Understanding the Income Statement: A Key to Business Success
The income statement is a critical component of financial reporting, providing stakeholders with a snapshot of a company’s financial performance over a specific period. It presents the revenues, expenses, and net income of a business, offering valuable insights into its profitability and cash flow. An income statement with depreciation expense is particularly important, as it helps to accurately reflect the cost of assets over their useful life. By analyzing an income statement with depreciation expense, investors, creditors, and management can make informed decisions about a company’s future prospects. In this article, we will explore the importance of the income statement, with a focus on depreciation expense, and provide guidance on how to analyze and report it effectively.
What is Depreciation Expense and Why Does it Matter?
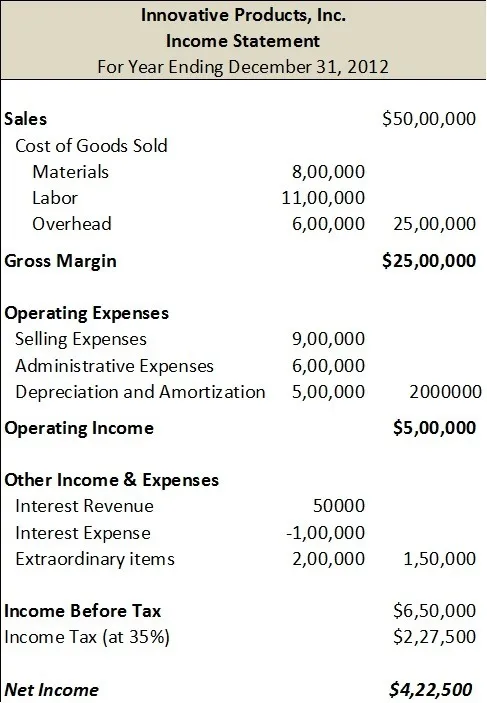
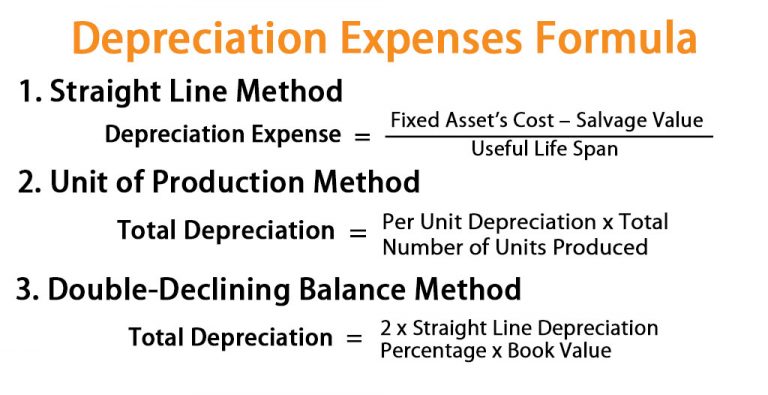
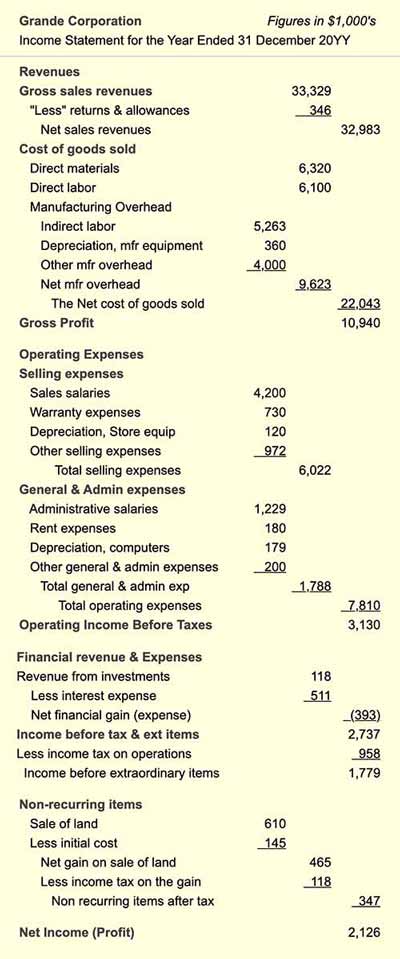
Depreciation expense is a critical component of a company’s financial statements, including the income statement. It represents the allocation of the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life. In other words, depreciation expense is the decrease in value of an asset over time, such as a building, machinery, or vehicle. This expense is calculated using various methods, including the straight-line method, declining balance method, and units-of-production method. The choice of method depends on the nature of the asset and the company’s accounting policies. Depreciation expense has a significant impact on a company’s financial statements, as it affects net income, cash flow, and asset values. An accurate calculation and reporting of depreciation expense on the income statement with depreciation expense is essential for stakeholders to make informed decisions about a company’s financial performance and position.
