Why Annualizing Matters: Understanding the Impact on Investment Decisions
Accurate investment analysis relies heavily on the ability to annualize monthly returns. This crucial step enables investors to make informed decisions, evaluate performance, and set realistic expectations. By understanding how to annualize monthly returns, investors can gain a deeper insight into their investment’s growth potential, identify areas for improvement, and optimize their portfolio for maximum returns. Annualizing monthly returns helps to provide a clear picture of an investment’s performance, allowing investors to compare different investment options and make data-driven decisions. In essence, annualizing monthly returns is a critical component of a successful investment strategy, and understanding how to do it correctly is essential for achieving long-term financial goals.
The Math Behind Annualization: A Step-by-Step Breakdown
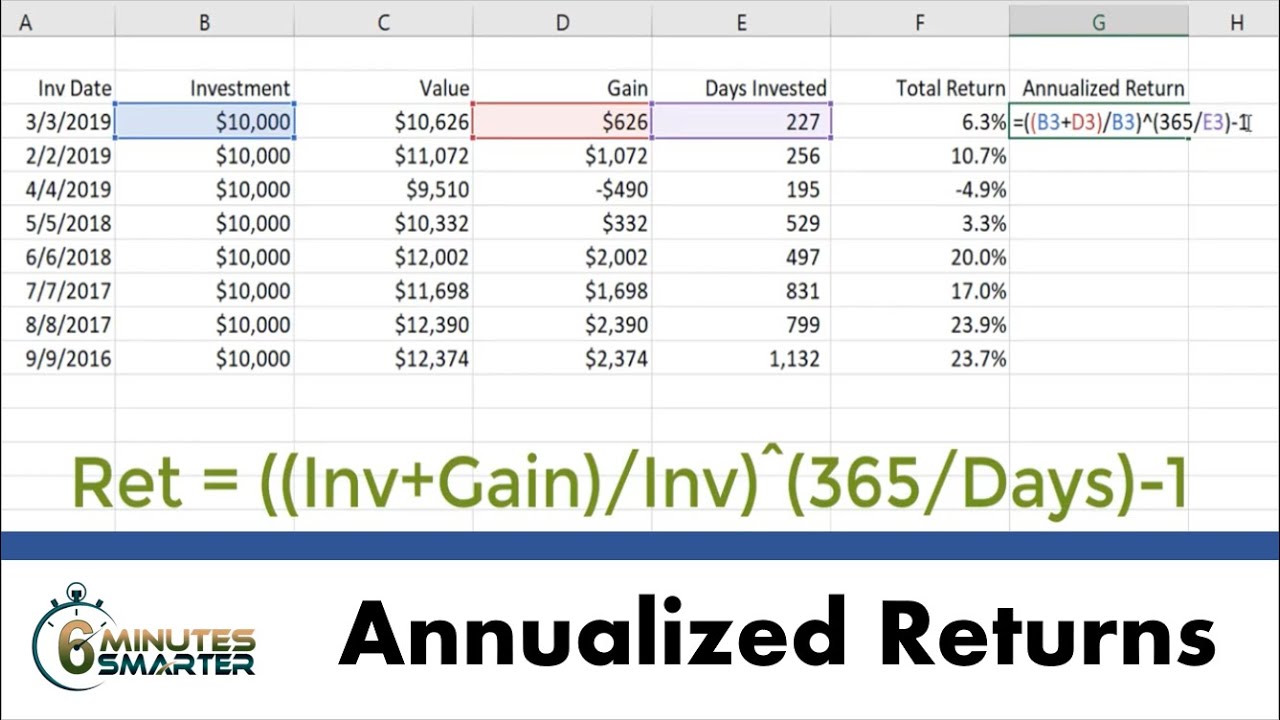
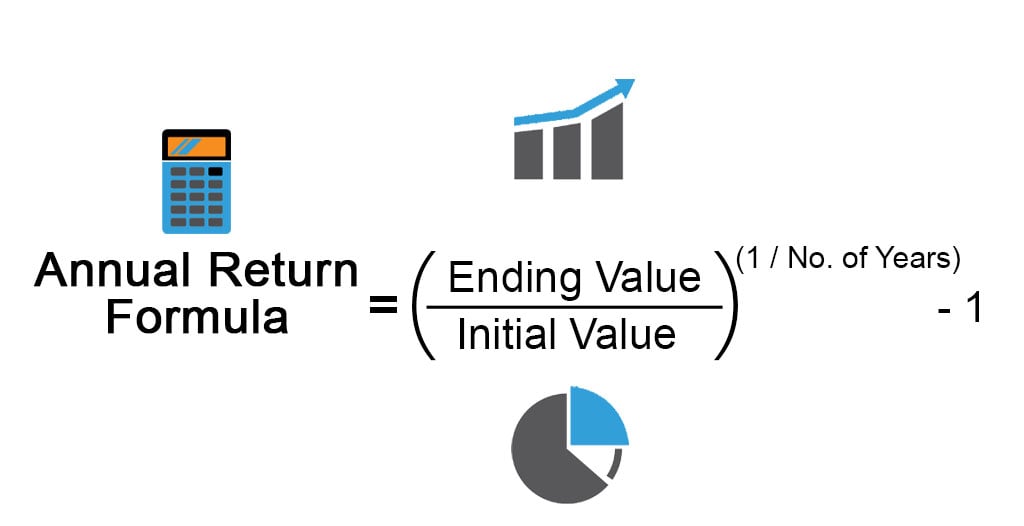
The annualization formula is a powerful tool for investors, allowing them to convert monthly returns into annual returns. To understand how to annualize monthly returns, it’s essential to grasp the underlying math. The annualization formula involves three key variables: the monthly return, the number of periods, and the desired frequency. The formula is as follows: (1 + monthly return)^number of periods – 1. For example, let’s say an investment has a monthly return of 2%. To annualize this return, we would use the following calculation: (1 + 0.02)^12 – 1, where 12 represents the number of months in a year. This would give us an annualized return of approximately 26.8%. By understanding this formula and how to apply it, investors can gain a deeper insight into their investment’s performance and make more informed decisions. Mastering the art of how to annualize monthly returns is crucial for achieving long-term financial success.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid When Annualizing Monthly Returns
