Navigating the Complex World of Swap Rates
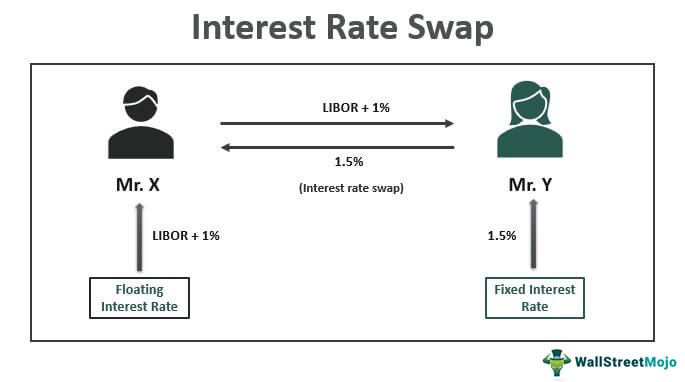
In the realm of financial markets, interest rate swaps play a vital role in managing risk and generating returns. An interest rate swap is a derivative instrument where two parties agree to exchange fixed and floating interest payments based on a notional amount. This complex financial instrument has become an essential tool for corporations, financial institutions, and investors seeking to hedge against interest rate fluctuations. However, the intricacies of swap rates and their fluctuations can be daunting, even for seasoned market participants. A deep understanding of swap rates is crucial to navigate the complexities of financial markets, particularly when it comes to interpreting a 5-year swap rate graph. By grasping the underlying dynamics of swap rates, investors and market participants can make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and capitalize on opportunities in the market.
How to Interpret a 5-Year Swap Rate Graph
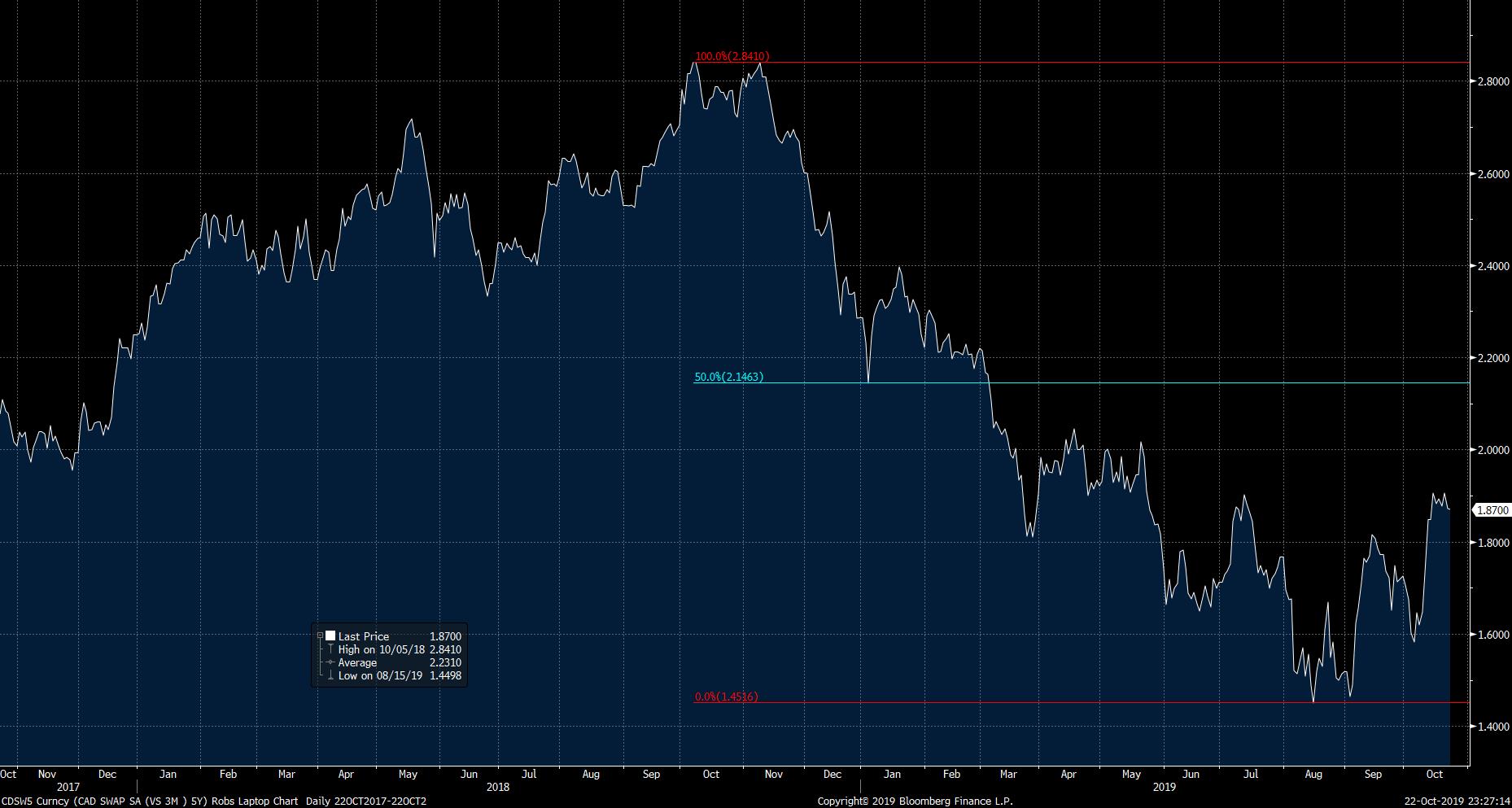
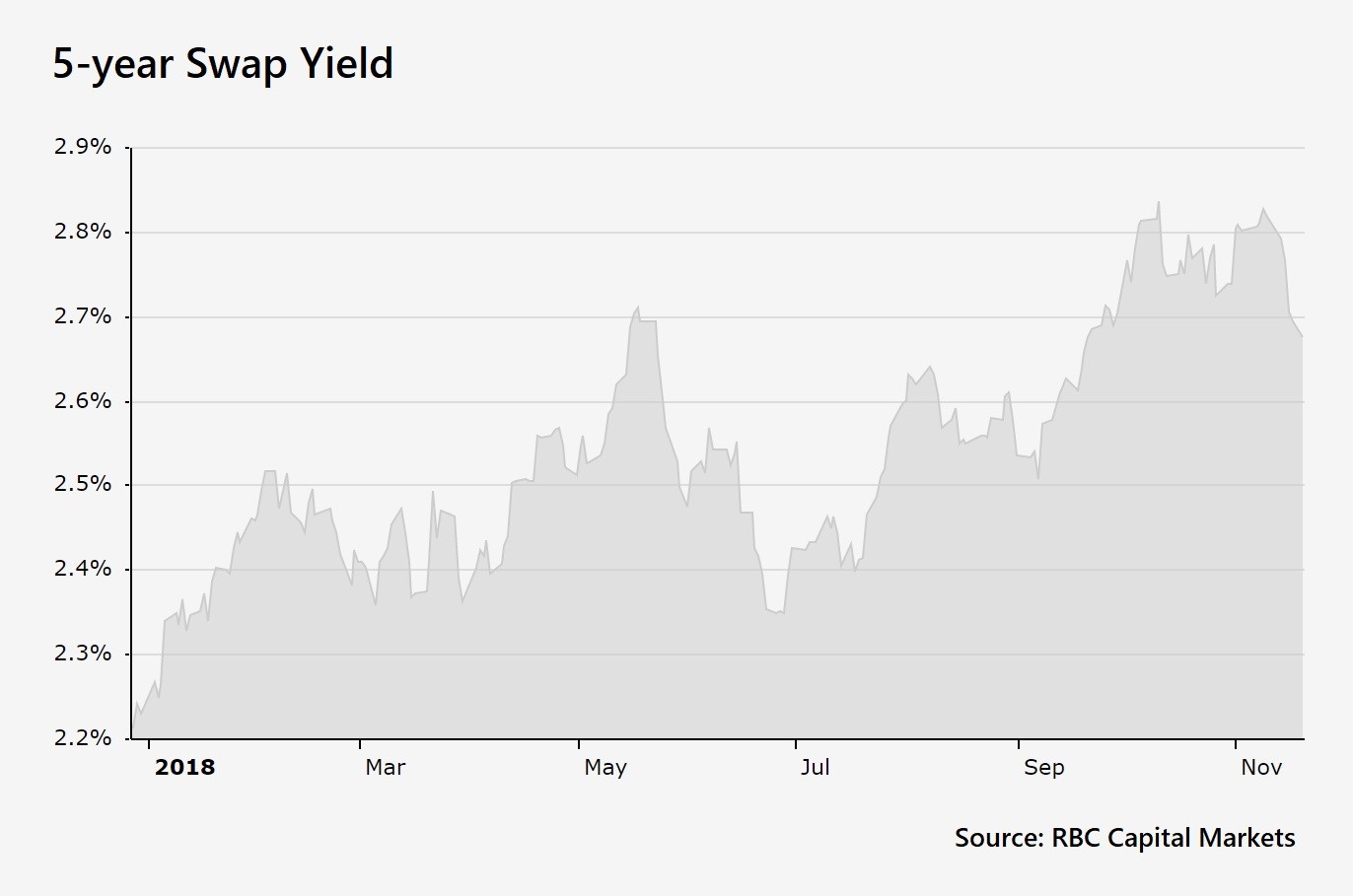
A 5-year swap rate graph is a powerful tool for investors and market participants seeking to understand interest rate trends and expectations. By analyzing the graph, one can gain valuable insights into market sentiment, interest rate forecasts, and the overall health of the economy. To effectively interpret a 5-year swap rate graph, it is essential to understand the underlying data and its implications. The graph typically plots the fixed leg of the swap against the floating leg, providing a visual representation of the interest rate swap market. By examining the graph’s shape, slope, and patterns, investors can identify trends, predict future rate movements, and make informed investment decisions. For instance, a steepening yield curve may indicate expectations of rising interest rates, while a flattening curve may suggest a more stable rate environment. A comprehensive understanding of a 5-year swap rate graph can help investors navigate the complexities of interest rate markets, optimize their investment strategies, and capitalize on opportunities in the market.
