What is the Order Book and Why it Matters
The order book is the cornerstone of level 2 market data, offering a real-time, transparent view of the supply and demand dynamics for a particular security. Understanding how to read level 2 market data starts with grasping the essence of the order book. This digital ledger meticulously records every buy and sell order placed by market participants, detailing the specific price at which each order is intended to be executed, alongside the corresponding volume of shares or contracts. The order book is not a static entity; it is continuously updated as new orders are entered, existing orders are modified or canceled, and trades are executed, making it a dynamic representation of the market’s current sentiment and intentions. In essence, the order book’s function is to match buyers and sellers, creating a price discovery process that ultimately determines the market price of an asset. This process provides an insightful glimpse into the depth of the market, illustrating not only the best bid and ask prices but also the accumulation of orders at various price levels, showcasing the potential for price movements based on the aggregated buy and sell interest.
The significance of the order book extends beyond mere price transparency, enabling traders to perceive the relative strength of buying and selling pressure at diverse price points. For individuals who want to know how to read level 2 market data, the order book is a vital tool for identifying potential areas of support and resistance. A large volume of buy orders at a particular price level, for example, could signal a robust support zone, indicating the price might find it difficult to break below that level. Similarly, a large concentration of sell orders at a certain price may suggest resistance, where the price might struggle to move higher. This level of market intelligence is crucial for informed trading decisions, and gives the trader the ability to anticipate likely price direction. Consequently, the order book, forming the foundation of level 2 data, is not just a list of orders but a valuable representation of the ongoing battle between buyers and sellers. It is what any trader will first need to look at to understand how to read level 2 market data and is essential for those attempting to gain an edge in the dynamic world of trading.
Understanding Bid and Ask Prices
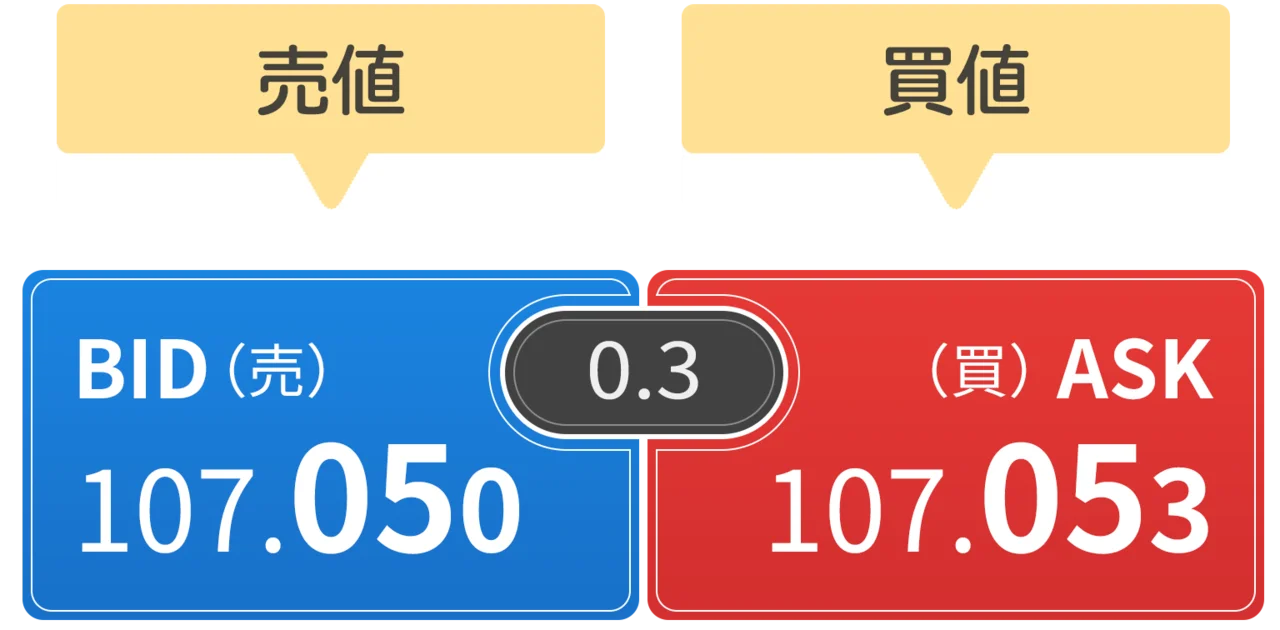
The bid and ask prices are fundamental components of level 2 market data, representing the core of the order book. The bid price is the highest price that a buyer is currently willing to pay for a specific security. Conversely, the ask price reflects the lowest price that a seller is willing to accept for that same security. These prices are not static; they fluctuate continuously as market participants place, modify, or cancel their orders. The difference between the bid and ask prices is known as the spread. A tighter spread, meaning a smaller difference between the bid and ask, generally indicates higher market liquidity, suggesting that it’s easier to buy or sell the security at a fair price. A wide spread, on the other hand, can signify lower liquidity and higher potential transaction costs, particularly impacting day traders who execute numerous trades. Knowing how to read level 2 market data in relation to the bid and ask is crucial for identifying favorable entry and exit points.