When learning how to annualize monthly returns, it’s essential to be aware of common mistakes that can lead to inaccurate results. One of the most significant pitfalls is ignoring compounding, which can significantly impact investment growth. Compounding is the process of earning returns on both the principal amount and any accrued interest, and failing to account for it can result in underestimating an investment’s potential. Another common mistake is using incorrect formulas or misunderstanding the variables involved in the annualization process. This can lead to incorrect calculations and a distorted view of an investment’s performance. Additionally, investors often fail to account for fees and expenses, which can significantly eat into returns. To avoid these pitfalls, it’s crucial to have a solid understanding of the annualization formula and to carefully consider all the variables involved. By being aware of these common mistakes, investors can ensure that they are accurately calculating annualized returns and making informed investment decisions.
How to Annualize Monthly Returns in Excel: A Practical Guide
When it comes to annualizing monthly returns, Excel can be a powerful tool to streamline the process. To get started, investors can use the POWER function in Excel, which is denoted by the caret symbol (^). The formula for annualizing monthly returns in Excel is: =(1+monthly return)^12-1. For example, if the monthly return is 2%, the formula would be: =(1+0.02)^12-1. This would give an annualized return of approximately 26.8%. To make the process even easier, investors can create a template in Excel with the formula already built in, allowing them to simply input the monthly returns and automatically calculate the annualized return. Additionally, Excel’s built-in functions, such as the EFFECT function, can be used to calculate the effective annual rate of return, taking into account compounding. By mastering how to annualize monthly returns in Excel, investors can quickly and accurately evaluate their investment’s performance and make informed decisions.
