Unlocking Short-Term Investment Opportunities
Understanding the 2-Month Treasury Bill Rate Landscape
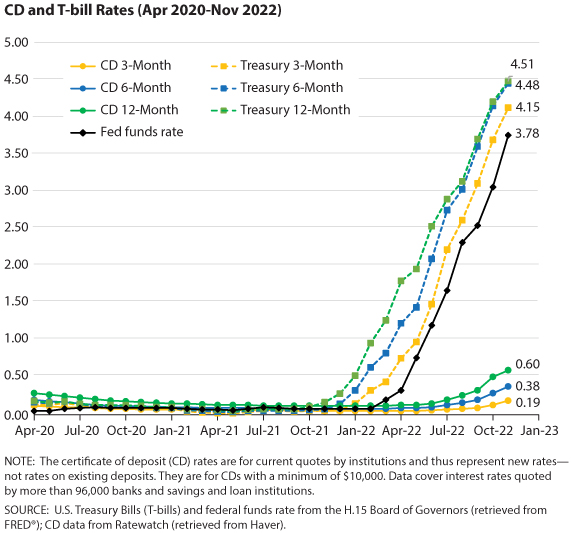
In the pursuit of short-term investment opportunities, it is essential to grasp the intricacies of the 2-month Treasury bill rate. This key indicator plays a vital role in shaping investment decisions, offering valuable insights into market sentiment and economic conditions. The 2-month T-bill rate represents the interest rate at which the US government borrows money for a two-month period, providing a benchmark for short-term investments. By understanding the 2-month Treasury bill rate, investors can make informed decisions about their investment portfolios, navigating the complexities of the market with confidence. In this article, we will delve into the world of short-term investments, exploring the factors that influence the 2-month T-bill rate and its implications for investment strategies.
What Drives the 2-Month T-Bill Rate: Economic Indicators and Market Forces
The 2-month Treasury bill rate is influenced by a complex array of economic indicators and market forces. At its core, the 2-month T-bill rate is a reflection of the market’s expectations of future interest rates and inflation. As such, it is closely tied to key economic indicators such as inflation, GDP growth, and unemployment rates. For instance, a rising inflation rate can lead to an increase in the 2-month T-bill rate, as investors demand higher returns to compensate for the erosion of purchasing power. Similarly, a strong GDP growth rate can lead to an increase in the 2-month T-bill rate, as investors become more optimistic about the economy and demand higher returns.
Monetary policy decisions by the Federal Reserve also play a significant role in shaping the 2-month T-bill rate. The Fed’s decisions on interest rates, quantitative easing, and forward guidance can all impact the 2-month T-bill rate, influencing the availability of credit and the overall direction of the economy. Additionally, market forces such as supply and demand, investor sentiment, and global economic trends can also influence the 2-month T-bill rate, making it a dynamic and constantly evolving indicator.
How to Navigate the 2-Month T-Bill Rate for Maximum Returns
To maximize returns and manage risk, investors must navigate the 2-month Treasury bill rate effectively. One key strategy is to monitor the 2-month T-bill rate closely, using it as a benchmark to evaluate other short-term investment options. By doing so, investors can identify opportunities to capitalize on rate discrepancies and optimize their portfolios. For instance, if the 2-month T-bill rate is higher than other short-term investment options, investors may consider allocating a larger portion of their portfolio to 2-month Treasury bills.
Another strategy is to use the 2-month T-bill rate as a hedge against inflation and interest rate risk. By investing in 2-month Treasury bills, investors can lock in a fixed return and mitigate the impact of rising inflation and interest rates on their portfolios. Additionally, investors can use the 2-month T-bill rate to inform their asset allocation decisions, shifting their portfolios towards assets that are less sensitive to interest rate changes.
It is also essential to consider the yield curve when navigating the 2-month T-bill rate. The yield curve, which plots the interest rates of Treasury securities with different maturities, can provide valuable insights into market expectations and interest rate trends. By analyzing the yield curve, investors can identify opportunities to capitalize on rate discrepancies and optimize their portfolios. For example, if the yield curve is steepening, investors may consider investing in shorter-term Treasury securities, such as 2-month Treasury bills, to take advantage of higher returns.
