Understanding these relationships is crucial in various fields, from business and finance to science and social sciences. It allows for informed decision-making, prediction, and the identification of key factors influencing specific outcomes. Discover how to do a correlation matrix in excel effortlessly.
Spreadsheet software, such as Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets, provides accessible and user-friendly tools for performing correlation analysis. Their intuitive interfaces and built-in functions make it easier to calculate correlation coefficients and visualize data, even for those without extensive statistical backgrounds. The advantage of using spreadsheets lies in their widespread availability and ease of use, enabling a broad audience to explore and understand relationships within their data. Learning how to do a correlation matrix in excel can be very simple.
Spreadsheets simplify how to do a correlation matrix in excel by offering a visual and interactive environment. Users can quickly input data, apply formulas, and generate charts to gain insights. The immediate feedback and visual representations facilitate a deeper understanding of the relationships between variables. This approach empowers individuals to conduct preliminary data exploration and identify potential areas for further investigation, using tools they already have at their disposal. Analyzing how to do a correlation matrix in excel provides accessible analytics for everyone.
Preparing Your Data for Correlation Analysis
Before exploring relationships in your data, preparation is key. Learning how to do a correlation matrix in excel starts with ensuring your dataset is ready for analysis. The first step involves data cleaning. This means identifying and correcting any errors or inconsistencies. Look for typos, incorrect entries, or formatting issues that could skew your results. Consistency in data entry is crucial for accurate correlation calculations.
Next, organize your data into columns. Each column should represent a different variable you want to analyze. Ensure that the data types within each column are consistent. For instance, a column representing age should only contain numerical values. When learning how to do a correlation matrix in excel, handling missing values becomes very important. Decide on a strategy for dealing with them. You might choose to remove rows with missing data. Alternatively, you could impute the missing values using methods like mean or median imputation. Outliers can also significantly impact correlation results. Identify any extreme values that might not accurately represent your data. Consider removing or transforming these outliers to minimize their influence. Proper data preparation is a foundational step. This step will make sure your correlation analysis is reliable and meaningful.
Finally, verify your data’s integrity. Double-check your entries. Validate the accuracy of your data sources. By ensuring your data is clean, organized, and free of errors, you lay a solid groundwork for performing correlation analysis in spreadsheets. The more time spent preparing the data, the better the result will be when exploring how to do a correlation matrix in excel, leading to more accurate insights into relationships. Consider that the steps mentioned above are part of the process on how to do a correlation matrix in excel, improving the understanding of data and providing insights.
Performing Correlation Calculations Within Spreadsheets
Performing correlation calculations within spreadsheets is a straightforward process, allowing users to quantify the relationship between two variables. Understanding how to do a correlation matrix in Excel, or similar spreadsheet software, begins with identifying the appropriate function. Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets both utilize the `CORREL` function for calculating the Pearson correlation coefficient. This coefficient measures the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two sets of data.
To implement the `CORREL` function, first ensure your data is arranged in two distinct columns. For instance, if you want to analyze the correlation between advertising expenditure and sales revenue, place the advertising data in one column (e.g., column A) and the sales data in another (e.g., column B). Next, select an empty cell where you want the correlation coefficient to appear. In that cell, type `=CORREL(array1, array2)`, replacing “array1” with the range of cells containing your first variable (e.g., A1:A10) and “array2” with the range of cells containing your second variable (e.g., B1:B10). Press Enter, and the cell will display the correlation coefficient. This number will fall between -1 and +1, indicating the strength and direction of the correlation.
Spreadsheet software also allows users to calculate how to do a correlation matrix in Excel or similar software if analyzing multiple variables. The `CORREL` function can be applied pairwise to each variable combination. Dedicated matrix functions or add-ins might further streamline this process. Remember that the correlation coefficient only describes the linear relationship between variables. Visual aids like scatter plots will add a richer understanding. They will let you assess the relationship’s nature before relying solely on the numerical coefficient. So, exploring how to do a correlation matrix in Excel requires both numerical calculation and visual inspection for comprehensive analysis.
Visualizing Correlation with Scatter Plots
Scatter plots offer a powerful visual complement to correlation coefficients, enhancing the understanding of relationships between two variables. While a correlation coefficient, such as Pearson’s r, quantifies the strength and direction of a linear relationship, a scatter plot reveals the nature of the association, including any non-linear patterns or outliers that might not be apparent from the coefficient alone. Understanding how to do a correlation matrix in excel, begins with visualizing your data, and scatter plots are the first step.