Analyzing the bid and ask prices is essential for comprehending the immediate market dynamics. The bid and ask offer not just the best prices but also show the amount of shares or contracts available at these respective levels. The sizes associated with the best bid and ask levels provide an immediate indication of supply and demand pressures and provide a way to see how to read level 2 market data to gauge short-term price direction. For instance, if there is a significantly higher volume at the best bid compared to the best ask, it might suggest a potential upward pressure on the price, as there is more buying interest at that level. The opposite scenario, with higher volume at the best ask, could signal potential downward pressure due to increased selling interest. These imbalances can be fleeting, but understanding them and how to read level 2 market data can inform immediate trading strategies. The speed with which these levels change further emphasizes the dynamic nature of the market and the need for constant monitoring.
Depth of Market: Unveiling the Hidden Orders
Level 2 market data offers a crucial advantage by revealing the depth of the market, going beyond the simple best bid and ask prices. Unlike level 1 data, which only shows the top prices at which buyers and sellers are willing to trade, level 2 displays multiple price levels on both the bid (buy) and ask (sell) sides of the order book. This detailed view provides a more comprehensive understanding of market sentiment and potential price movements. By showing the volume of orders at each price level, traders can gain insights into areas of potential support and resistance, which are essential for making informed trading decisions. Learning how to read level 2 market data involves understanding how this depth provides context, allowing traders to see where significant buying or selling interest lies.
The “depth” aspect is key because it shows the immediate liquidity at various price points. A large amount of buy orders clustered at a particular price, for example, can indicate a potential support level. Conversely, a substantial volume of sell orders at a specific price may signal an area of resistance. This visibility allows traders to anticipate how price may react when it approaches these levels, offering valuable insights for entry and exit strategies. Furthermore, examining the depth provides a sense of market intensity, as the size of the order book at various prices gives a glimpse of the commitment behind market trends. Observing these levels carefully becomes a vital component of learning how to read level 2 market data.
The ability to see the entire order book, not just the top prices, is particularly useful for scalpers and day traders. It provides a much clearer picture of the supply and demand dynamics. This granularity allows for spotting potential hidden orders or iceberg orders, large orders hidden from the public view, which can also indicate institutional activity and can signal areas where future price direction could be potentially influenced. Understanding how to read level 2 market data includes interpreting the size and concentration of orders at various price points. This analysis can significantly enhance a trader’s ability to navigate the market and make more informed decisions. This data, however, requires some practice to be correctly interpreted.
How to Identify Potential Price Support and Resistance
Understanding how to read level 2 market data is crucial for identifying potential price support and resistance levels. The volume of orders at different price points offers valuable insights. When observing the order book, a significant accumulation of buy orders at a specific price level suggests strong demand, potentially acting as a price floor, also known as a support level. If the price approaches this level, the sheer volume of buy orders may prevent further price declines, as buyers are readily available to absorb selling pressure. Conversely, a large number of sell orders clustered at a specific price can act as resistance. This indicates a zone where sellers are likely to enter the market, making it difficult for the price to move higher. These areas of support and resistance are not always precise, they are more like zones. For example, if there is an area with strong buying demand at 50, it might not mean that price will not go slightly below 50, but it signals the possibility that the price will likely not remain too long below that level. These areas are not always permanent and can be broken or re-established, understanding this dynamic is fundamental for a trader to assess the probabilities of a given price action.
