Understanding the 10-Year Treasury Rate: A Key Indicator of Economic Health
The 10-year treasury rate, as reported by Bloomberg, is a crucial indicator of the US economy’s health. This rate, which represents the yield on 10-year US government bonds, plays a significant role in shaping monetary policy and influencing investment decisions. It serves as a benchmark for long-term interest rates, affecting the cost of borrowing for consumers and businesses alike. A change in the 10-year treasury rate can have far-reaching consequences, impacting everything from mortgage rates to corporate bond yields. As a result, investors, economists, and policymakers closely monitor the 10-year treasury rate to gauge the economy’s performance and make informed decisions. The 10 year treasury rate Bloomberg data provides valuable insights into the economy’s trajectory, allowing market participants to adjust their strategies accordingly.
How to Make Sense of Bloomberg’s Treasury Rate Data
Bloomberg’s treasury rate data is a valuable resource for investors, economists, and policymakers seeking to understand the intricacies of the 10-year treasury rate. To access this data, users can simply log in to Bloomberg’s terminal or website and navigate to the treasury rate section. Once there, they can view current and historical data on the 10-year treasury rate, as well as other treasury rates and economic indicators. Interpreting this data requires a solid understanding of the factors that influence the 10-year treasury rate, including monetary policy decisions, inflation expectations, and economic growth. By analyzing Bloomberg’s treasury rate data, market participants can gain valuable insights into the economy’s trajectory and make informed investment decisions. For instance, a rising 10 year treasury rate Bloomberg data may indicate a strengthening economy, while a declining rate may suggest a slowdown. By staying up-to-date with Bloomberg’s treasury rate data, investors can stay ahead of the curve and adjust their strategies accordingly.
The Impact of Treasury Rates on the Bond Market and Beyond
Changes in the 10-year treasury rate have far-reaching consequences, affecting not only the bond market but also the stock market and overall economy. When the 10-year treasury rate rises, it can lead to higher borrowing costs for consumers and businesses, which can slow down economic growth. Conversely, a decline in the rate can stimulate economic activity by making borrowing cheaper. The bond market is particularly sensitive to changes in the 10-year treasury rate, as it serves as a benchmark for long-term interest rates. As a result, changes in the rate can impact the yields of other bonds, influencing the attractiveness of various investment opportunities. For instance, a rising 10 year treasury rate Bloomberg data may lead to higher yields on corporate bonds, making them more attractive to investors. Furthermore, the impact of treasury rates can also be felt in the stock market, as changes in interest rates can influence the performance of various sectors and industries. By understanding the ripple effects of changes in the 10-year treasury rate, investors and policymakers can better navigate the complexities of the bond market and overall economy.
A Historical Perspective: Analyzing Treasury Rate Trends and Patterns
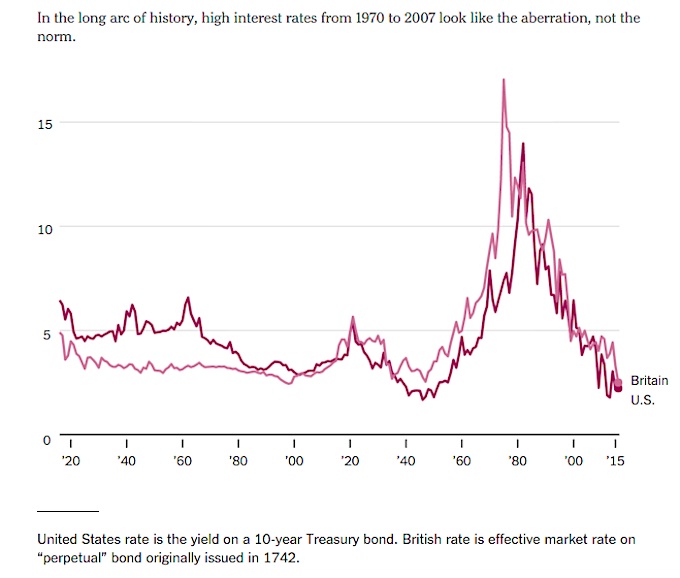
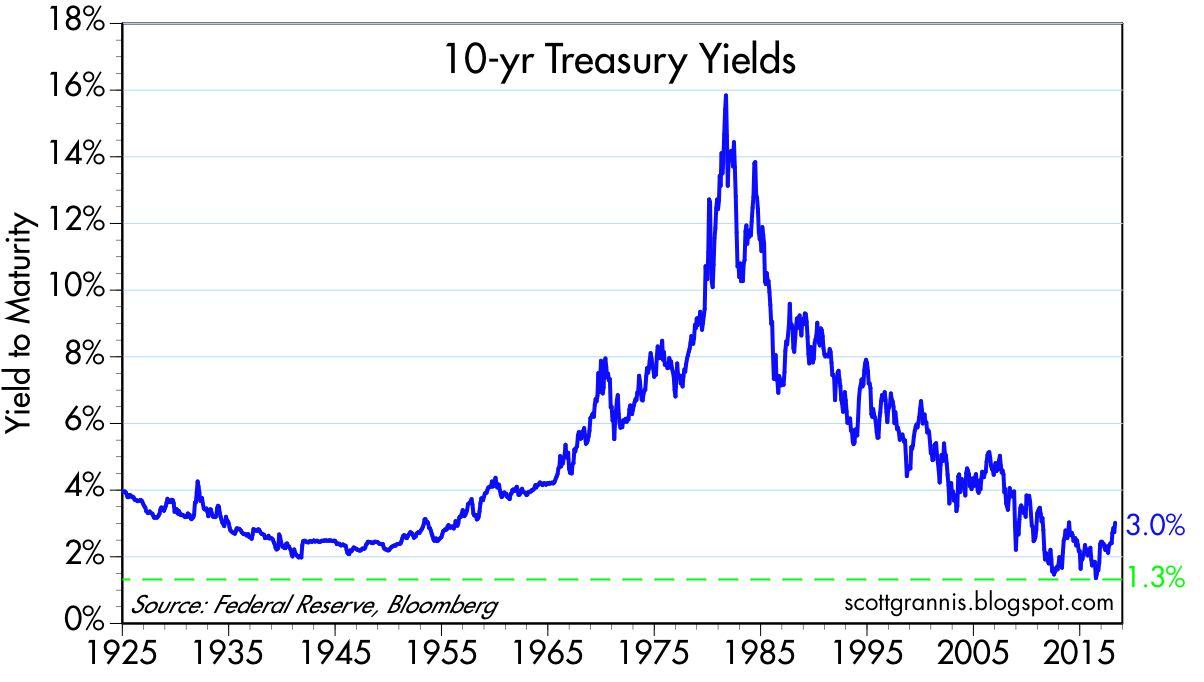
A historical analysis of the 10-year treasury rate reveals valuable insights into the trends and patterns that have shaped its fluctuations over time. By examining the rate’s behavior during different economic cycles, investors and economists can gain a deeper understanding of the factors that influence its movements. For instance, during the 1980s, the 10-year treasury rate peaked at around 15% as the Federal Reserve, led by Chairman Paul Volcker, raised interest rates to combat high inflation. In contrast, during the 2008 financial crisis, the rate plummeted to historic lows as central banks implemented quantitative easing policies to stimulate economic growth. More recently, the 10 year treasury rate Bloomberg data has reflected the ongoing impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the global economy. By studying these historical trends and patterns, market participants can identify key drivers of the 10-year treasury rate and make more informed investment decisions. Additionally, analyzing the rate’s historical volatility can help investors develop strategies to mitigate potential risks and capitalize on opportunities in the bond market.
The Role of Central Banks in Shaping Treasury Rates
