Decoding Treasury Bill Returns
Treasury Bills, commonly known as T-bills, are short-term debt instruments issued by the United States government. These bills are typically offered with maturities of 4 weeks to fund short-term government obligations. The 4 week treasury bill rate represents the annualized return an investor receives for purchasing the bill at a discount and holding it until maturity. Because they are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government, T-bills are considered a low-risk investment. The attractiveness of the 4 week treasury bill rate lies in its stability and the ease with which investors can access this segment of the debt market.
Understanding the basics of Treasury Bills is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the complexities of government debt. The 4 week treasury bill rate serves as an indicator of investor confidence in the government’s ability to meet its immediate financial obligations. These bills are sold at a discount to their face value, and the difference between the purchase price and the face value represents the investor’s return. For example, an investor might pay $9,990 for a $10,000 T-bill, earning $10 in interest over the 4-week period. This annualized interest rate is what is reported as the 4 week treasury bill rate.
The 4 week treasury bill rate plays a significant role in the broader financial landscape. It offers a safe haven for investors seeking to preserve capital while earning a modest return. Moreover, the rate influences other short-term interest rates and can impact borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. Monitoring the 4 week treasury bill rate provides valuable insights into the overall health of the economy and the direction of monetary policy. As a low-risk investment, T-bills are an essential component of many diversified investment portfolios, especially for those looking for short-term, liquid assets.
Factors Influencing T-Bill Performance
The fluctuations in the 4 week treasury bill rate are governed by several key economic factors. The Federal Reserve’s monetary policy plays a central role. Changes to the federal funds rate directly impact the yields of short-term debt instruments. Inflation expectations also significantly influence the 4 week treasury bill rate. When inflation is anticipated to rise, investors typically demand higher yields to compensate for the decreased purchasing power of their returns. This increased demand pushes the 4 week treasury bill rate upward.
Overall economic conditions have a profound effect on the 4 week treasury bill rate. Strong economic growth often leads to higher interest rates as demand for capital increases. Conversely, during economic slowdowns or recessions, the Federal Reserve may lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing and investment. This can lead to a decrease in the 4 week treasury bill rate. Market sentiment and investor confidence further contribute to the dynamic. During times of uncertainty, investors may seek the safety of Treasury Bills, driving up demand and potentially lowering yields, depending on the Fed’s policy response.
The interplay between these factors creates a constantly evolving landscape for the 4 week treasury bill rate. The Federal Reserve’s actions are often influenced by inflation data and economic growth indicators. Expectations about future Fed policy drive market behavior. Monitoring these indicators and understanding their potential impact is crucial for anyone tracking or investing in 4 week treasury bills. Keeping abreast of economic news and announcements from the Federal Reserve provides valuable insights into potential shifts in the 4 week treasury bill rate. These insights help in making informed financial decisions.
How to Monitor Changes in Government Debt Yields
Tracking the 4 week treasury bill rate is essential for investors and those involved in financial planning. Several resources are available for monitoring these changes effectively. By utilizing these resources and understanding how to interpret the data, one can remain informed about the current trends in government debt yields. Regularly checking the 4 week treasury bill rate is critical for making timely and informed financial decisions.
Reputable financial news sources, such as The Wall Street Journal, Bloomberg, and Reuters, provide up-to-date information on the 4 week treasury bill rate. These sources offer detailed analysis of the factors influencing the yields. Government websites like TreasuryDirect.gov are also valuable resources. They provide official data directly from the source. Financial data providers, such as Yahoo Finance and Google Finance, offer easy-to-access tools for tracking the 4 week treasury bill rate and other financial instruments. These platforms often include historical data, charting tools, and real-time updates, allowing users to monitor trends over time.
Interpreting the data is just as crucial as accessing it. Understanding the trend of the 4 week treasury bill rate involves looking at both the current yield and its historical performance. An increasing 4 week treasury bill rate may indicate rising interest rates or growing concerns about inflation. Conversely, a decreasing rate could signal a weakening economy or expectations of lower interest rates. By monitoring the 4 week treasury bill rate regularly and comparing it to other economic indicators, one can develop a more complete picture of the financial landscape. Staying informed about the 4 week treasury bill rate is vital for making sound investment decisions and managing financial risk effectively.
The Relationship Between Economic Indicators and T-Bill Rates
The 4 week treasury bill rate doesn’t exist in isolation; its fluctuations are intricately linked to key economic indicators. Understanding this correlation is crucial for investors seeking to interpret market signals and make informed decisions. The most influential indicators include GDP growth, unemployment rate, and inflation data. A strong economy, characterized by robust GDP growth, often leads to higher interest rates, including the 4 week treasury bill rate, as demand for capital increases. Conversely, during periods of economic slowdown or recession, the Federal Reserve might lower interest rates to stimulate borrowing and investment, which can lead to a decrease in the 4 week treasury bill rate.