How to Analyze an Income Statement with Depreciation Expense
When analyzing an income statement with depreciation expense, it’s essential to follow a step-by-step approach to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial performance. Here’s a guide to help you navigate the process:
Step 1: Identify the Depreciation Expense – Locate the depreciation expense line item on the income statement and note its value. This will give you an idea of the total amount of depreciation expense recorded during the period.
Step 2: Calculate the Depreciation Expense Ratio – Divide the depreciation expense by the total revenue to calculate the depreciation expense ratio. This ratio will help you understand the proportion of revenue allocated to depreciation expense.
Step 3: Analyze the Impact on Net Income – Evaluate how depreciation expense affects net income by calculating the net income margin with and without depreciation expense. This will help you understand the true profitability of the company.
Step 4: Review Asset Utilization – Assess the company’s asset utilization by analyzing the relationship between depreciation expense and total assets. This will provide insights into the company’s asset management efficiency.
Step 5: Compare to Industry Benchmarks – Compare the company’s depreciation expense ratio and asset utilization to industry benchmarks to identify areas of improvement.
By following these steps, you’ll be able to gain a deeper understanding of a company’s financial performance and make informed decisions about its future prospects. An income statement with depreciation expense is a powerful tool for analysis, and by mastering its analysis, you’ll be better equipped to unlock the secrets of financial reporting.
The Impact of Depreciation Expense on Net Income
Depreciation expense has a significant impact on a company’s net income, and understanding this relationship is crucial for stakeholders to make informed decisions. Net income, also known as the bottom line, represents a company’s profitability after deducting all expenses, including depreciation expense, from revenue. The inclusion of depreciation expense on the income statement with depreciation expense can significantly affect net income, leading to a decrease in profitability.
The impact of depreciation expense on net income can be twofold. Firstly, it reduces net income, which can lead to a decrease in a company’s market value and investor confidence. Secondly, it can affect a company’s cash flow, as depreciation expense is a non-cash item that does not require an immediate outlay of cash. However, it can influence a company’s ability to generate cash, as it reduces net income, which is a key driver of cash flow.
For instance, a company with a high depreciation expense may report a lower net income, which can lead to a decrease in its market value. Conversely, a company with a low depreciation expense may report a higher net income, which can lead to an increase in its market value. Therefore, it is essential to analyze the impact of depreciation expense on net income to gain a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial performance.
In conclusion, the impact of depreciation expense on net income is a critical aspect of financial reporting, and stakeholders must carefully consider this relationship when analyzing a company’s income statement with depreciation expense. By doing so, they can gain a deeper understanding of a company’s profitability and cash flow, making informed decisions about its future prospects.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Accounting for Depreciation Expense
When accounting for depreciation expense on an income statement with depreciation expense, companies often make mistakes that can lead to inaccurate financial reporting and misinformed decision-making. To avoid these errors, it’s essential to be aware of the common mistakes and take steps to prevent them.
One common mistake is incorrect asset classification, which can lead to incorrect depreciation expense calculations. For instance, classifying a short-term asset as a long-term asset can result in incorrect depreciation expense amounts. To avoid this, companies should ensure that assets are correctly classified and depreciation expense is calculated accordingly.
Another mistake is failing to update depreciation schedules regularly, which can lead to inaccurate depreciation expense amounts. Companies should regularly review and update their depreciation schedules to ensure that they reflect the current asset base and depreciation rates.
In addition, companies may incorrectly estimate the useful life of an asset, leading to incorrect depreciation expense amounts. To avoid this, companies should conduct regular asset assessments to determine the accurate useful life of each asset.
Furthermore, companies may fail to account for depreciation expense on intangible assets, such as patents and copyrights. This can lead to inaccurate financial reporting and misinformed decision-making. Companies should ensure that they account for depreciation expense on all assets, including intangible assets.
