What is Depreciation and Why Does it Matter?
In the world of finance, depreciation is a fundamental concept that plays a vital role in a company’s financial performance. It represents the decrease in value of an asset over time, resulting from wear and tear, obsolescence, or other factors. Depreciation is a non-cash expense that is recorded on the income statement, providing a more accurate representation of a company’s financial position. The main question that arises is, is depreciation on the income statement? The answer lies in understanding the importance of depreciation in financial reporting. Depreciation is often confused with amortization, which is the process of allocating the cost of an intangible asset over its useful life. While both concepts are related to asset valuation, they differ in their application and treatment in financial statements. Accurate depreciation reporting is crucial for companies to maintain transparency, comply with regulations, and make informed business decisions.
Where Does Depreciation Appear on the Income Statement?
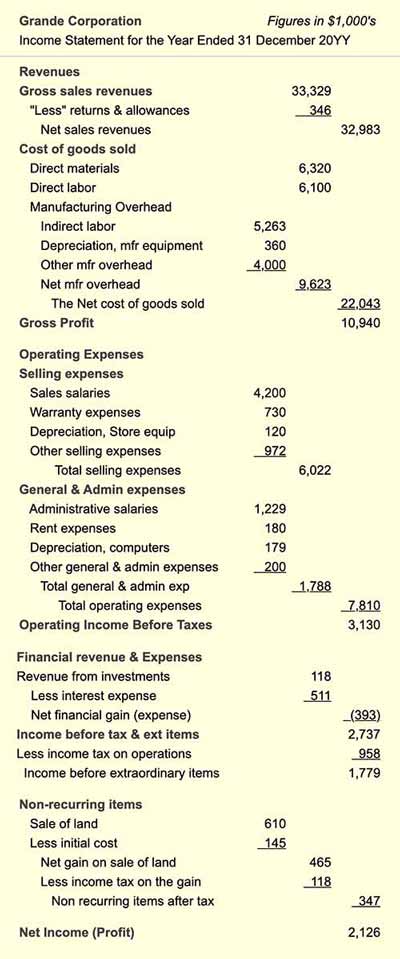
Depreciation is a critical component of a company’s income statement, as it represents the allocation of an asset’s cost over its useful life. The question of is depreciation on the income statement is answered by understanding its relationship with the income statement. Depreciation is recorded as an expense on the income statement, typically under the “Operating Expenses” or “Depreciation and Amortization” section. This expense is calculated by dividing the asset’s cost by its useful life, resulting in a depreciation expense that is reported on the income statement. For example, if a company purchases a piece of equipment for $10,000 with a useful life of 5 years, the annual depreciation expense would be $2,000. This expense is then subtracted from revenue to calculate net income. Accurate reporting of depreciation on the income statement is essential for stakeholders to understand a company’s financial performance and make informed decisions.
How to Calculate Depreciation for Accurate Financial Reporting
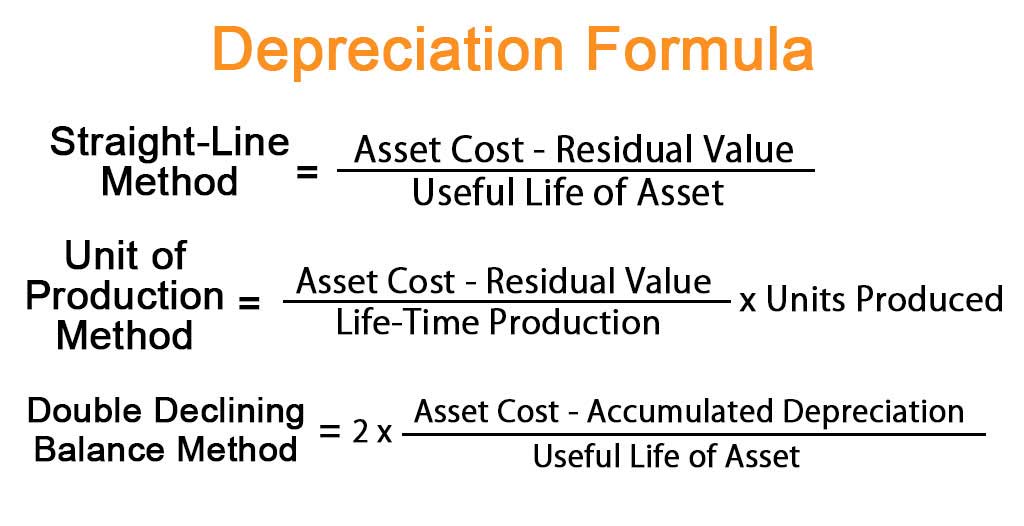
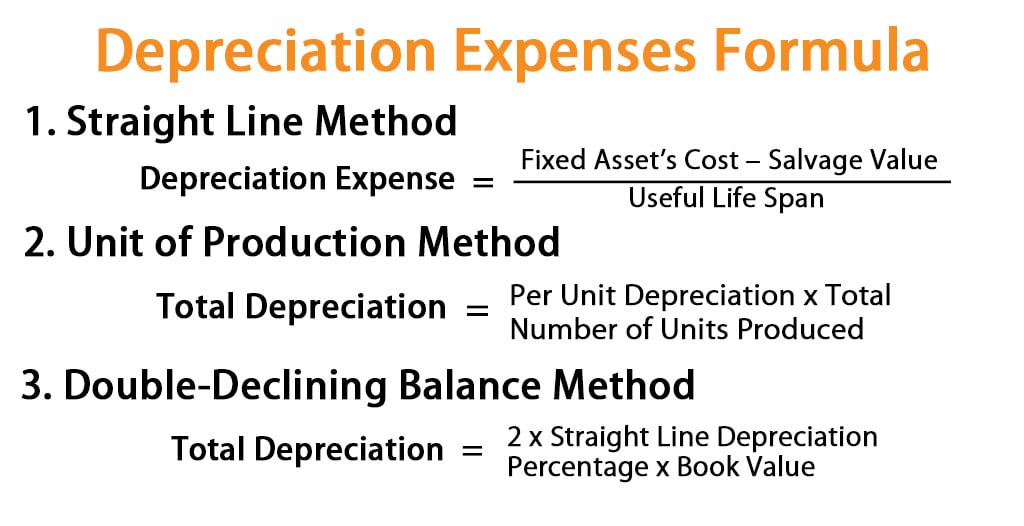
Calculating depreciation is a crucial step in financial reporting, as it directly affects a company’s net income and financial performance. There are several methods to calculate depreciation, including the straight-line method, declining balance method, and units-of-production method. The straight-line method is the most commonly used, where the asset’s cost is divided by its useful life to determine the annual depreciation expense. For example, if a company purchases a piece of equipment for $10,000 with a useful life of 5 years, the annual depreciation expense would be $2,000. The formula for straight-line depreciation is: Depreciation Expense = (Cost – Residual Value) / Useful Life. The declining balance method, on the other hand, involves applying a depreciation rate to the asset’s book value each year. This method is more complex and requires a thorough understanding of the asset’s usage and maintenance. Regardless of the method chosen, accurate calculation of depreciation is essential to ensure that a company’s financial statements accurately reflect its financial position. Remember, is depreciation on the income statement is a critical question to answer when calculating depreciation, as it directly affects a company’s net income and financial performance.
