Navigating the Complex World of SOFR Swap Rates
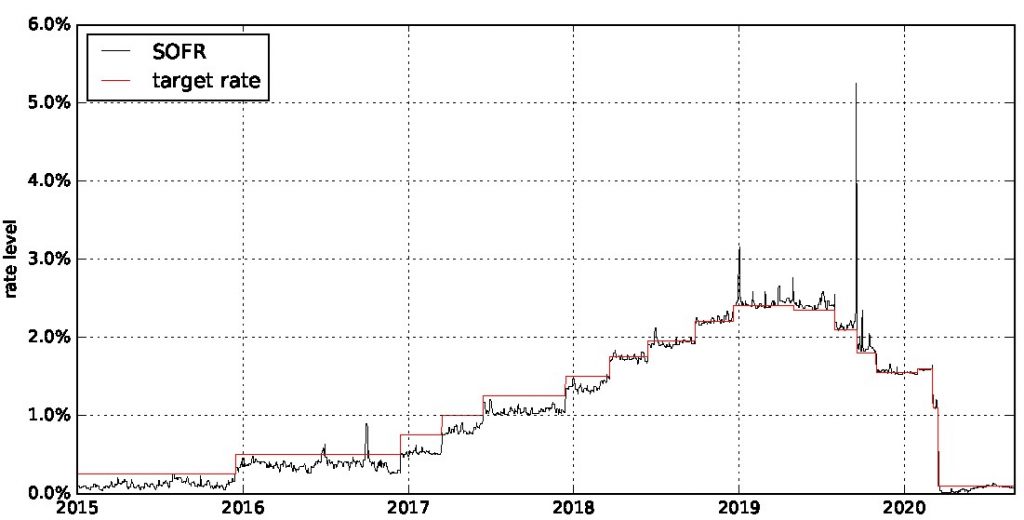
In the financial market, the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR) has emerged as a prominent benchmark rate, particularly in the context of long-term interest rate swaps. SOFR swap rates play a vital role in managing risk and optimizing investment returns. Understanding SOFR swap rates is crucial for informed investment decisions, as they have a direct impact on the overall performance of a portfolio. A 7 year SOFR swap rate, in particular, offers a unique set of benefits and challenges that investors must carefully consider. With the increasing adoption of SOFR as a replacement for LIBOR, it is essential to grasp the intricacies of SOFR swap rates and their applications in risk management strategies.
What is a 7-Year SOFR Swap Rate and How Does it Work?
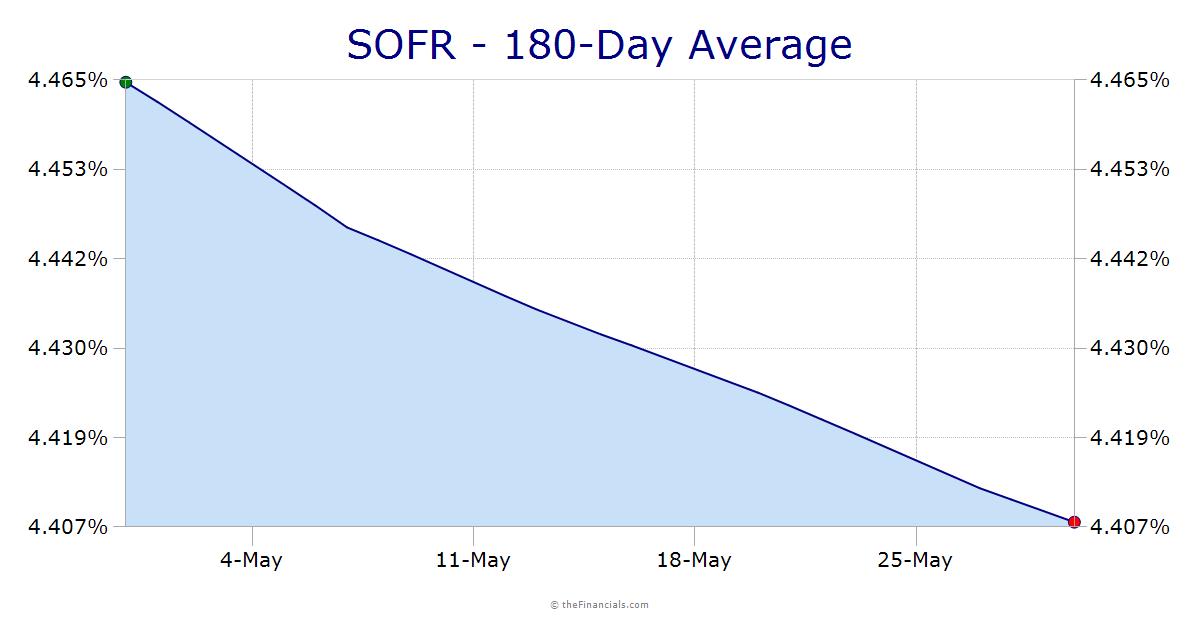
A 7-year SOFR swap rate is a type of interest rate swap that allows parties to exchange fixed and floating interest payments based on the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR). This benchmark rate is calculated daily by the New York Federal Reserve, reflecting the cost of borrowing cash overnight, collateralized by U.S. Treasury securities. In a 7-year SOFR swap, one party agrees to pay a fixed rate, while the other party