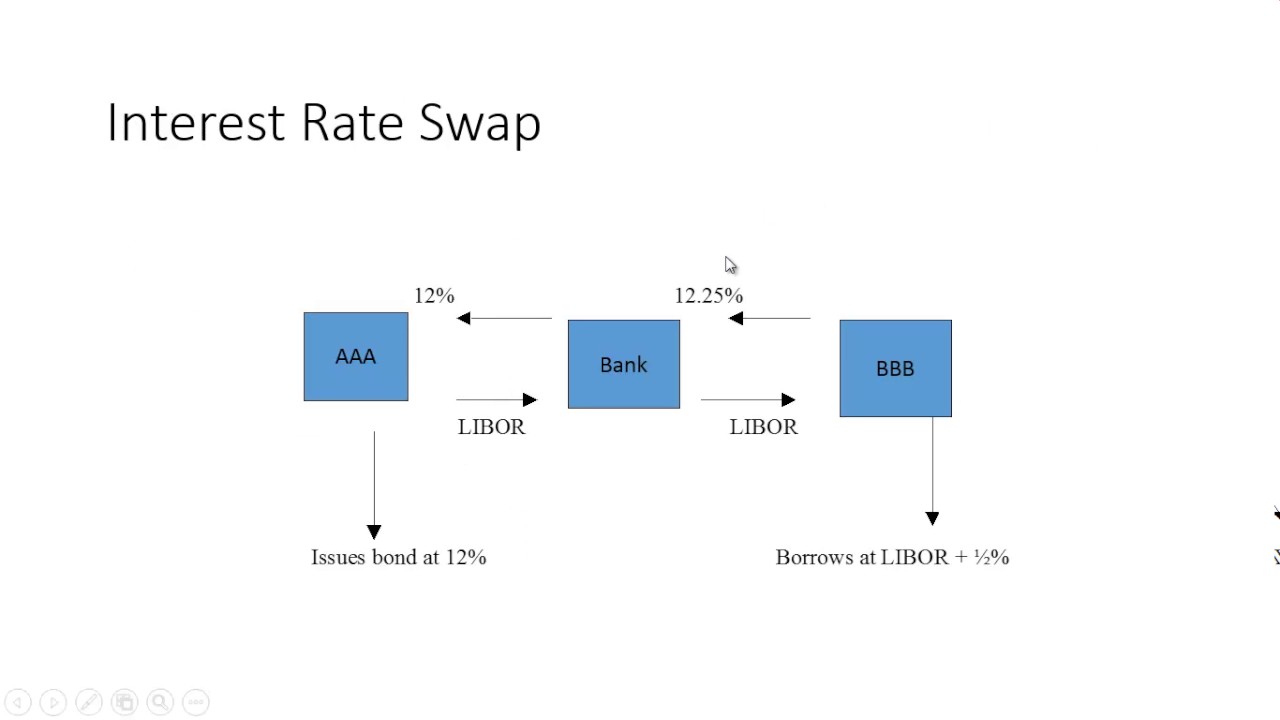
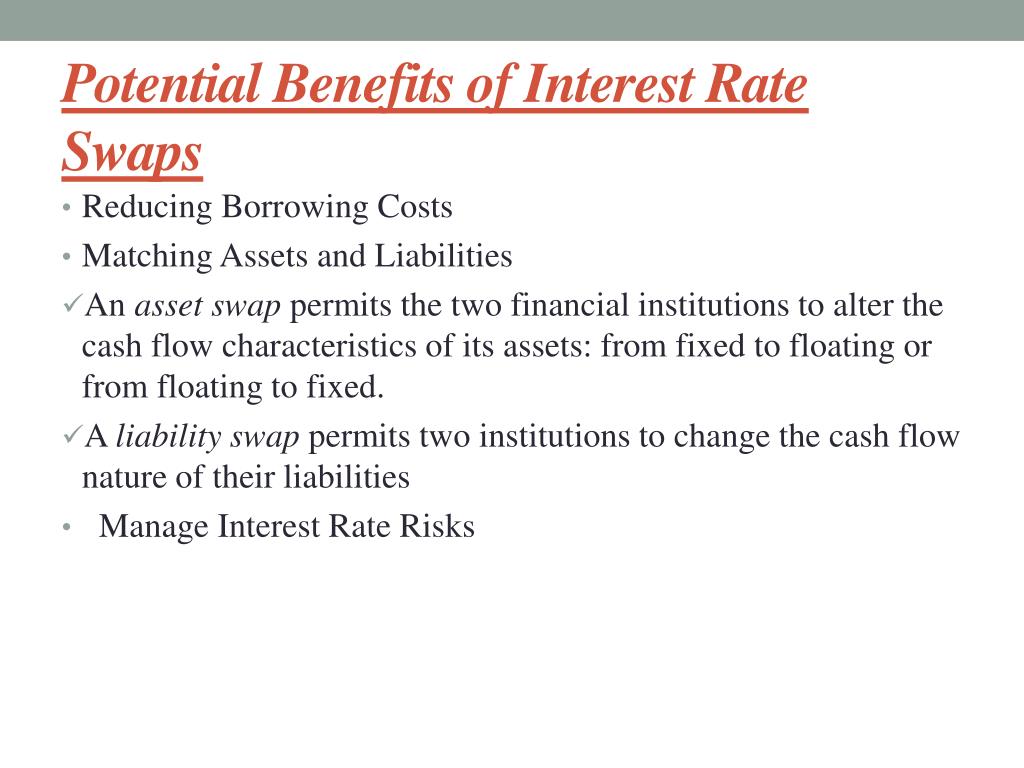
Understanding the Role of Long-Term Interest Rates
Interest rate swaps are a crucial tool in modern finance, enabling companies and financial institutions to manage financial risk and optimize their investments. By exchanging fixed and floating interest payments based on a notional amount, interest rate swaps allow parties to hedge against potential losses and capitalize on opportunities. The significance of interest rate swaps lies in their ability to mitigate interest rate risk, which can have a profound impact on a company’s bottom line. Long-term interest rates, such as the 10-year interest rate swap rate, play a critical role in shaping the economy and financial markets. The 10-year interest rate swap rate, in particular, serves as a benchmark for long-term interest rates, influencing the cost of borrowing, the value of investments, and the overall direction of the economy. As a result, understanding the 10-year interest rate swap rate is essential for businesses, investors, and policymakers alike, as it enables them to make informed decisions about investments, funding, and risk management. In essence, the 10-year interest rate swap rate provides valuable insights into market sentiment, allowing companies to adjust their financial strategies accordingly.
How to Analyze the 10-Year Interest Rate Swap Rate
When analyzing the 10-year interest rate swap rate, it is essential to understand the various factors that influence its movement. Economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation, and unemployment rates, play a significant role in shaping the 10-year interest rate swap rate. Monetary policy decisions, including changes to interest rates and quantitative easing, also have a profound impact on the rate. Additionally, market sentiment, including investor confidence and risk appetite, can influence the 10-year interest rate swap rate. To effectively analyze the rate, it is crucial to consider these factors in conjunction