Real-World Examples: Annualizing Monthly Returns in Different Investment Scenarios
To better understand how to annualize monthly returns, it’s helpful to explore real-world examples in different investment scenarios. For instance, let’s consider a stock investment with a monthly return of 1.5%. To annualize this return, we can use the formula: =(1+0.015)^12-1, which gives an annualized return of approximately 19.6%. In contrast, a bond investment with a monthly return of 0.5% would have an annualized return of around 6.2%. Mutual funds and ETFs can also be annualized in a similar manner. For example, a mutual fund with a monthly return of 2% would have an annualized return of around 26.8%. By examining these real-world examples, investors can gain a deeper understanding of how to annualize monthly returns and make more informed investment decisions. Additionally, understanding how to annualize monthly returns can help investors compare the performance of different investments and identify opportunities for growth. By applying the annualization formula to different investment scenarios, investors can unlock the power of compounding and make the most of their investments.
The Role of Compounding in Annualizing Monthly Returns
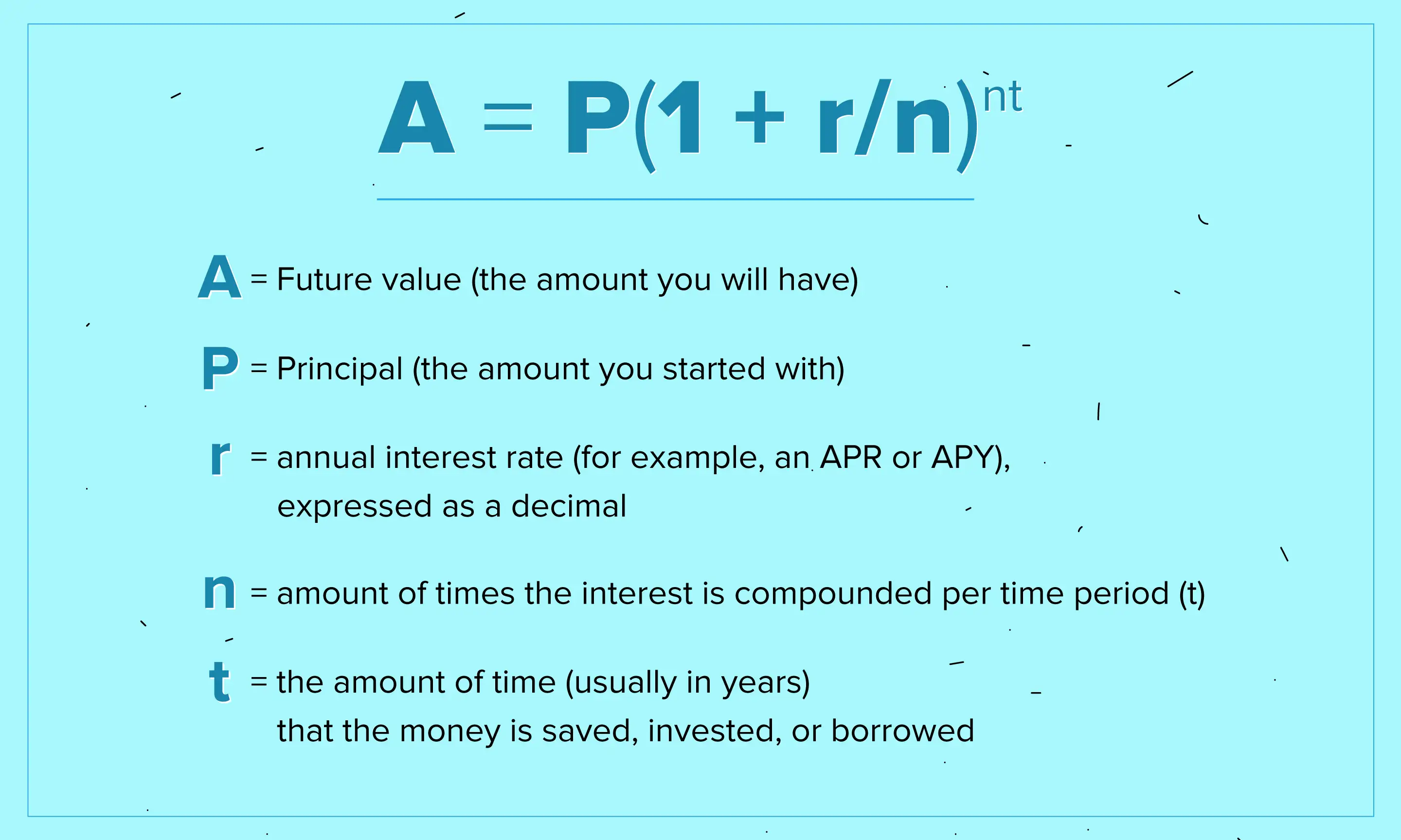
Compounding plays a crucial role in annualizing monthly returns, as it significantly affects investment growth over time. When investors annualize monthly returns, they are essentially calculating the rate of return that would have been required to produce the same total return over a year, assuming compounding. This means that the returns are reinvested to generate even more returns, creating a snowball effect that can lead to substantial growth over the long term. For example, if an investment has a monthly return of 2%, the annualized return would be approximately 26.8%. However, if the returns are compounded monthly, the actual return would be higher, around 29.5%. This demonstrates the power of compounding in annualizing monthly returns and highlights the importance of considering it when evaluating investment performance. By understanding the role of compounding, investors can make more informed decisions and set realistic expectations for their investments. Additionally, compounding can help investors identify opportunities for growth and optimize their investment strategies to maximize returns.
Annualizing Monthly Returns vs. Average Annual Returns: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to evaluating investment performance, investors often encounter two distinct methods: annualizing monthly returns and average annual returns. While both methods provide valuable insights, they serve different purposes and are used in different contexts. Annualizing monthly returns involves calculating the rate of return that would have been required to produce the same total return over a year, assuming compounding. This method is useful for evaluating the performance of an investment