pays a floating rate based on the SOFR, with the exchange of payments occurring over a 7-year period. This type of swap is commonly used in hedging and risk management strategies, as it provides a way to manage interest rate risk and lock in a fixed rate for a specified period.
How to Analyze and Interpret 7-Year SOFR Swap Rate Trends
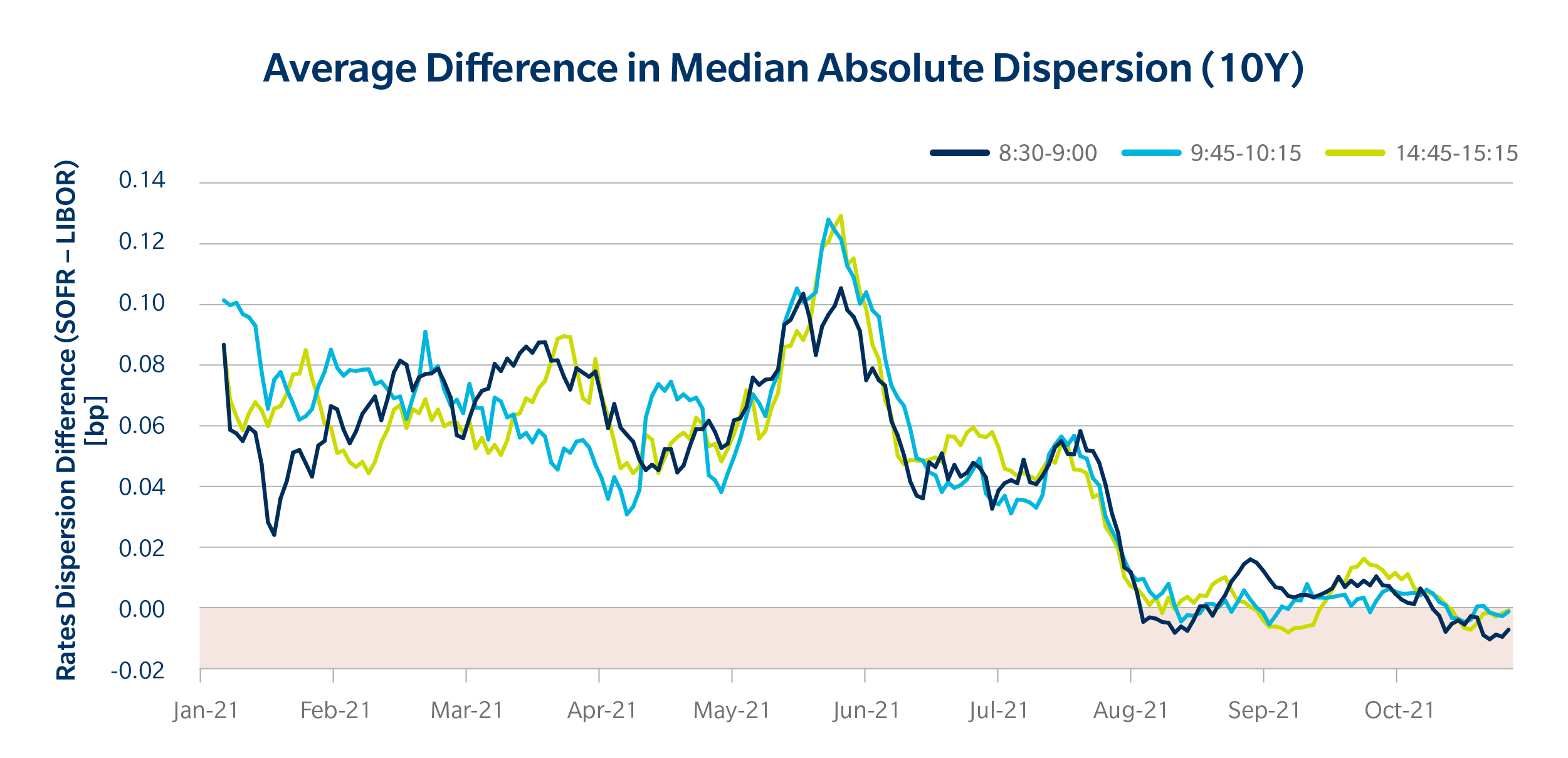
Accurately analyzing and interpreting 7-year SOFR swap rate trends is crucial for making informed investment decisions. To do so, it’s essential to identify patterns and understand market sentiment. One approach is to examine historical data on 7-year SOFR swap rates, looking for trends and correlations with other economic indicators. This can help investors anticipate potential rate changes and adjust their portfolios accordingly. Additionally, analyzing market sentiment through tools such as sentiment analysis and positioning data can provide valuable insights into market expectations and potential rate movements. By combining these approaches, investors can gain a deeper understanding of 7-year SOFR swap rate trends and make more informed investment decisions. Furthermore, staying up-to-date with market news and developments can help investors anticipate potential changes in 7-year SOFR swap rates and adjust their strategies accordingly. By adopting a data-driven approach and staying informed, investors can navigate the complexities of 7-year SOFR swap rates and optimize their investment returns.
The Impact of Economic Indicators on 7-Year SOFR Swap Rates
The 7-year SOFR swap rate is closely tied to various economic indicators, which can significantly influence its movement. One of the key indicators is GDP, which has a direct impact on interest rates. When GDP growth is strong, it can lead to higher interest rates, and subsequently, higher 7-year SOFR swap rates. On the other hand, a slowing economy can result in lower interest rates and 7-year SOFR swap rates. Inflation is another crucial indicator, as rising inflation can lead to higher interest rates to combat inflationary pressures. This, in turn, can cause 7-year SOFR swap rates to increase. Unemployment rates also play a role, as low unemployment can lead to higher interest rates and 7-year SOFR swap rates. Furthermore, other indicators such as consumer spending, housing market trends, and manufacturing data can also influence 7-year SOFR swap rates. By monitoring these economic indicators, investors can gain a better understanding of the factors that influence 7-year SOFR swap rates and make more accurate predictions about future rate movements. This can help investors make informed investment decisions and optimize their portfolios.