The Role of the Federal Reserve in Shaping the 2-Month T-Bill Rate
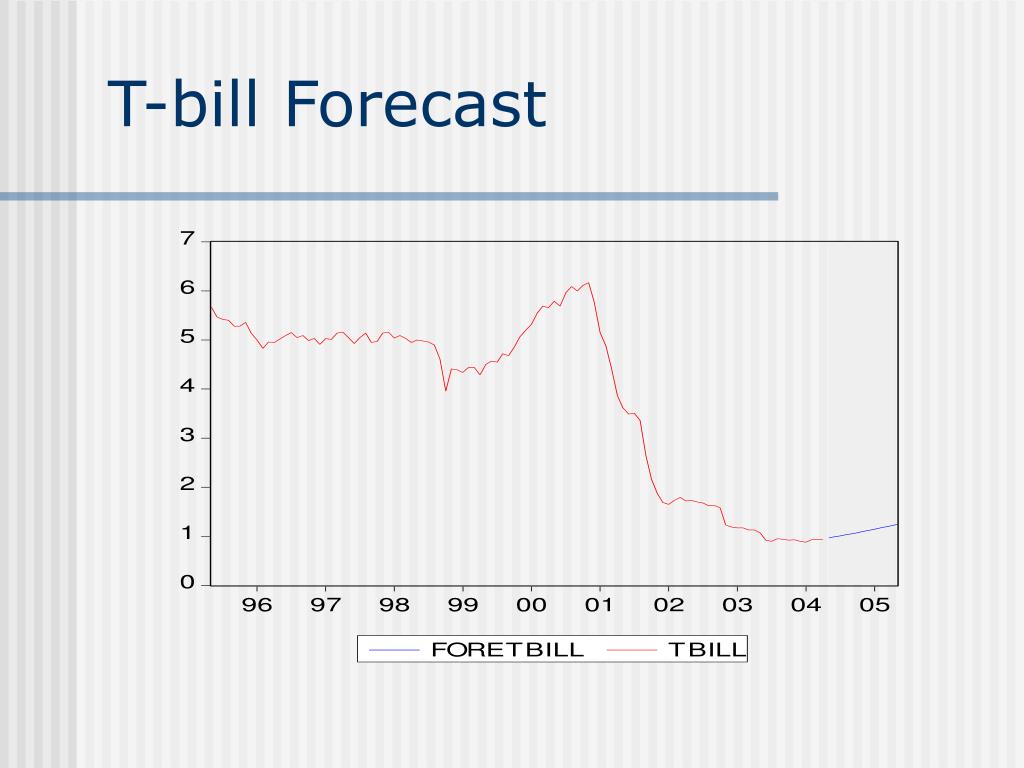
The Federal Reserve plays a crucial role in influencing the 2-month Treasury bill rate through its monetary policy decisions. The Fed’s actions have a direct impact on the availability of credit, interest rates, and the overall direction of the economy, all of which affect the 2-month T-bill rate. For instance, when the Fed raises interest rates to combat inflation, it increases the attractiveness of 2-month Treasury bills, causing their rates to rise. Conversely, when the Fed cuts interest rates to stimulate economic growth, it reduces the appeal of 2-month Treasury bills, leading to lower rates.
The Fed’s forward guidance, which communicates its future policy intentions, also influences the 2-month T-bill rate. When the Fed signals a hawkish stance, indicating future rate hikes, investors may demand higher returns on 2-month Treasury bills, driving up their rates. On the other hand, a dovish stance, indicating future rate cuts, may lead to lower 2-month T-bill rates.
In addition, the Fed’s quantitative easing policies, which involve buying or selling government securities, can impact the 2-month T-bill rate. During times of quantitative easing, the Fed’s purchases of longer-term securities can drive down their yields, making 2-month Treasury bills more attractive and causing their rates to rise. Conversely, when the Fed sells securities, it can increase their yields, making 2-month Treasury bills less attractive and causing their rates to fall.
Comparing the 2-Month T-Bill Rate to Other Short-Term Investment Options
When evaluating short-term investment opportunities, it’s essential to compare the 2-month Treasury bill rate to other options, such as commercial paper and certificates of deposit (CDs). Each of these investment vehicles has its unique characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks, which can impact their attractiveness to investors.
Commercial paper, for instance, is a short-term debt instrument issued by companies to raise capital. It typically offers higher yields than 2-month Treasury bills, but carries a higher credit risk. In contrast, CDs are time deposits offered by banks with fixed interest rates and maturity dates. They tend to be less liquid than 2-month Treasury bills and may come with penalties for early withdrawal.
In terms of liquidity, 2-month Treasury bills are generally considered to be the most liquid short-term investment option, as they can be easily bought and sold on the market. Commercial paper and CDs, on the other hand, may have lower liquidity, making it more difficult to sell them before maturity.
When deciding between these short-term investment options, investors should consider their individual financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. For example, if an investor is seeking a highly liquid, low-risk investment with a short time horizon, the 2-month Treasury bill rate may be an attractive option. However, if an investor is willing to take on more credit risk in exchange for higher yields, commercial paper may be a better fit.