The concept of psychological barriers plays a significant role in how to read level 2 market data and identify potential support and resistance. Large orders at round number price levels, such as $50, $100 or $200, often act as psychological barriers. These levels are easily remembered and thus tend to attract attention. This is also a common price point for placing limit orders, leading to higher volumes at these specific levels. When these orders are executed, they can cause the price to reverse its direction or, at the very least, slow its momentum. However, it is important to note that these levels are not infallible and can be breached by strong market forces, particularly when there is an imbalance of aggressive buying or selling pressure. Therefore, traders should not treat them as impenetrable walls but instead as areas of interest that offer clues about the overall market sentiment. Also understanding the relative volume is important. For example, a large order for a very low volume stock might not be as significant as a similar size order for a heavily traded security.
Spotting Large Buyers and Sellers: The Whale Watching Guide
Level 2 market data offers a unique perspective into the activities of large market participants, often referred to as “whales.” These entities, with their substantial order sizes, can significantly influence short-term price movements. Learning how to read level 2 market data to identify these large orders is not an exact science, but understanding the nuances can be valuable. The key is to observe the order book for unusually large volumes placed at specific price levels. A substantial order, noticeably larger than the surrounding orders, can indicate the presence of a whale. For example, if you consistently see orders for several thousand shares at a particular bid or ask price, while most other orders are for hundreds, it may be a sign of a large player attempting to accumulate or distribute a position. These large orders can act as temporary support or resistance levels, influencing the price. However, it’s crucial to remember that these orders might be split into multiple smaller orders or hidden entirely, especially through the use of iceberg orders, where only a portion of the full order volume is visible at any given time, so reading level 2 market data can be a little tricky.
While identifying large players through level 2 data can be a tool, traders should understand that it’s not a foolproof method. Large orders may not always reflect genuine buy or sell intentions; sometimes they are placed to manipulate the price or test market liquidity. Recognizing how to read level 2 market data to distinguish between genuine and manipulative orders requires experience and careful observation. Observing how price reacts to the presence of a large order is also essential; if a stock price struggles to breach the price level with the large order, that could indicate genuine support or resistance. Conversely, if the price quickly moves through it, it may indicate the large order was simply a test. Furthermore, it’s also important to note that different trading platforms might display level 2 information differently, making it important to be familiar with how your chosen platform displays this type of data. By combining level 2 analysis with other forms of technical analysis and risk management, you can refine your strategies and improve your understanding of market dynamics. Learning how to read level 2 market data provides an additional data point in your trading toolbox.
Analyzing Order Book Imbalances: Predicting Price Direction
The analysis of order book imbalances is a crucial aspect of understanding how to read level 2 market data, offering insights into potential price movements. This involves assessing the relative strength between the bid and ask sides of the order book. A significant imbalance, where the volume of buy orders far outweighs the volume of sell orders at various price levels, may suggest an increased likelihood of upward price pressure. This is because a higher demand for purchasing, as reflected by the stronger bid side, can propel the price higher as buyers compete for available shares. Conversely, when the ask side dominates with substantially more sell orders, it can be indicative of potential downward pressure on the price. This happens as sellers try to offload their positions, potentially driving the price lower. However, it’s crucial to understand that these imbalances are not foolproof predictors; they represent a potential trend and should be combined with other indicators. Market depth analysis is one of the keys to understanding how to read level 2 market data, and examining these imbalances provides a snapshot of the buying and selling interest at a specific time, which may or may not translate into a price movement. The actual price behavior depends on other market forces, including the actions of large traders, news releases, and other factors.
Understanding the subtleties of order book imbalances requires keen observation and constant learning of how to read level 2 market data. It’s not just about comparing the raw number of buy and sell orders but also about considering the size of these orders and their placement within the order book. For example, a large cluster of sell orders just above the current price could act as a strong resistance level, potentially halting upward price movement even if there is a higher number of buy orders at lower price points. Likewise, if there are a higher number of buy orders that are very close to the current price with little to no volume on the ask side, it may indicate that a breakout may occur. The best way to read level 2 market data, is to analyze the order book in real-time and identify trends that may present a potentially profitable trade. Furthermore, the pace at which these orders are being placed and removed from the order book gives you added insight into how to read level 2 market data. A rapid increase in buy orders could signal a sudden surge in demand, whereas a rapid increase in sell orders might indicate that investors are closing their positions. This is particularly useful for identifying when strong momentum might be forming or when a move may be losing steam. The ability to analyze and react to these nuances allows you to have a deeper insight into the markets.