Comparing 7-Year SOFR Swap Rates to Other Benchmark Rates
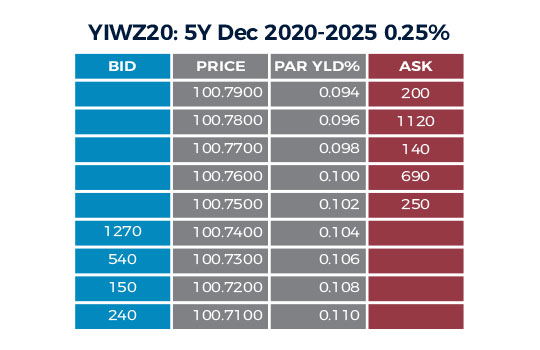
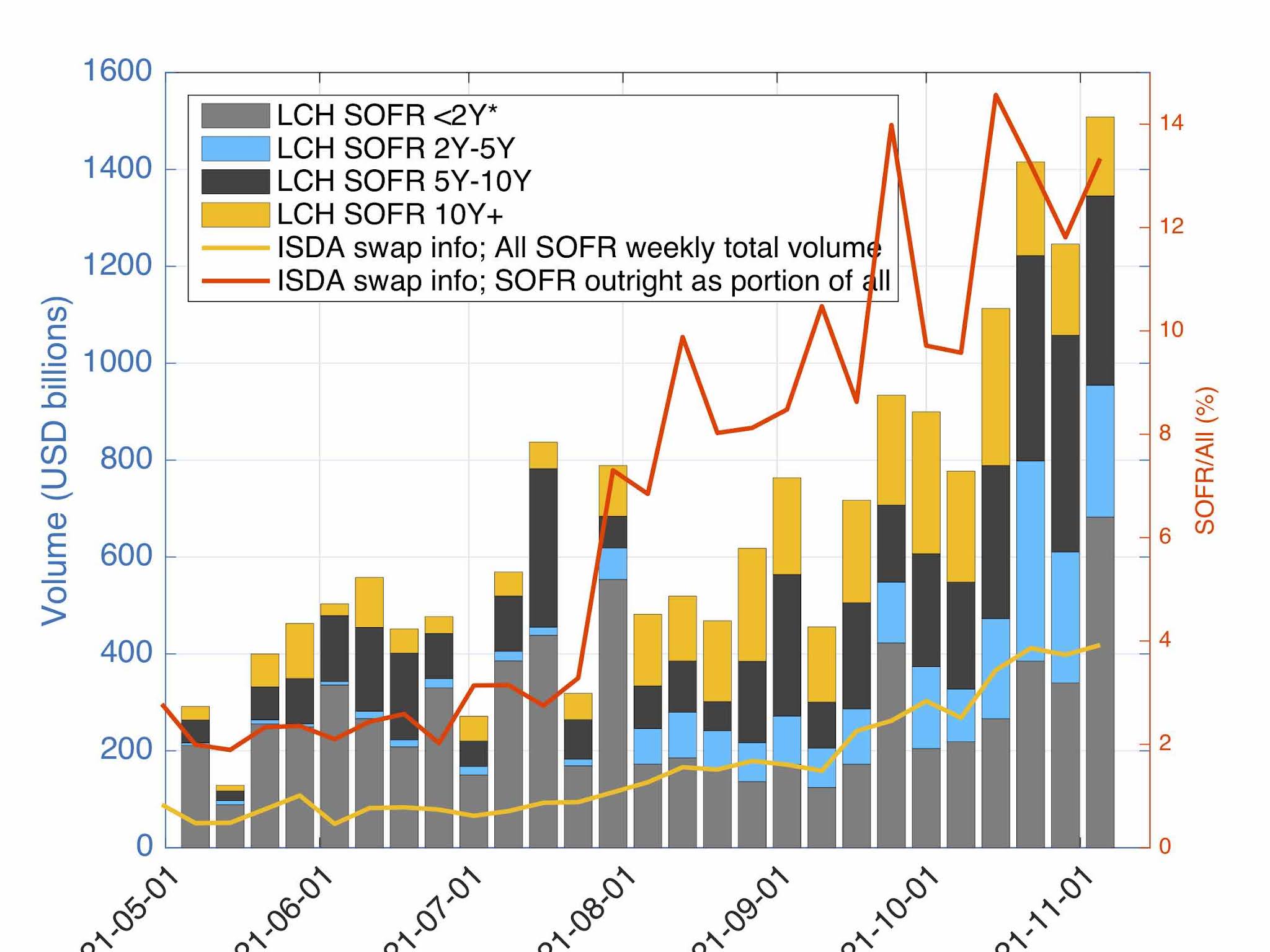
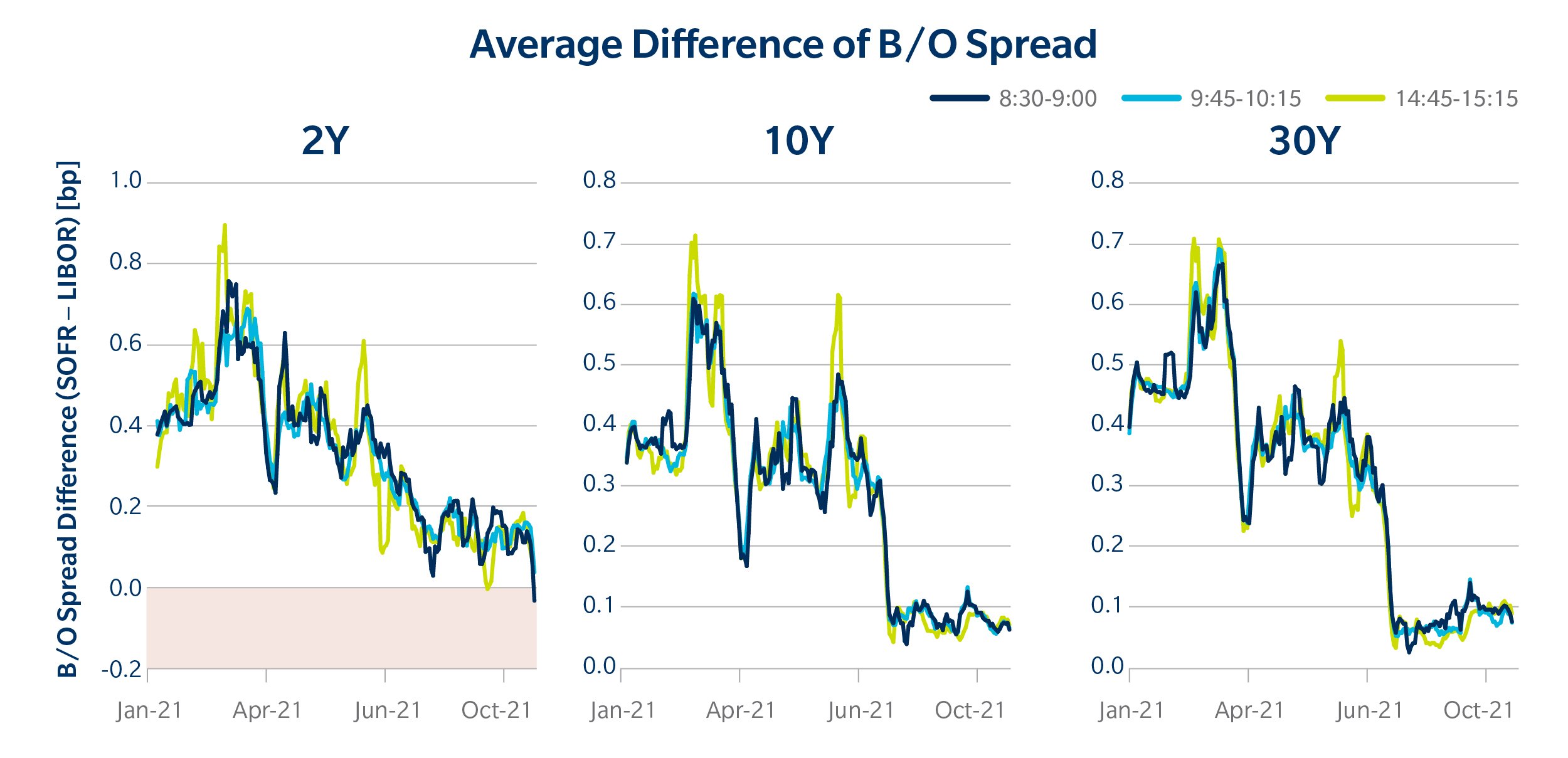
When evaluating 7-year SOFR swap rates, it’s essential to understand how they compare to other benchmark rates. One of the most widely used benchmark rates is LIBOR (London Interbank Offered Rate), which has been the standard for decades. However, LIBOR has its limitations, and the financial industry has been shifting towards alternative rates like SOFR. The 7-year SOFR swap rate is considered a more robust and reliable benchmark rate compared to LIBOR, as it’s based on a broader set of transactions and is less susceptible to manipulation. Another key benchmark rate is the Treasury yield, which is influenced by government bond prices. While Treasury yields are often used as a proxy for long-term interest rates, they don’t reflect the same credit risk as 7-year SOFR swap rates. Understanding the differences between these benchmark rates is crucial for investors, as it can impact their investment decisions and risk management strategies. For instance, a 7-year SOFR swap rate may be more suitable for hedging purposes due to its closer alignment with market conditions, whereas a Treasury yield may be more appropriate for asset allocation decisions. By comparing and contrasting these benchmark rates, investors can make more informed decisions and optimize their portfolios.