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve, play a crucial role in shaping the 10-year treasury rate through their monetary policy decisions. By setting short-term interest rates and implementing quantitative easing policies, central banks can influence the entire yield curve, including the 10-year treasury rate. For instance, when the Federal Reserve lowers short-term interest rates, it can lead to a decrease in the 10-year treasury rate, making borrowing cheaper and stimulating economic growth. Conversely, when the Fed raises short-term rates, it can lead to an increase in the 10-year treasury rate, making borrowing more expensive and slowing down economic growth. The 10 year treasury rate Bloomberg data reflects the ongoing impact of central banks’ monetary policy decisions on the bond market and broader economy. By understanding the complex relationship between central banks and the 10-year treasury rate, investors and policymakers can better navigate the complexities of the bond market and make more informed decisions. Furthermore, analyzing the historical interactions between central banks and the 10-year treasury rate can provide valuable insights into the potential effects of future monetary policy decisions.
What Do Treasury Rates Reveal About Inflation Expectations?
The 10-year treasury rate is closely tied to inflation expectations, providing valuable insights into the market’s inflation outlook. When the 10-year treasury rate rises, it can signal increasing inflation expectations, as investors demand higher returns to compensate for the potential erosion of purchasing power. Conversely, a decline in the 10-year treasury rate may indicate decreasing inflation expectations, as investors become more optimistic about the economy’s ability to manage inflation. By analyzing the 10 year treasury rate Bloomberg data, investors and economists can gain a better understanding of the market’s inflation expectations and make more informed investment decisions. For instance, during periods of high inflation, the 10-year treasury rate may rise to reflect the increased inflation risk, while during periods of low inflation, the rate may decline as investors become more confident in the economy’s ability to manage prices. By recognizing the connection between the 10-year treasury rate and inflation expectations, market participants can develop more effective investment strategies and better navigate the complexities of the bond market.
Investment Strategies for a Low-Rate Environment
In a low-interest-rate environment, investors face unique challenges in generating returns. However, by understanding the implications of a low 10-year treasury rate Bloomberg data, investors can adapt their strategies to thrive in this environment. One approach is to focus on bond allocation, diversifying across different maturities and credit ratings to minimize risk. Dividend investing can also be an attractive option, as dividend-paying stocks can provide a relatively stable source of income. Additionally, alternative assets such as real estate, commodities, or private equity can offer a hedge against inflation and provide a diversification benefit. Furthermore, investors can consider investing in high-yield bonds, emerging market debt, or convertible bonds to enhance returns. By adopting a flexible and diversified investment approach, investors can navigate the complexities of a low-rate environment and achieve their long-term investment objectives. It is essential to stay informed about the 10-year treasury rate and its implications on the bond market, as well as to adapt investment strategies accordingly.
Navigating the Complexities of Treasury Rate Forecasting
Predicting treasury rate movements is a challenging task, even for experienced investors and economists. The 10-year treasury rate Bloomberg data is influenced by a multitude of factors, including monetary policy decisions, economic indicators, and market sentiment. As a result, forecasting treasury rate movements requires a deep understanding of these factors and their complex interactions. One of the key challenges is that treasury rates can be affected by unexpected events, such as geopolitical tensions or natural disasters, which can lead to sudden and significant changes in the rate. Furthermore, the relationship between the 10-year treasury rate and other economic indicators, such as inflation and GDP growth, can be nonlinear and subject to changes over time. To navigate these complexities, investors and economists must stay informed about the latest developments in the economy and financial markets, and be prepared to adapt their forecasts and investment strategies accordingly. By recognizing the limitations of treasury rate forecasting and staying flexible, investors can make more informed investment decisions and better navigate the uncertainties of the bond market.