What Drives the 10-Year Treasury Yield?
The 10-year treasury yield is a critical economic indicator that influences investment decisions and market trends. Several factors contribute to its fluctuations, including economic indicators, monetary policy, and market sentiment. Understanding these drivers is essential for investors seeking to make informed decisions.
Economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation rates, and unemployment numbers, significantly impact the 10-year treasury yield. For instance, a strong economy with low unemployment and rising inflation may lead to higher yields as investors demand higher returns to compensate for increased risk. On the other hand, a slowing economy may result in lower yields as investors seek safer havens.
Monetary policy decisions, such as interest rate hikes or quantitative easing, also affect the 10-year treasury yield. Central banks’ actions can influence the supply and demand of government bonds, thereby impacting yields. For example, during times of economic uncertainty, central banks may implement quantitative easing, which increases the demand for government bonds and drives yields lower.
Market sentiment, including investor confidence and risk appetite, also plays a crucial role in shaping the 10-year treasury yield. When investors are optimistic about the economy and willing to take on risk, they may demand lower yields, driving prices higher. Conversely, during times of market uncertainty, investors may seek safer assets, driving yields higher.
By understanding these factors, investors can better navigate the complexities of the 10-year treasury yield and make more informed investment decisions. Whether tracking the yield on Google Finance or incorporating it into a broader investment strategy, recognizing the drivers of this critical indicator is essential for long-term success.
How to Track the 10-Year Treasury Yield on Google Finance
Tracking the 10-year treasury yield is a crucial step in making informed investment decisions. Google Finance provides a convenient and user-friendly platform to monitor the yield. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to find and track the 10-year treasury yield on Google Finance:
Step 1: Access Google Finance by visiting finance.google.com in your web browser.
Step 2: Type “10 year treasury yield” in the search bar and press enter. This will take you to the dedicated page for the 10-year treasury yield.
Step 3: Customize the chart by selecting the desired time frame, ranging from 1 day to 5 years. You can also compare the 10-year treasury yield to other economic indicators, such as the S&P 500 or the Federal Funds Rate.
Step 4: Set up alerts to notify you of significant changes in the 10-year treasury yield. Click on the “Alerts” button and enter your desired threshold for notifications.
Step 5: Analyze the chart and data to identify trends and patterns in the 10-year treasury yield. This will help you make more informed investment decisions and stay ahead of market trends.
By following these steps, you can easily track the 10-year treasury yield on Google Finance and incorporate it into your investment strategy. Remember to regularly monitor the yield and adjust your strategy accordingly to maximize returns and minimize risk.
The Significance of the 10-Year Treasury Yield in Investment Decisions
The 10-year treasury yield plays a crucial role in investment decisions, as it serves as a benchmark for long-term interest rates and influences various asset classes. Understanding the significance of the 10-year treasury yield is essential for investors seeking to optimize their portfolios and minimize risk.
One of the primary ways the 10-year treasury yield impacts investment decisions is through its influence on bond prices. When the yield rises, existing bond prices fall, and vice versa. This inverse relationship means that investors must carefully consider the yield when making bond investment decisions. For example, if the 10-year treasury yield is high, investors may opt for shorter-term bonds to minimize potential losses from falling prices.
The 10-year treasury yield also has a significant impact on stock market performance. A rising yield can lead to higher borrowing costs for companies, which can negatively affect their stock prices. Conversely, a falling yield can make borrowing cheaper, boosting stock prices. Investors must consider the yield’s influence on the overall economy and stock market trends when making investment decisions.
In addition, the 10-year treasury yield plays a critical role in portfolio allocation. Investors often use the yield as a benchmark for other investments, such as corporate bonds or dividend-paying stocks. By comparing the yield to other investment options, investors can determine the most attractive opportunities and allocate their portfolios accordingly.
Furthermore, the 10-year treasury yield serves as a indicator of market sentiment and economic conditions. A rising yield may indicate a strong economy with rising inflation, while a falling yield may signal a slowing economy. Investors can use the yield to inform their investment strategies and adjust their portfolios in response to changing market conditions.
In conclusion, the 10-year treasury yield is a critical component of investment decisions, influencing bond prices, stock market performance, and portfolio allocation. By understanding the significance of the yield, investors can make more informed decisions and optimize their portfolios for long-term success.