To create a scatter plot in spreadsheet software, select the two columns of data representing the variables you wish to compare. Then, utilize the chart creation tool and choose the scatter plot option (often labeled as “Scatter” or “XY Scatter”). The spreadsheet software will generate a graph with one variable plotted on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis. Each point on the plot represents a pair of values from your dataset. Examining the scatter plot allows you to visually assess the direction and strength of the relationship. A positive correlation will typically show a trend where the points generally rise from left to right, while a negative correlation will show a trend where the points generally fall from left to right. The closer the points are clustered around an imaginary line, the stronger the correlation.
Furthermore, scatter plots can reveal important characteristics of the data that correlation coefficients alone might miss. For example, a scatter plot can highlight non-linear relationships, such as a curvilinear association, where the correlation coefficient might be close to zero despite a clear relationship being present. Outliers, which are data points that deviate significantly from the general trend, are also easily identifiable on scatter plots. These outliers can unduly influence the correlation coefficient, potentially leading to misleading interpretations. Therefore, scatter plots are a vital tool in correlation analysis, providing a visual check and a more nuanced understanding of how to do a correlation matrix in excel and the relationship between variables.
Deciphering Correlation Coefficients: Understanding the Results
The correlation coefficient, often denoted as ‘r’, is a crucial indicator of the strength and direction of a linear relationship between two variables. Understanding how to interpret this value is essential when learning how to do a correlation matrix in excel. The r-value ranges from -1 to +1. The closer the value is to either extreme, the stronger the correlation.
A strong positive correlation is indicated by an r-value close to +1. This means that as one variable increases, the other tends to increase as well. For instance, there might be a strong positive correlation between hours studied and exam scores. Conversely, an r-value close to -1 signifies a strong negative correlation. This suggests that as one variable increases, the other tends to decrease. An example is the correlation between exercise and body fat percentage. When understanding how to do a correlation matrix in excel, remember a correlation near zero suggests a weak or no linear relationship. This doesn’t necessarily mean there’s no relationship at all, just that it’s not a linear one. It is important to remember how to do a correlation matrix in excel and properly analyze the output.
Specifically, an r-value between 0.7 and 1.0 (or -0.7 and -1.0) generally indicates a strong correlation. A value between 0.3 and 0.7 (or -0.3 and -0.7) suggests a moderate correlation. Values between 0 and 0.3 (or 0 and -0.3) indicate a weak correlation. It’s important to consider the context of the data when interpreting these values. Even a weak correlation might be meaningful in some situations. Remember that correlation only measures linear relationships. Always consider visualizing your data with scatter plots to understand the nature of the relationship better. Learning how to do a correlation matrix in excel is a useful skill for data analysis.
Beyond Pearson: Exploring Different Correlation Methods
While the Pearson correlation coefficient is a widely used method to quantify the linear relationship between two variables, it is essential to recognize its limitations. It works best when relationships are linear and data is normally distributed. When these assumptions are not met, alternative correlation methods may be more appropriate. Several scenarios exist where Pearson’s method may not be the best option, such as when the relationship is non-linear, or when dealing with ordinal data, where the order matters, but not the interval between values.
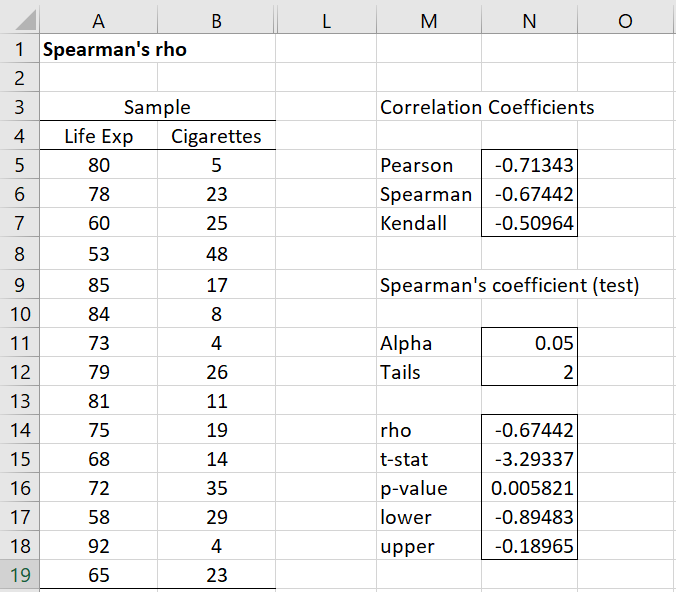
Spearman’s rank correlation is one such alternative. Instead of using the raw data values, Spearman’s correlation assesses the monotonic relationship between the ranked values of the variables. This means it captures how consistently the variables increase or decrease together, regardless of whether the increase or decrease is linear. Spearman’s rank correlation is less sensitive to outliers and can be more suitable for non-linear relationships. Another scenario where Spearman’s rank correlation becomes useful is when analyzing ordinal data. Since the ranks of the values are used, the impact of extreme values is diminished, providing a more robust measure of association. Determining how to do a correlation matrix in excel often starts with using Pearson’s method, however, exploring Spearman’s method broadens the possibilities for analysis.