Unemployment rates also play a significant role. High unemployment typically signals a weaker economy, prompting the Federal Reserve to maintain low interest rates to encourage job creation. This environment generally results in lower yields on short-term instruments like the 4 week treasury bill. Inflation, however, presents a more complex relationship. A rising inflation rate often leads to expectations of the Federal Reserve increasing interest rates to combat rising prices. This expectation pushes the 4 week treasury bill rate higher, as investors demand a greater return to compensate for the eroding purchasing power of their investment. For example, if the Consumer Price Index (CPI) shows a significant increase in inflation, the market anticipates the Fed’s response, leading to an immediate uptick in the 4 week treasury bill rate.
Furthermore, consider the interplay between these indicators. Stagflation, a combination of high inflation and economic stagnation, presents a particularly challenging scenario. In this situation, the Federal Reserve faces a difficult choice between controlling inflation by raising rates (potentially hindering economic growth) or stimulating the economy by lowering rates (potentially exacerbating inflation). The market’s anticipation of the Fed’s chosen course of action will significantly impact the 4 week treasury bill rate. By closely monitoring these key economic indicators and understanding their potential impact on Federal Reserve policy, investors can gain a valuable perspective on the likely future movements of the 4 week treasury bill rate and adjust their investment strategies accordingly. Therefore, understanding the correlation between economic indicators and the 4 week treasury bill rate is paramount for any investor navigating the complexities of the financial markets.
Treasury Bills Versus Other Short-Term Investments
The 4 week treasury bill rate represents a foundational element in the landscape of short-term investments. Comparing 4-week T-bills with alternatives like money market accounts, certificates of deposit (CDs), and commercial paper reveals distinct trade-offs in risk, return, and liquidity. Money market accounts, often offered by banks and credit unions, provide easy access to funds and typically offer yields that mirror prevailing short-term interest rates. However, these yields may fluctuate frequently and might not always keep pace with the 4 week treasury bill rate, especially during periods of rapid interest rate changes.
Certificates of Deposit (CDs) offer a fixed interest rate for a specified term, ranging from a few months to several years. While CDs may offer higher yields than money market accounts or 4-week T-bills, especially for longer terms, they come with the drawback of limited liquidity. Early withdrawal of funds from a CD usually incurs a penalty, reducing the overall return. Commercial paper, representing short-term debt issued by corporations, can offer competitive yields, but carries a higher degree of credit risk compared to 4-week Treasury Bills, which are backed by the full faith and credit of the U.S. government. The 4 week treasury bill rate is thus seen as a benchmark for virtually risk-free returns.
The specific advantages of 4-week T-bills lie in their safety, liquidity, and simplicity. As direct obligations of the U.S. government, they are considered among the safest investments available. Although the return may be modest, their exemption from state and local taxes enhances their appeal for some investors. Furthermore, the consistent availability of 4-week T-bills provides a reliable instrument for managing short-term cash flow needs. Conversely, the relatively low yield compared to riskier alternatives like commercial paper or longer-term CDs, might deter investors seeking higher returns. Understanding these nuanced differences is crucial for investors aiming to optimize their short-term investment strategies in relation to the prevailing 4 week treasury bill rate.
The Impact of Federal Reserve Policy On Short Term Yields
The Federal Reserve (Fed) plays a crucial role in influencing the 4 week treasury bill rate. Its primary tool is the federal funds rate, which is the target rate that commercial banks charge each other for the overnight lending of reserves. Changes to the federal funds rate directly impact other short-term interest rates, including the yield on the 4 week treasury bill rate. When the Fed raises the federal funds rate, borrowing becomes more expensive for banks, and this cost is passed on to consumers and businesses, typically leading to higher yields on short-term government debt. Conversely, when the Fed lowers the federal funds rate, borrowing becomes cheaper, which can result in lower yields on instruments like the 4 week treasury bill rate.
The Fed uses open market operations to control the money supply and indirectly affect short-term interest rates. These operations involve the buying and selling of government securities in the open market. When the Fed buys securities, it injects money into the banking system, increasing the supply of reserves and putting downward pressure on interest rates, potentially lowering the 4 week treasury bill rate. Conversely, when the Fed sells securities, it withdraws money from the banking system, decreasing the supply of reserves and putting upward pressure on interest rates, potentially raising the 4 week treasury bill rate. The scale and frequency of these open market operations are carefully calibrated to achieve the Fed’s desired monetary policy objectives. The market’s anticipation of these actions significantly impacts the 4 week treasury bill rate.