A Historical Perspective: Analyzing the 10-Year Treasury Yield Over Time
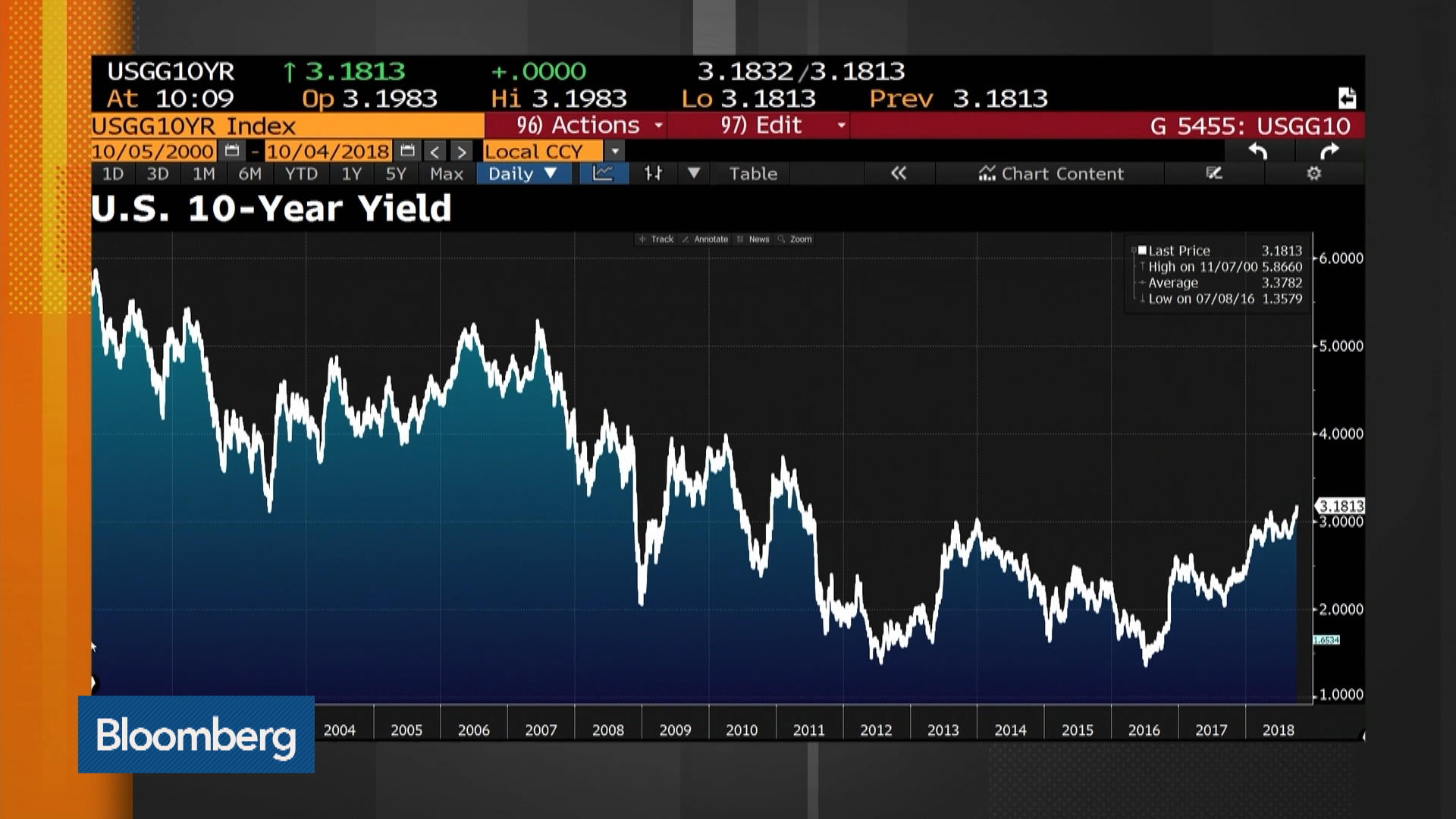
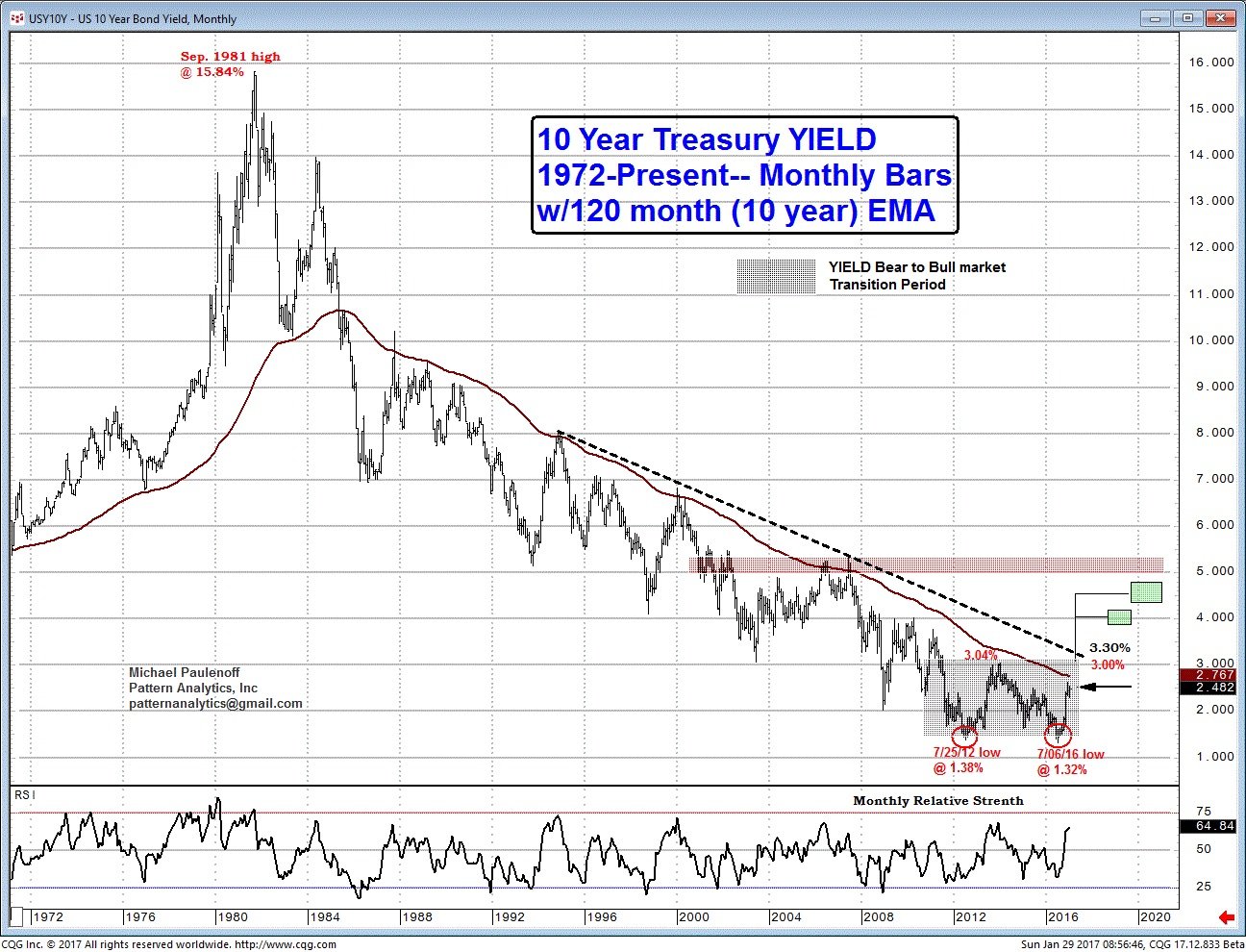
Examining the historical trends and patterns of the 10-year treasury yield provides valuable insights into its behavior during different economic conditions. By analyzing the yield’s response to economic downturns, recessions, and periods of growth, investors can better understand its role in investment decisions.
Historically, the 10-year treasury yield has been sensitive to changes in economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment rates. During periods of economic growth, the yield tends to rise as investors become more optimistic about the economy and demand higher returns. Conversely, during recessions, the yield tends to fall as investors seek safer assets and central banks implement monetary easing policies.