By avoiding these common mistakes, companies can ensure that their income statement with depreciation expense accurately reflects their financial performance. This will enable stakeholders to make informed decisions about the company’s future prospects.
Real-World Examples of Income Statements with Depreciation Expense
To illustrate how companies report and analyze depreciation expense on their income statement with depreciation expense, let’s examine real-world examples from well-known companies.
For instance, Amazon’s 2020 income statement reports depreciation and amortization expense of $10.9 billion, which represents a significant portion of its total operating expenses. By analyzing this expense, investors can gain insight into Amazon’s asset base and its impact on the company’s profitability.
Another example is Apple’s 2020 income statement, which reports depreciation and amortization expense of $4.3 billion. This expense is a significant component of Apple’s cost of sales and operating expenses, and its analysis provides valuable information about the company’s asset utilization and profitability.
Additionally, Microsoft’s 2020 income statement reports depreciation and amortization expense of $2.5 billion, which is a significant portion of its total operating expenses. By analyzing this expense, investors can gain insight into Microsoft’s asset base and its impact on the company’s profitability and cash flow.
These real-world examples demonstrate how companies report and analyze depreciation expense on their income statement with depreciation expense. By examining these examples, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of the importance of depreciation expense in financial reporting and its impact on a company’s financial performance.
By analyzing income statements with depreciation expense from various companies, stakeholders can identify trends and patterns in depreciation expense reporting and analysis. This can provide valuable insights into a company’s financial performance and inform investment decisions.
Best Practices for Reporting Depreciation Expense on the Income Statement
When reporting depreciation expense on the income statement with depreciation expense, companies should follow best practices to ensure accurate and transparent financial reporting. Here are some guidelines to follow:
Firstly, companies should clearly disclose depreciation expense in a separate line item on the income statement, providing stakeholders with a clear understanding of this expense. This disclosure should include the amount of depreciation expense, the method of calculation, and the assets to which it relates.
Secondly, companies should ensure that depreciation expense is properly classified on the income statement, distinguishing between operating and non-operating depreciation expense. This classification is essential for stakeholders to understand the impact of depreciation expense on a company’s operating performance.
Thirdly, companies should provide detailed notes to the financial statements, explaining the depreciation policies and methods used, including the estimated useful lives of assets and the depreciation rates applied. This disclosure enables stakeholders to understand the assumptions underlying depreciation expense calculations.
Fourthly, companies should consider presenting depreciation expense as a percentage of revenue or total assets, providing stakeholders with a better understanding of the relative significance of this expense. This presentation can help stakeholders identify trends and patterns in depreciation expense over time.
Finally, companies should ensure that depreciation expense is consistently reported and analyzed across different reporting periods, enabling stakeholders to make meaningful comparisons and identify trends in a company’s financial performance.
By following these best practices, companies can ensure that depreciation expense is accurately reported and analyzed on the income statement with depreciation expense, providing stakeholders with a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial performance.
Conclusion: Mastering the Income Statement with Depreciation Expense
In conclusion, accurately reporting and analyzing depreciation expense on the income statement with depreciation expense is crucial for stakeholders to understand a company’s financial performance. By grasping the concept of depreciation expense, its calculation, and its impact on financial statements, stakeholders can make informed decisions about a company’s profitability and cash flow.
This comprehensive guide has provided a step-by-step approach to analyzing an income statement with depreciation expense, highlighting key metrics and ratios to focus on. Additionally, it has discussed the impact of depreciation expense on net income, common mistakes to avoid, and best practices for reporting depreciation expense on the income statement.
By mastering the income statement with depreciation expense, stakeholders can gain a deeper understanding of a company’s financial performance and make more informed investment decisions. Remember, accurate reporting and analysis of depreciation expense are essential for stakeholders to unlock the secrets of financial reporting and make informed decisions.
In today’s competitive business environment, companies must prioritize accurate and transparent financial reporting to maintain stakeholder trust and confidence. By following the guidelines and best practices outlined in this article, companies can ensure that their income statement with depreciation expense provides a clear and comprehensive picture of their financial performance.
Ultimately, mastering the income statement with depreciation expense is essential for business success. By understanding the intricacies of depreciation expense and its impact on financial statements, stakeholders can make informed decisions and drive business growth.