Anticipated actions by the Federal Reserve can influence Treasury Bill prices even before they occur. Market participants closely monitor the Fed’s statements, minutes from Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) meetings, and speeches by Fed officials for clues about future policy changes. If the market anticipates that the Fed will raise interest rates, investors may sell their existing Treasury Bills, causing their prices to fall and yields to rise. This is because newly issued Treasury Bills are expected to offer higher yields reflecting the anticipated rate hike. The opposite is true if the market anticipates that the Fed will lower interest rates; investors may buy Treasury Bills, pushing prices up and yields down. Therefore, understanding and anticipating Federal Reserve policy is essential for anyone monitoring or investing in the 4 week treasury bill rate.
Using Government Debt Yields as a Financial Planning Tool
The 4 week treasury bill rate serves as a valuable benchmark in financial planning, especially for assessing the risk-free rate of return. Understanding this rate assists in making well-informed investment decisions. It plays a role in evaluating the minimum return an investor should expect from any investment, considering the time value of money. This rate is often used as a baseline for comparing the potential returns of other, riskier assets. Investors use the 4 week treasury bill rate to gauge overall market conditions and investor sentiment.
The 4 week treasury bill rate informs decisions regarding asset allocation and overall portfolio strategy. Financial planners use it to determine the appropriate mix of assets based on an investor’s risk tolerance and investment goals. For risk-averse investors, T-bills represent a safe haven. A portion of their portfolio can be allocated to these instruments to preserve capital. The yield on the 4 week treasury bill rate can also influence decisions about the duration of fixed-income investments. When rates are expected to rise, investors may prefer shorter-term securities like T-bills. This helps to minimize potential losses from rising interest rates. This rate provides a stable and predictable return, especially when compared to more volatile assets like stocks.
Furthermore, the 4 week treasury bill rate is used in discounting future cash flows to determine present values. This is crucial in various financial analyses, such as valuing businesses or evaluating investment projects. By discounting future cash flows at a rate that reflects the time value of money, analysts can determine the present value of those cash flows. The 4 week treasury bill rate serves as a proxy for the risk-free rate. It is a fundamental component of many valuation models. Any changes in the 4 week treasury bill rate will affect these calculations and influence investment decisions. Awareness of the current 4 week treasury bill rate is essential for accurate financial planning and investment analysis. The 4 week treasury bill rate can inform decisions on investments, savings, and overall financial well-being.
Analyzing Trends in Short Term Treasury Yields
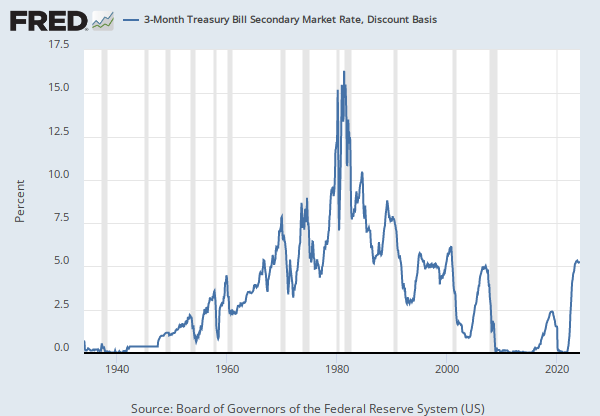
Analyzing historical trends of the 4 week treasury bill rate offers valuable insights. It aids in understanding market sentiment. It also helps in predicting future interest rate movements. Such analysis is crucial for making informed investment decisions. Examining past patterns reveals how the 4 week treasury bill rate behaves during various economic cycles. These cycles include recessions and expansions. Historical data provides a context for current market conditions.
Understanding the historical performance of the 4 week treasury bill rate involves studying its behavior during different economic phases. During recessions, investors often seek safe-haven assets. This increased demand can drive down the 4 week treasury bill rate. Conversely, during economic expansions, higher growth expectations may lead to increased interest rates. Monitoring these trends assists investors in anticipating shifts in monetary policy. Changes in the 4 week treasury bill rate reflect the market’s expectations regarding future economic conditions. Analyzing historical data provides a basis for assessing risk and return. This becomes instrumental for adjusting investment strategies.
Accessing historical data for the 4 week treasury bill rate is relatively straightforward. The U.S. Department of the Treasury provides this information on its website, TreasuryDirect.gov. Financial data providers like Bloomberg and Reuters also offer detailed historical data. These resources allow investors to chart the 4 week treasury bill rate over time. By observing these trends, one can identify periods of stability and volatility. Recognizing these patterns enhances an investor’s ability to make strategic decisions. A thorough analysis of the 4 week treasury bill rate, combined with economic data, is essential. This approach contributes to sound financial planning and investment management. Examining long-term trends in the 4 week treasury bill rate allows for a more complete understanding of market dynamics. The 4 week treasury bill rate is a key indicator. Its historical patterns provide valuable information for investors and economists alike.