Implementing Spearman’s rank correlation within a spreadsheet environment, like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets, requires a slightly different approach than simply using the `CORREL` function. First, the data needs to be transformed into ranks. This can be done using the `RANK.AVG` or `RANK.EQ` functions. Once both variables have been ranked, the `CORREL` function can be applied to the ranked data to calculate Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient. While Pearson’s correlation is a great starting point, recognizing when to use alternate methods such as Spearman’s enhances your ability to accurately assess relationships within your data. Furthermore, keep in mind that understanding how to do a correlation matrix in excel empowers users to make informed decisions based on a comprehensive analysis. It is important to select the correlation method that best suits the characteristics of your data and the nature of the relationship you are trying to understand.
Avoiding Common Pitfalls in Correlation Analysis
A critical aspect of data analysis involves understanding and avoiding common pitfalls, especially when exploring how to do a correlation matrix in excel. A frequent mistake is assuming that correlation implies causation. Just because two variables move together does not mean one causes the other. There might be other confounding variables influencing both, or the relationship could be purely coincidental.
Another pitfall is neglecting to consider the influence of outliers. Outliers can significantly skew the correlation coefficient, leading to misleading conclusions about the relationship between variables. Before performing correlation analysis, it’s important to identify and appropriately handle outliers, possibly by removing them or using robust correlation methods less sensitive to extreme values. Ensuring data accuracy is also vital; errors in data entry can introduce spurious correlations or mask genuine relationships. Always double-check your data for inconsistencies and inaccuracies before proceeding with the analysis. When determining how to do a correlation matrix in excel, one must consider all of these variables.
Furthermore, be mindful of the limitations of the Pearson correlation coefficient, particularly when dealing with non-linear relationships. Pearson’s r measures the strength and direction of linear association only. If the relationship between variables is curved or follows a different pattern, Pearson’s r may underestimate the true strength of the association. In such cases, exploring alternative correlation methods, such as Spearman’s rank correlation, is more appropriate. Lastly, remember that correlation is context-dependent. The interpretation of a correlation coefficient should always be done within the specific context of the data and research question. A correlation that is statistically significant may not be practically meaningful or relevant. Understanding how to do a correlation matrix in excel requires a detailed understanding of the data and the techniques used.
Elevating Your Insights: Advanced Correlation Techniques in Data Software
While spreadsheets provide a foundational understanding of correlation analysis, certain advanced techniques demand more specialized tools. The basic Pearson correlation, readily calculated in Excel, measures linear relationships. However, real-world data often presents complexities that necessitate more sophisticated approaches. Exploring how to do a correlation matrix in Excel reveals its limitations when facing non-linear relationships, time-series data, or the need to control for confounding variables.
Partial correlation, for instance, allows isolating the relationship between two variables while holding one or more other variables constant. This helps to remove the influence of potential confounders, providing a more accurate assessment of the direct association. Lagged correlation, on the other hand, is invaluable when analyzing time-series data. It examines the correlation between two variables at different points in time, revealing potential lead-lag relationships. These advanced methods typically require statistical software packages like R, SPSS, or Python with libraries such as NumPy, SciPy, and Pandas. These tools offer the necessary algorithms and functionalities to perform these analyses effectively. While you can learn how to do a correlation matrix in Excel, you’ll eventually outgrow its capabilities for complex research.
Furthermore, specialized software allows for the implementation of non-parametric correlation methods beyond Spearman’s rank correlation. These methods are crucial when dealing with data that doesn’t meet the assumptions of Pearson correlation, such as non-normally distributed data or ordinal variables. Techniques like Kendall’s tau offer robust alternatives. By transitioning to dedicated data analysis tools, researchers gain access to a wider array of correlation techniques. They can also have better control over data manipulation, visualization, and statistical inference. When considering how to do a correlation matrix in Excel, remember that it’s a starting point. Statistical software offers the depth and flexibility needed for rigorous and comprehensive correlation analysis, especially when dealing with intricate datasets and research questions.