The Impact of Economic Indicators on Swap Rates
Economic indicators play a crucial role in shaping the 5-year swap rate graph, as they provide valuable insights into the overall health of the economy and interest rate expectations. Three key economic indicators that significantly influence swap rates are GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment rates.
GDP growth, for instance, has a direct impact on swap rates. A strong GDP growth rate indicates a robust economy, which can lead to higher interest rates and, subsequently, higher swap rates. Conversely, a slow GDP growth rate may result in lower interest rates and swap rates. The 5-year swap rate graph can help investors and market participants identify trends in GDP growth and adjust their investment strategies accordingly.
Inflation is another critical economic indicator that affects swap rates. Rising inflation can lead to higher interest rates, as central banks aim to curb inflationary pressures. This, in turn, can cause swap rates to increase. The 5-year swap rate graph can help investors identify inflationary trends and adjust their investment strategies to mitigate potential losses.
Unemployment rates also have a significant impact on swap rates. Low unemployment rates can lead to higher interest rates, as a strong labor market can fuel economic growth and inflation. The 5-year swap rate graph can help investors identify trends in unemployment rates and adjust their investment strategies to capitalize on emerging opportunities.
By analyzing the 5-year swap rate graph in conjunction with these economic indicators, investors and market participants can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying market trends and make informed investment decisions. The graph can help identify potential risks and opportunities, enabling investors to adjust their strategies and optimize their returns.
