Understanding the Investment Landscape: A Brief Overview
Investment returns are the lifeblood of any successful investment strategy. Whether you’re a seasoned investor or just starting out, understanding the different types of returns is crucial for achieving your financial goals. Two prominent return strategies, total return and absolute return, have garnered significant attention in the investment community. As investors seek to maximize their returns, it’s essential to grasp the fundamental concepts of these strategies and how they can be leveraged to achieve long-term investment success. In this article, we’ll explore the world of total return vs absolute return, providing a comprehensive guide to help investors make informed decisions.
What is Total Return: A Deep Dive into the Concept
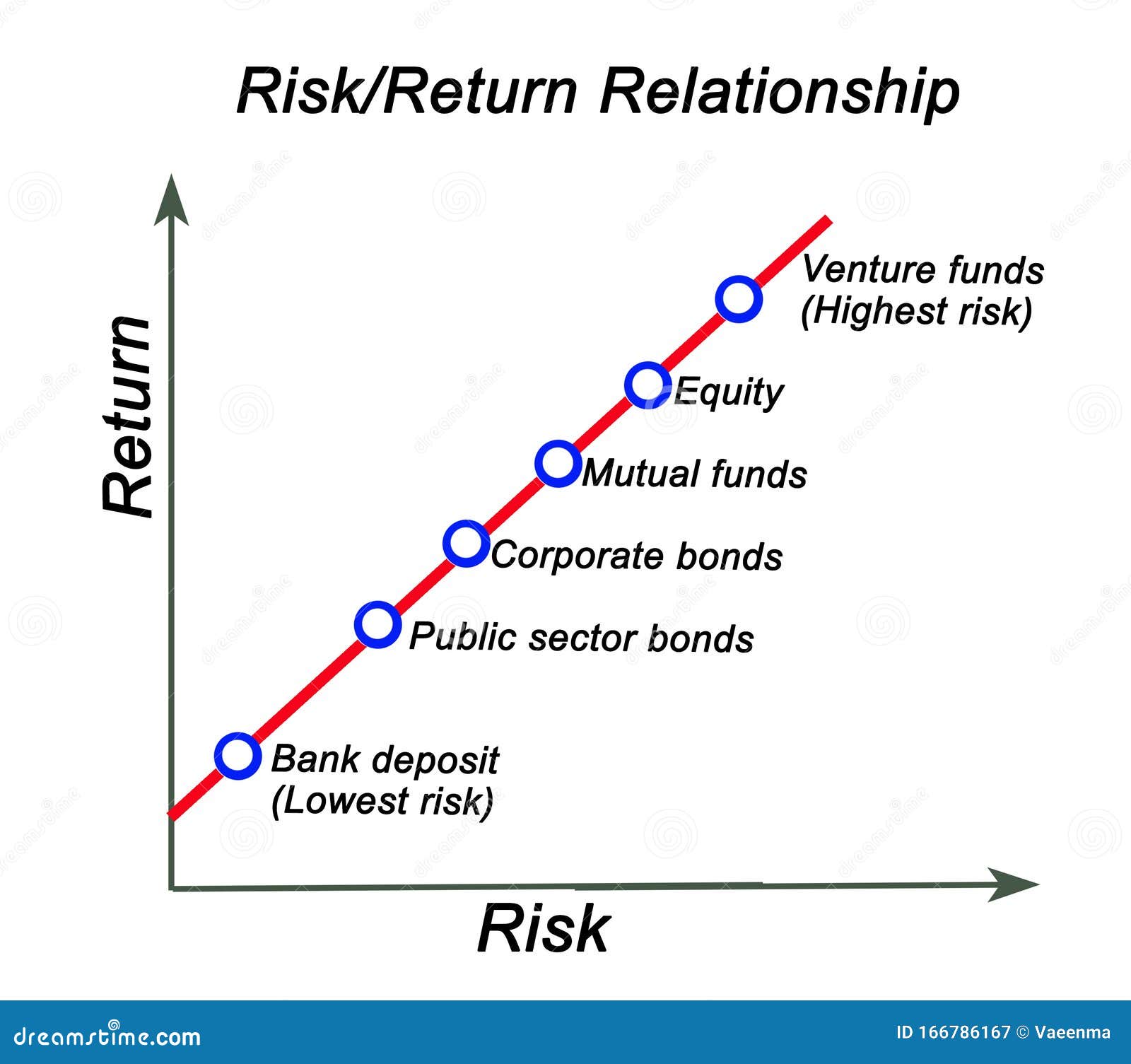
Total return is a comprehensive measure of an investment’s performance, encompassing both income and capital gains. It’s calculated by adding the investment’s income, such as dividends or interest, to its capital appreciation, or the increase in its market value. This approach provides a complete picture of an investment’s profitability, allowing investors to make informed decisions. Total return is particularly useful for investments that generate regular income, such as bonds, dividend-paying stocks, and real estate investment trusts (REITs). For instance, a bond with a 4% coupon rate and a 2% capital appreciation would have a total return of 6%. By understanding total return, investors can better evaluate their investments and make adjustments to optimize their portfolios, ultimately leading to more effective total return vs absolute return strategies.
Uncovering Absolute Return: A Contrarian Approach to Investing
Absolute return is a return strategy that focuses on generating positive returns, regardless of the overall market performance. This approach is often employed by investors seeking to mitigate risk and preserve capital during turbulent market conditions. In contrast to total return, which measures an investment’s performance relative to a benchmark, absolute return strategies aim to deliver positive returns in both rising and falling markets. This contrarian approach can be particularly beneficial during periods of market volatility, as it allows investors to capitalize on opportunities that arise from market inefficiencies. By incorporating absolute return strategies into a diversified investment portfolio, investors can reduce their exposure to market risk and increase their potential for long-term success. When considering total return vs absolute return, it’s essential to understand the distinct benefits and limitations of each approach, and how they can be leveraged to achieve specific investment objectives.