For example, during the 2008 financial crisis, the 10-year treasury yield plummeted to historic lows as investors fled to safe-haven assets and central banks implemented quantitative easing policies. In contrast, during the post-crisis period, the yield gradually rose as the economy recovered and central banks began to normalize monetary policy.
The yield’s response to monetary policy decisions is also evident in its historical patterns. During periods of interest rate hikes, the yield tends to rise as investors anticipate higher borrowing costs and inflation. Conversely, during periods of quantitative easing, the yield tends to fall as central banks inject liquidity into the economy and reduce borrowing costs.
By analyzing the 10-year treasury yield’s historical patterns, investors can identify trends and relationships that inform their investment decisions. For instance, investors may use the yield to gauge the likelihood of future interest rate hikes or to identify potential opportunities in other asset classes.
Furthermore, the yield’s historical patterns can also provide insights into the broader economy. By examining the yield’s response to economic indicators and monetary policy decisions, investors can gain a better understanding of the economy’s underlying trends and potential risks.
In conclusion, analyzing the 10-year treasury yield’s historical patterns provides valuable insights into its behavior during different economic conditions. By understanding these patterns, investors can make more informed investment decisions and optimize their portfolios for long-term success.
Comparing the 10-Year Treasury Yield to Other Investment Options
When considering investment opportunities, it’s essential to compare the 10-year treasury yield to other investment options, such as stocks, bonds, and commodities. Each investment option has its unique characteristics, benefits, and drawbacks, and understanding these differences is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
Stocks, for instance, offer the potential for higher returns over the long term, but they also come with higher volatility and risk. In contrast, the 10-year treasury yield provides a relatively stable and low-risk investment option, but with lower potential returns. Investors seeking higher yields may opt for corporate bonds or high-yield bonds, but these investments come with higher credit risk and default risk.
Commodities, such as gold or oil, offer a hedge against inflation and market volatility, but their prices can be highly volatile and influenced by global events. In contrast, the 10-year treasury yield is less susceptible to commodity price fluctuations and provides a more stable investment option.
Another key difference between the 10-year treasury yield and other investment options is their correlation with economic indicators. The yield is closely tied to economic growth, inflation, and monetary policy, making it a valuable indicator of the overall economy. Stocks, bonds, and commodities, on the other hand, have varying degrees of correlation with economic indicators, and their performance can be influenced by a range of factors.
Investors seeking to diversify their portfolios may consider combining the 10-year treasury yield with other investment options. For example, a portfolio consisting of 60% stocks and 40% bonds, with a portion of the bond allocation invested in 10-year treasury notes, can provide a balanced and diversified investment strategy.
In conclusion, comparing the 10-year treasury yield to other investment options is essential for making informed investment decisions. By understanding the benefits and drawbacks of each investment option, investors can create a diversified portfolio that aligns with their investment goals and risk tolerance.
The Impact of Monetary Policy on the 10-Year Treasury Yield
Central banks’ monetary policy decisions have a significant impact on the 10-year treasury yield, influencing its movement and volatility. Understanding how monetary policy affects the yield is crucial for investors seeking to make informed investment decisions.
Interest rate hikes, for instance, tend to increase the 10-year treasury yield as investors anticipate higher borrowing costs and inflation. During periods of tightening monetary policy, the yield may rise as investors demand higher returns to compensate for the increased risk of inflation. Conversely, during periods of easing monetary policy, the yield may fall as central banks inject liquidity into the economy and reduce borrowing costs.
Quantitative easing, a monetary policy tool used during times of economic stress, has a profound impact on the 10-year treasury yield. By injecting liquidity into the economy and purchasing government bonds, central banks reduce the supply of bonds available for investors, driving down yields and making borrowing cheaper. This, in turn, can stimulate economic growth and increase inflation expectations, causing the yield to rise.
The forward guidance provided by central banks also influences the 10-year treasury yield. When central banks communicate their future policy intentions, investors adjust their expectations of future interest rates and inflation, which in turn affects the yield. For example, if a central bank signals a future rate hike, investors may bid up the yield in anticipation of higher borrowing costs.