For instance, if the 5-year swap rate graph indicates a rising trend, accompanied by strong GDP growth and low unemployment rates, investors may consider investing in assets that benefit from a rising interest rate environment. Conversely, if the graph indicates a declining trend, accompanied by slow GDP growth and high unemployment rates, investors may consider investing in assets that benefit from a low-interest-rate environment.
By incorporating economic indicators into their analysis of the 5-year swap rate graph, investors and market participants can develop a more comprehensive understanding of the market and make more informed investment decisions.
Understanding the Role of Central Banks in Shaping Swap Rates
Central banks play a pivotal role in influencing swap rates, and their monetary policy decisions have a significant impact on the 5-year swap rate graph. By understanding the role of central banks, investors and market participants can gain valuable insights into the factors that shape swap rates and make more informed investment decisions.
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, the European Central Bank, and the Bank of England, use monetary policy tools to regulate the economy and maintain price stability. One of the primary tools at their disposal is setting interest rates, which has a direct impact on swap rates. When central banks raise interest rates, it can lead to higher swap rates, and conversely, when they lower interest rates, it can lead to lower swap rates.
The 5-year swap rate graph can help investors and market participants identify trends in central bank monetary policy decisions and their impact on swap rates. For instance, if the graph indicates a rising trend in swap rates, it may be a sign that central banks are tightening monetary policy, which can lead to higher interest rates and a stronger economy. Conversely, if the graph indicates a declining trend, it may be a sign that central banks are easing monetary policy, which can lead to lower interest rates and a weaker economy.