Practical Tips for Using Level 2 Data Effectively
To effectively utilize level 2 market data, it’s crucial to understand that it’s just one tool in a trader’s arsenal, not a standalone solution for guaranteed profits. Begin by focusing on a specific security and become intimately familiar with its typical order book patterns. Observe how the depth of market changes, noting the size and placement of bids and asks. Avoid the common pitfall of overreacting to every small change; instead, look for significant shifts in the order book’s dynamics. For example, if a large block order appears on the bid side, it might suggest potential support, but it’s not a definitive signal to buy. Similarly, a sudden withdrawal of bids or offers can indicate a potential shift in market sentiment; however, it should be seen as a potential clue, not as a crystal ball. Learning how to read level 2 market data requires consistent observation and practice. It is also essential to practice these skills in a simulator before risking real capital.
Always combine your analysis of level 2 data with other forms of technical analysis, such as chart patterns and volume indicators. This multi-faceted approach can help confirm signals and reduce the risk of false positives. For instance, a large buy order might be more significant if it appears when the price is near a support level identified on a chart. Remember, level 2 data can be volatile and fast-moving, so having a solid trading plan with clearly defined entry and exit points is vital for success. Effective risk management is also key; never risk more than you can afford to lose on any single trade. Level 2 data, while powerful, can be misleading if not used with proper caution and in combination with other analysis tools and a robust trading system. The ability to accurately interpret level 2 data will improve with experience, but it must be combined with other methods to become a highly accurate method to understand potential market moves.
Furthermore, consider that market makers can sometimes use “spoofing” techniques, where they place large orders that are quickly canceled. This creates a false impression of demand or supply and aims to move the price in the desired direction. Understanding these tactics is as important as knowing how to read level 2 market data, and you should use this data to supplement your own research and analysis. Finally, be aware of the potential for latency issues; the data feed might not always be perfectly synchronized, so high-speed trading based solely on level 2 market data carries an increased risk. With consistent practice, risk management, and the right platform, the ability to analyze the order book can become a powerful tool, but it’s essential to understand that it is a tool and not a magical key to success.
Choosing the Right Level 2 Data Platform for Your Needs
Selecting the appropriate platform for accessing level 2 market data is a crucial step for any trader looking to delve into the intricacies of order book analysis. Several brokerages and trading platforms offer this feature, each with its own set of functionalities, user interfaces, and associated costs. Popular options often include well-known brokers that cater to active traders, providing real-time level 2 data feeds as part of their premium services or through subscription-based models. It’s essential to explore different platforms to identify one that best aligns with individual trading styles and preferences. For example, some platforms might offer more advanced charting tools alongside level 2 data, while others may focus on providing a streamlined and easy-to-navigate interface, helping users understand how to read level 2 market data effectively. When considering options, look for features like customizable order book displays, volume analysis tools, and the capability to set alerts based on specific order activities. The importance of this cannot be overstated, as a user-friendly interface can significantly impact the speed and efficiency with which traders make decisions using level 2 data.
Before committing to a particular platform, traders should carefully evaluate the associated costs and ensure they understand how to read level 2 market data within the specific system they are using. Level 2 data feeds often come with a subscription fee, either directly or bundled into a premium account package. These costs can vary significantly between providers and are typically dependent on the depth of the data provided and the speed of updates. It’s therefore important to balance the desire for comprehensive market data against the associated expenses. Some platforms may offer free level 2 data on a delayed basis or with limited depth, which could be a viable option for beginners or those with less frequent trading activity. On the other hand, active day traders who rely heavily on the speed and detail of level 2 data may benefit more from a real-time, full depth subscription, even if it is at a higher cost. Taking time to research and compare different level 2 data platforms is a worthwhile investment, as choosing the right one can greatly enhance the effectiveness of a trader’s market analysis and decision-making capabilities. Furthermore, traders should consider how well the platform integrates with their current trading setup and workflow for optimal performance when using level 2 market data.