Managing Risk with 7-Year SOFR Swap Rates in Investment Portfolios
Effective risk management is crucial in investment portfolios, and 7-year SOFR swap rates can play a vital role in achieving this goal. By incorporating 7-year SOFR swap rates into their risk management strategies, investors can hedge against potential losses and optimize their returns. One way to manage risk is through hedging, which involves taking a position in a 7-year SOFR swap rate to offset potential losses in another investment. For example, an investor holding a long-term bond may hedge against interest rate risk by taking a short position in a 7-year SOFR swap rate. This can help to reduce the overall risk of the portfolio and increase its resilience to market fluctuations. Diversification is another key strategy for managing risk, and 7-year SOFR swap rates can be used to diversify a portfolio by adding a new asset class. By allocating a portion of the portfolio to 7-year SOFR swap rates, investors can reduce their reliance on traditional assets and increase their potential returns. Additionally, 7-year SOFR swap rates can be used to inform asset allocation decisions, helping investors to optimize their portfolios and achieve their investment objectives. By understanding how to manage risk with 7-year SOFR swap rates, investors can create more robust and resilient investment portfolios that are better equipped to navigate the complexities of the financial markets.
The Role of Central Banks in Shaping 7-Year SOFR Swap Rates
Central banks play a crucial role in shaping 7-year SOFR swap rates through their monetary policy decisions, forward guidance, and communication strategies. By setting interest rates and regulating the money supply, central banks can influence the overall direction of 7-year SOFR swap rates. For instance, when central banks lower interest rates to stimulate economic growth, 7-year SOFR swap rates may decrease, making borrowing cheaper and increasing investment activity. Conversely, when central banks raise interest rates to combat inflation, 7-year SOFR swap rates may increase, making borrowing more expensive and reducing investment activity. Additionally, central banks’ forward guidance, which provides insight into future monetary policy decisions, can also impact 7-year SOFR swap rates. By communicating their intentions clearly, central banks can influence market expectations and shape the trajectory of 7-year SOFR swap rates. Furthermore, central banks’ communication strategies, including speeches, press conferences, and economic reports, can also impact 7-year SOFR swap rates by providing insight into their views on the economy and monetary policy. By understanding the role of central banks in shaping 7-year SOFR swap rates, investors can better navigate the complexities of the financial markets and make more informed investment decisions.
Looking Ahead: Predicting Future Trends in 7-Year SOFR Swap Rates
As the financial landscape continues to evolve, predicting future trends in 7-year SOFR swap rates is crucial for investors and financial institutions. Several factors are likely to shape the trajectory of 7-year SOFR swap rates in the coming years. Emerging market trends, such as the growth of sustainable finance and the increasing importance of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations, may lead to a greater emphasis on socially responsible investing and impact 7-year SOFR swap rates. Regulatory changes, such as the ongoing transition from LIBOR to SOFR, will also continue to influence 7-year SOFR swap rates. Furthermore, technological advancements, including the development of artificial intelligence and machine learning, may improve the accuracy of 7-year SOFR swap rate predictions and enhance risk management strategies. Additionally, shifts in global economic power dynamics, such as the rise of Asia as a major economic hub, may lead to changes in the way 7-year SOFR swap rates are calculated and interpreted. By understanding these potential trends and their implications, investors can better position themselves to capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks in the 7-year SOFR swap rate market.