Central banks also use forward guidance to communicate their future monetary policy intentions, which can influence swap rates and the 5-year swap rate graph. By analyzing the language and tone of central bank statements, investors and market participants can gain insights into their future policy decisions and adjust their investment strategies accordingly.
In addition, central banks can influence swap rates through their quantitative easing policies, which involve buying or selling government bonds to inject liquidity into the market or reduce inflationary pressures. These policies can have a significant impact on the 5-year swap rate graph, as they can influence the supply and demand of government bonds and, subsequently, swap rates.
By understanding the role of central banks in shaping swap rates, investors and market participants can develop a more comprehensive understanding of the factors that influence the 5-year swap rate graph and make more informed investment decisions. The graph can provide valuable insights into central bank monetary policy decisions and their impact on swap rates, enabling investors to adjust their strategies and optimize their returns.
A Historical Analysis of 5-Year Swap Rate Trends
A historical analysis of 5-year swap rate trends provides valuable insights into the factors that have shaped the graph over time. By examining key events and market shifts, investors and market participants can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying market trends and make more informed investment decisions.
One of the most significant events that has influenced the 5-year swap rate graph is the 2008 global financial crisis. During this period, swap rates plummeted as central banks slashed interest rates to stimulate economic growth. The 5-year swap rate graph during this period reflects the unprecedented monetary policy easing, with rates falling to historic lows.
In the aftermath of the crisis, the 5-year swap rate graph has been characterized by a slow and steady rise, reflecting the gradual recovery of the global economy. However, the graph has also been influenced by other key events, such as the European sovereign debt crisis and the Brexit referendum, which have led to periods of heightened market volatility.
A closer examination of the 5-year swap rate graph reveals that it has been influenced by shifts in monetary policy, changes in economic indicators, and geopolitical events. For instance, the graph shows that swap rates tend to rise during periods of economic growth and fall during periods of economic contraction. It also highlights the impact of central bank forward guidance, which has influenced market expectations and shaped the graph.
The 5-year swap rate graph has also been influenced by changes in the yield curve, which reflects the market’s expectations of future interest rates. During periods of rising interest rates, the yield curve tends to steepen, leading to higher swap rates. Conversely, during periods of falling interest rates, the yield curve tends to flatten, leading to lower swap rates.
By analyzing the historical trends and patterns in the 5-year swap rate graph, investors and market participants can gain a deeper understanding of the underlying market forces that shape the graph. This can help them identify opportunities and manage risk, as well as inform their investment decisions and optimize their returns.
The historical analysis of the 5-year swap rate graph also highlights the importance of staying up-to-date with market developments and trends. By monitoring the graph and staying informed about key events and market shifts, investors and market participants can stay ahead of the curve and make more informed investment decisions.
The Relationship Between Swap Rates and Bond Yields
The relationship between swap rates and bond yields is a crucial aspect of understanding the 5-year swap rate graph. Swap rates and bond yields are closely linked, and changes in one can have a significant impact on the other. This interdependence is essential for investors and market participants to grasp, as it can inform their investment decisions and risk management strategies.
Swap rates and bond yields are both influenced by market expectations of future interest rates. When market participants expect interest rates to rise, they tend to push up swap rates and bond yields. Conversely, when they expect interest rates to fall, they tend to push down swap rates and bond yields. This means that changes in swap rates can be a leading indicator of changes in bond yields, and vice versa.
The 5-year swap rate graph can provide valuable insights into the relationship between swap rates and bond yields. By analyzing the graph, investors and market participants can identify trends and patterns that can inform their investment decisions. For instance, a rising 5-year swap rate graph may indicate that market participants expect interest rates to rise, which could lead to higher bond yields. Conversely, a falling 5-year swap rate graph may indicate that market participants expect interest rates to fall, which could lead to lower bond yields.
The relationship between swap rates and bond yields is also influenced by the term premium, which is the excess return that investors demand for holding longer-term bonds. When the term premium is high, bond yields tend to be higher, and swap rates tend to be lower. Conversely, when the term premium is low, bond yields tend to be lower, and swap rates tend to be higher. By understanding the term premium, investors and market participants can gain a deeper understanding of the relationship between swap rates and bond yields.
In addition, the relationship between swap rates and bond yields is influenced by the credit spread, which is the difference between the yield on a corporate bond and the yield on a comparable government bond. When credit spreads are high, bond yields tend to be higher, and swap rates tend to be lower. Conversely, when credit spreads are low, bond yields tend to be lower, and swap rates tend to be higher. By understanding the credit spread, investors and market participants can gain a deeper understanding of the relationship between swap rates and bond yields.