over a specific period, such as a year, and for comparing the performance of different investments. On the other hand, average annual returns represent the average return of an investment over a specific period, usually several years. This method is useful for evaluating the long-term performance of an investment and for understanding its volatility. To illustrate the difference, consider an investment with a monthly return of 2%. The annualized return would be approximately 26.8%, while the average annual return over a 5-year period might be 10%. By understanding the distinction between these two methods, investors can choose the most appropriate approach for their investment analysis and make more informed decisions. For instance, when evaluating a mutual fund’s performance, annualizing monthly returns might be more relevant, while when assessing a stock’s long-term performance, average annual returns might be more suitable. By grasping the nuances of these two methods, investors can gain a deeper understanding of how to annualize monthly returns and make more effective investment decisions.
Best Practices for Annualizing Monthly Returns in Investment Analysis
When it comes to annualizing monthly returns in investment analysis, following best practices is crucial to ensure accurate and reliable results. Here are some tips to help investors and analysts get the most out of this powerful tool: First, prioritize data quality by using reliable sources and ensuring that the data is consistent and up-to-date. This will help to minimize errors and ensure that the annualized returns accurately reflect the investment’s performance. Second, use a consistent methodology when annualizing monthly returns, such as using the same formula and assumptions throughout the analysis. This will help to ensure that the results are comparable and reliable. Third, consider the impact of fees and expenses on the investment’s performance, as these can significantly affect the annualized returns. Fourth, present the results in a clear and concise manner, using visual aids such as charts and graphs to help illustrate the findings. Finally, be mindful of the limitations of annualizing monthly returns, such as the assumption of compounding, and consider using other methods, such as average annual returns, to provide a more comprehensive view of the investment’s performance. By following these best practices, investors and analysts can unlock the full potential of annualizing monthly returns and make more informed investment decisions. For example, when using Excel to annualize monthly returns, it’s essential to use the correct formula and functions, such as the POWER function, to ensure accurate results. Additionally, using shortcuts and formulas can help to streamline the process and reduce errors. By mastering how to annualize monthly returns and following these best practices, investors can gain a deeper understanding of their investments and make more effective decisions.