Ultimately, by comparing the 2-month Treasury bill rate to other short-term investment options, investors can make informed decisions about their portfolios and optimize their returns. By understanding the benefits and drawbacks of each investment vehicle, investors can create a diversified portfolio that aligns with their financial objectives and risk tolerance.
Using the 2-Month T-Bill Rate to Inform Long-Term Investment Strategies
The 2-month Treasury bill rate is often viewed as a short-term investment option, but it can also provide valuable insights for long-term investment strategies. By understanding the 2-month T-bill rate and its relationship with other economic indicators, investors can make more informed decisions about their long-term investments.
One key aspect to consider is the yield curve, which plots the yields of Treasury securities with different maturities. The 2-month T-bill rate is a key component of the yield curve, and changes in this rate can influence the shape of the curve. For example, a steepening yield curve, where long-term yields rise faster than short-term yields, may indicate expectations of higher inflation or economic growth. In this scenario, investors may want to consider shifting their investments to longer-term assets, such as 10-year Treasury notes or stocks.
Interest rate expectations also play a crucial role in informing long-term investment strategies. When the 2-month T-bill rate is rising, it may signal that the Federal Reserve is tightening monetary policy, which can lead to higher interest rates across the yield curve. In this environment, investors may want to consider reducing their exposure to long-term bonds or other fixed-income securities, as rising interest rates can lead to capital losses.
Furthermore, the 2-month T-bill rate can serve as a benchmark for other short-term investment options, such as commercial paper or certificates of deposit. By comparing the yields of these instruments to the 2-month T-bill rate, investors can determine which option offers the most attractive return for their risk tolerance and investment horizon.
Ultimately, the 2-month Treasury bill rate is a valuable tool for investors seeking to inform their long-term investment strategies. By understanding the relationships between the 2-month T-bill rate, the yield curve, and interest rate expectations, investors can make more informed decisions about their investments and optimize their returns over the long term.
The Impact of Geopolitical Events on the 2-Month T-Bill Rate
Geopolitical events, such as trade wars, elections, and natural disasters, can have a significant impact on the 2-month Treasury bill rate. These events can influence investor sentiment, affect economic growth, and alter the trajectory of monetary policy, all of which can impact the 2-month T-bill rate.
For example, during times of heightened geopolitical uncertainty, investors may seek safe-haven assets, such as U.S. Treasury bills, driving up demand and pushing yields lower. This can result in a decrease in the 2-month T-bill rate, making it more attractive to investors seeking a low-risk, short-term investment.
On the other hand, geopolitical events that disrupt global trade or lead to economic sanctions can increase inflation expectations and reduce investor appetite for short-term investments, causing the 2-month T-bill rate to rise. The impact of these events can be particularly pronounced if they occur during times of monetary policy tightening, as the Federal Reserve may need to adjust its interest rate decisions in response to changing economic conditions.
In addition, elections and changes in government can also influence the 2-month T-bill rate. For instance, a change in administration may lead to shifts in fiscal policy, which can impact the economy and, in turn, influence the 2-month T-bill rate. Investors must stay informed about these events and their potential impact on the 2-month T-bill rate to make informed investment decisions.
Ultimately, the 2-month Treasury bill rate is sensitive to geopolitical events, and investors must be aware of these factors when making investment decisions. By understanding the impact of these events on the 2-month T-bill rate, investors can better navigate the complexities of the short-term investment landscape and optimize their returns.
Staying Ahead of the Curve: Tracking the 2-Month T-Bill Rate for Investment Success
To make informed investment decisions, it is essential to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in the 2-month Treasury bill rate. By tracking the 2-month T-bill rate and understanding its movements, investors can optimize their returns and manage risk more effectively.
One way to stay informed is to monitor the weekly Treasury bill auction results, which provide insight into the current market demand and supply dynamics. Additionally, investors can track the 2-month T-bill rate in real-time through financial news websites and mobile applications, allowing them to respond quickly to changes in the market.
Another key resource is the Federal Reserve’s website, which provides a wealth of information on monetary policy decisions, economic indicators, and market data. By analyzing this data, investors can gain a deeper understanding of the factors influencing the 2-month T-bill rate and make more informed investment decisions.
Furthermore, investors can also benefit from following reputable financial news sources and market analysts, who provide expert insights and analysis on the 2-month T-bill rate and its implications for the broader economy. By staying informed and up-to-date, investors can stay ahead of the curve and make the most of short-term investment opportunities.
Ultimately, tracking the 2-month Treasury bill rate is crucial for investment success. By understanding the factors that influence the 2-month T-bill rate and staying informed about market developments, investors can make informed decisions and optimize their returns in the short-term investment landscape.