In conclusion, the relationship between swap rates and bond yields is a complex and multifaceted one. By understanding the factors that influence this relationship, investors and market participants can gain a deeper understanding of the 5-year swap rate graph and make more informed investment decisions. The 5-year swap rate graph can provide valuable insights into market trends and interest rate expectations, and can inform investment decisions and risk management strategies.
Using 5-Year Swap Rate Graphs for Investment Decisions
Investors and market participants can use 5-year swap rate graphs to inform their investment decisions and optimize their returns. By analyzing the graph, they can identify trends and patterns that can help them make more informed investment decisions. For instance, a rising 5-year swap rate graph may indicate that interest rates are expected to rise, which could lead to higher yields on fixed-income investments. Conversely, a falling 5-year swap rate graph may indicate that interest rates are expected to fall, which could lead to lower yields on fixed-income investments.
The 5-year swap rate graph can also be used to identify opportunities and manage risk. For example, investors can use the graph to identify periods of high volatility, which may present opportunities for arbitrage or other trading strategies. They can also use the graph to identify periods of low volatility, which may be more suitable for long-term investments.
In addition, the 5-year swap rate graph can be used to inform hedging strategies. By analyzing the graph, investors can identify potential risks and opportunities in their portfolios and adjust their hedging strategies accordingly. For instance, if the graph indicates that interest rates are expected to rise, investors may want to hedge against potential losses by taking short positions in fixed-income investments.
The 5-year swap rate graph can also be used to inform asset allocation decisions. By analyzing the graph, investors can identify the most attractive asset classes and adjust their portfolios accordingly. For instance, if the graph indicates that interest rates are expected to fall, investors may want to allocate more assets to fixed-income investments, such as bonds or treasury bills.
Furthermore, the 5-year swap rate graph can be used to inform currency trading decisions. By analyzing the graph, investors can identify potential trends and patterns in currency markets and adjust their trading strategies accordingly. For instance, if the graph indicates that interest rates are expected to rise in a particular country, investors may want to take long positions in that country’s currency.
In conclusion, the 5-year swap rate graph is a powerful tool that can be used to inform investment decisions and optimize returns. By analyzing the graph, investors and market participants can identify trends and patterns, identify opportunities and manage risk, inform hedging strategies, inform asset allocation decisions, and inform currency trading decisions. The 5-year swap rate graph is an essential tool for anyone looking to navigate the complex world of interest rate swaps and optimize their investment returns.
Looking Ahead: The Future of 5-Year Swap Rate Graphs
As the global economy continues to evolve, the 5-year swap rate graph is likely to remain a crucial tool for investors and market participants. Looking ahead, several trends and shifts in the market may impact the graph and influence investment decisions.
One potential trend is the increasing importance of central banks in shaping swap rates. As central banks continue to play a more active role in monetary policy, their decisions will likely have a significant impact on the 5-year swap rate graph. Investors and market participants will need to closely monitor central bank actions and adjust their investment strategies accordingly.
Another potential trend is the growing influence of macroeconomic factors on swap rates. As the global economy becomes increasingly interconnected, macroeconomic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment rates will likely have a greater impact on the 5-year swap rate graph. Investors and market participants will need to stay up-to-date on the latest macroeconomic trends and adjust their investment strategies to reflect changing market conditions.
In addition, the rise of alternative data sources and advanced analytics is likely to revolutionize the way investors and market participants analyze the 5-year swap rate graph. With the ability to access vast amounts of data and apply sophisticated analytical techniques, investors will be able to gain a deeper understanding of the graph and make more informed investment decisions.
Furthermore, the increasing popularity of passive investment strategies is likely to lead to a greater focus on the 5-year swap rate graph as a key indicator of market trends. As more investors turn to passive strategies, the graph will become an essential tool for identifying opportunities and managing risk.
Finally, the ongoing evolution of financial markets and instruments is likely to lead to new and innovative applications of the 5-year swap rate graph. As new products and instruments are developed, the graph will remain a crucial tool for investors and market participants looking to navigate the complex world of interest rate swaps.
In conclusion, the future of the 5-year swap rate graph looks bright. As the global economy continues to evolve, the graph will remain a vital tool for investors and market participants. By staying up-to-date on the latest trends and developments, investors can use the 5-year swap rate graph to inform their investment decisions and optimize their returns.