The Impact of Depreciation on a Company’s Bottom Line
Depreciation has a significant impact on a company’s financial performance, affecting its net income, cash flow, and tax liabilities. The depreciation expense recorded on the income statement reduces a company’s net income, which in turn affects its profitability and financial ratios. For instance, a company with high depreciation expenses may report lower net income, which could impact its ability to secure loans or attract investors. Additionally, depreciation affects a company’s cash flow, as it represents a non-cash expense that does not require an immediate outlay of cash. This can be beneficial for companies with limited cash reserves, as they can still claim the depreciation expense without incurring a cash outflow. Furthermore, depreciation has tax implications, as it reduces a company’s taxable income, resulting in lower tax liabilities. It is essential to understand how depreciation influences a company’s financial performance, as it can significantly impact its bottom line. Remember, is depreciation on the income statement is a critical consideration when evaluating a company’s financial health and making informed business decisions.
Common Depreciation Mistakes to Avoid in Financial Reporting
Depreciation is a complex and nuanced concept, and even small mistakes can have significant consequences on a company’s financial reporting. One common error is incorrect asset classification, where assets are misclassified as either tangible or intangible, leading to inaccurate depreciation calculations. Another mistake is inadequate record-keeping, where depreciation schedules are not regularly updated, resulting in inaccurate financial statements. Additionally, failing to update depreciation schedules to reflect changes in asset usage or market value can lead to inaccurate financial reporting. Furthermore, not considering the impact of depreciation on tax liabilities can result in unnecessary tax payments or penalties. It is essential to avoid these common mistakes to ensure accurate financial reporting and compliance with accounting standards. Remember, is depreciation on the income statement is a critical consideration when evaluating a company’s financial health, and accurate depreciation reporting is crucial for informed decision-making.
Depreciation and Tax Implications: What You Need to Know
Depreciation has significant tax implications that can impact a company’s taxable income, tax deductions, and capital gains. When calculating depreciation, companies can claim a tax deduction for the depreciation expense, which reduces their taxable income and subsequently lowers their tax liability. Additionally, depreciation can affect capital gains, as the gain or loss on the sale of an asset is calculated based on its depreciated value. It is essential to comply with tax laws and regulations, such as the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS), to ensure accurate depreciation reporting and minimize tax liabilities. Furthermore, companies should be aware of the tax implications of depreciation methods, such as the straight-line method and the declining balance method, as they can impact tax deductions and liabilities. Remember, is depreciation on the income statement is a critical consideration when evaluating a company’s financial health, and understanding the tax implications of depreciation is crucial for informed decision-making and compliance with tax laws.
Best Practices for Depreciation Accounting and Financial Analysis
To ensure accurate and reliable financial reporting, it is essential to follow best practices for depreciation accounting and financial analysis. One key practice is to maintain accurate and detailed records of assets, including their purchase date, cost, and expected useful life. Regular asset evaluations should also be performed to ensure that depreciation schedules are up-to-date and reflect any changes in asset usage or market value. Additionally, companies should use depreciation to inform business decisions, such as asset replacement or upgrade strategies. By following these best practices, companies can ensure that their financial statements accurately reflect the impact of depreciation and provide stakeholders with a clear understanding of their financial performance. Remember, is depreciation on the income statement is a critical consideration when evaluating a company’s financial health, and accurate depreciation reporting is crucial for informed decision-making and compliance with accounting standards. By implementing these best practices, companies can ensure that their depreciation accounting and financial analysis are accurate, reliable, and informative.
Conclusion: The Importance of Accurate Depreciation Reporting
In conclusion, accurate depreciation reporting is crucial for financial transparency, compliance, and informed decision-making. By understanding the concept of depreciation, its significance in accounting, and its impact on a company’s financial performance, stakeholders can make informed decisions about investments, funding, and resource allocation. Remember, is depreciation on the income statement is a critical consideration when evaluating a company’s financial health, and accurate depreciation reporting is essential for a comprehensive understanding of a company’s financial position. By following best practices for depreciation accounting and financial analysis, companies can ensure that their financial statements accurately reflect the impact of depreciation and provide stakeholders with a clear understanding of their financial performance. Ultimately, accurate depreciation reporting is essential for building trust, credibility, and long-term success in the business world.