The impact of monetary policy on the 10-year treasury yield is not limited to the yield itself. It also has a ripple effect on the broader economy, influencing stock market performance, bond prices, and portfolio allocation. Investors must therefore consider the implications of monetary policy decisions when making investment decisions and adjust their strategies accordingly.
In the context of Google Finance, investors can track the 10-year treasury yield and monitor its response to monetary policy decisions. By analyzing the yield’s movement and volatility, investors can gain insights into the economy and make more informed investment decisions.
Using the 10-Year Treasury Yield to Inform Investment Strategies
The 10-year treasury yield is a valuable tool for investors seeking to inform their investment strategies. By analyzing the yield, investors can gain insights into the economy and make more informed decisions about their investments.
One strategy that investors can use is laddering, which involves investing in a series of bonds with staggered maturity dates. By laddering their investments, investors can take advantage of the 10-year treasury yield to manage their risk and returns. For example, an investor may invest in a 10-year treasury note and simultaneously invest in a series of shorter-term bonds, such as 2-year and 5-year notes, to create a ladder of investments.
Diversification is another strategy that investors can use to inform their investment decisions. By diversifying their portfolios across different asset classes, such as stocks, bonds, and commodities, investors can reduce their risk and increase their potential returns. The 10-year treasury yield can be used as a benchmark to evaluate the performance of other investments and to make adjustments to the portfolio as needed.
Hedging is another strategy that investors can use to inform their investment decisions. By investing in assets that are negatively correlated with the 10-year treasury yield, investors can reduce their risk and increase their potential returns. For example, an investor may invest in gold or other commodities to hedge against inflation, which can cause the 10-year treasury yield to rise.
In addition to these strategies, investors can also use the 10-year treasury yield to inform their investment decisions by analyzing its movement and volatility. By tracking the yield on Google Finance, investors can gain insights into the economy and make more informed decisions about their investments. For example, an increase in the 10-year treasury yield may signal a strengthening economy, while a decrease may signal a weakening economy.
By using the 10-year treasury yield to inform their investment strategies, investors can make more informed decisions and increase their potential returns. Whether through laddering, diversification, or hedging, the 10-year treasury yield is a valuable tool that can help investors achieve their investment goals.
Staying Ahead of the Curve: Tips for Monitoring the 10-Year Treasury Yield
Monitoring the 10-year treasury yield is crucial for investors seeking to make informed investment decisions. By staying ahead of the curve, investors can anticipate changes in the economy and adjust their investment strategies accordingly. Here are some tips and best practices for monitoring the 10-year treasury yield:
Set up a watchlist: Create a watchlist on Google Finance to track the 10-year treasury yield and other relevant economic indicators. This will enable investors to receive real-time updates and notifications when the yield changes.
Track economic indicators: Keep an eye on key economic indicators such as GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment rates. These indicators can provide insights into the economy and help investors anticipate changes in the 10-year treasury yield.
Stay informed about market news and trends: Stay up-to-date with market news and trends to understand the factors driving the 10-year treasury yield. This can include news about monetary policy decisions, economic downturns, and periods of growth.
Customize charts and graphs: Use Google Finance to customize charts and graphs to visualize the 10-year treasury yield and other economic indicators. This can help investors identify trends and patterns and make more informed investment decisions.
Set up alerts: Set up alerts on Google Finance to notify investors when the 10-year treasury yield reaches a certain level or changes by a certain percentage. This can help investors stay ahead of the curve and make timely investment decisions.
Monitor the yield curve: The yield curve, which plots the yields of different maturity bonds, can provide insights into the economy and the direction of interest rates. By monitoring the yield curve, investors can anticipate changes in the 10-year treasury yield and adjust their investment strategies accordingly.
Consider the 10 year treasury yield Google Finance data: When monitoring the 10-year treasury yield, consider the data provided by Google Finance, including the current yield, historical data, and charts. This can help investors make more informed investment decisions and stay ahead of the curve.
By following these tips and best practices, investors can stay ahead of the curve and make more informed investment decisions. By monitoring the 10-year treasury yield and other economic indicators, investors can anticipate changes in the economy and adjust their investment strategies accordingly.