How to Choose the Right Return Strategy for Your Investment Goals
Selecting the appropriate return strategy is crucial for achieving investment success. When deciding between total return and absolute return, investors must consider their investment objectives, risk tolerance, and time horizon. For instance, investors seeking long-term growth may opt for a total return strategy, which can provide higher returns over an extended period. On the other hand, investors with a shorter time horizon or those who prioritize capital preservation may prefer an absolute return strategy, which can help mitigate losses during market downturns. Additionally, investors with a higher risk tolerance may be more suited to a total return approach, while those with a lower risk tolerance may benefit from an absolute return strategy. By understanding their individual circumstances and goals, investors can choose the return strategy that best aligns with their needs, ultimately leading to more effective total return vs absolute return strategies. For example, a retiree seeking stable income may opt for an absolute return strategy, while a young professional seeking long-term growth may prefer a total return approach.
Total Return vs Absolute Return: A Head-to-Head Comparison
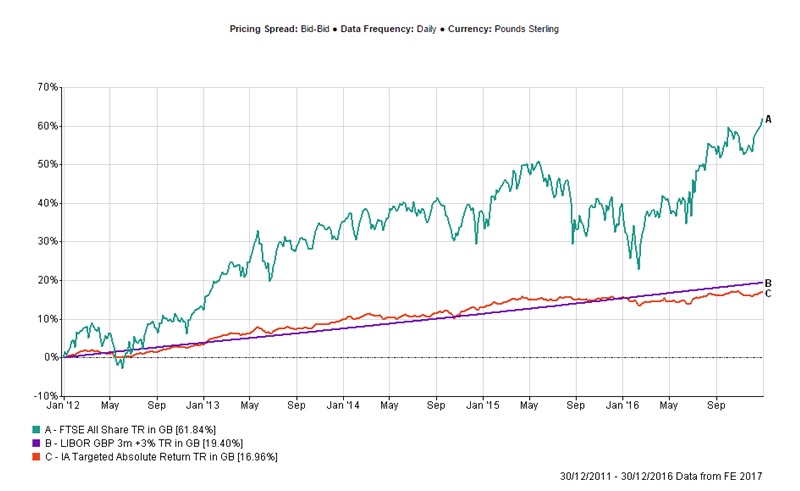
In the realm of investment returns, two strategies stand out: total return and absolute return. While both approaches aim to generate profits, they differ significantly in their objectives, calculation methods, and risk profiles. When considering total return vs absolute return, it’s essential to understand the strengths and weaknesses of each strategy. Total return, which measures an investment’s performance relative to a benchmark, is often preferred by investors seeking long-term growth. In contrast, absolute return, which focuses on generating positive returns regardless of market conditions, is ideal for investors prioritizing capital preservation. In a bull market, total return strategies tend to outperform, while in a bear market, absolute return strategies can provide a hedge against losses. However, total return strategies can be more volatile, whereas absolute return strategies may sacrifice potential upside for downside protection. By understanding the nuances of total return vs absolute return, investors can make informed decisions about which strategy to employ in different market scenarios, ultimately leading to more effective investment outcomes.
Real-World Examples: How Top Investors Utilize Return Strategies
Successful investors often employ a combination of total return and absolute return strategies to achieve their investment goals. For instance, Warren Buffett’s value investing approach focuses on generating total returns through long-term growth, while also considering absolute return principles to mitigate potential losses. Similarly, Ray Dalio’s All Weather portfolio, which aims to provide consistent returns in various market conditions, incorporates both total return and absolute return strategies. In another example, the Yale Endowment’s investment approach, led by David Swensen, balances total return-seeking assets like equities with absolute return-generating assets like hedge funds. These real-world examples demonstrate how top investors effectively utilize total return vs absolute return strategies to achieve their investment objectives. By studying these approaches, investors can gain valuable insights into the practical application of return strategies and develop their own effective investment strategies.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Implementing Return Strategies
When implementing total return vs absolute return strategies, investors often fall prey to common pitfalls that can hinder their investment success. One common mistake is failing to clearly define investment objectives, leading to a mismatch between the chosen return strategy and the desired outcomes. Another pitfall is neglecting to diversify a portfolio, which can result in overexposure to a particular asset class or market sector. Additionally, investors may underestimate the importance of risk management, leading to inadequate protection against potential losses. Furthermore, chasing past performance or relying too heavily on a single investment strategy can also lead to suboptimal results. To overcome these challenges, investors should carefully assess their investment goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon, and develop a well-diversified portfolio that balances total return and absolute return strategies. By avoiding these common pitfalls, investors can increase their chances of achieving long-term investment success.
Conclusion: Mastering Return Strategies for Long-Term Investment Success
In conclusion, understanding the nuances of total return vs absolute return strategies is crucial for achieving long-term investment success. By grasping the concepts of total return and absolute return, investors can make informed decisions about their investment approach, balancing growth and income generation with risk management and capital preservation. By avoiding common pitfalls and selecting the right return strategy for their investment goals, investors can increase their chances of achieving their desired outcomes. Whether an investor is seeking long-term growth, income generation, or capital preservation, a deep understanding of total return and absolute return strategies is essential for navigating the complex investment landscape and unlocking investment success.