with technical analysis, such as chart patterns and trend lines. By doing so, market participants can gain a deeper understanding of the 10-year interest rate swap rate and make more informed investment decisions. Furthermore, analyzing the 10-year interest rate swap rate in relation to other economic indicators, such as bond yields and stock prices, can provide valuable insights into the overall direction of the economy and financial markets. By developing a comprehensive understanding of the 10-year interest rate swap rate, investors and financial institutions can better navigate the complexities of interest rate swaps and optimize their investment strategies.
The Impact of Interest Rate Swaps on Corporate Finance
Interest rate swaps play a vital role in corporate finance, enabling companies to manage financial risk and optimize their investments. One of the primary ways in which interest rate swaps are used in corporate finance is by hedging against interest rate risk. By entering into an interest rate swap agreement, companies can fix their interest payments and protect themselves against potential losses resulting from changes in interest rates. For example, a company with a floating-rate loan can use an interest rate swap to convert its floating interest payments into fixed interest payments, thereby reducing its exposure to interest rate risk. Additionally, interest rate swaps can be used to manage cash flows, allowing companies to better anticipate and plan for their future financial obligations. Many companies have successfully used interest rate swaps to manage their financial risk, including multinational corporations such as General Electric and Coca-Cola. By leveraging interest rate swaps, these companies have been able to reduce their financial risk and improve their overall financial performance. Furthermore, the 10-year interest rate swap rate serves as a benchmark for long-term interest rates, influencing the cost of borrowing and the value of investments. As such, understanding the 10-year interest rate swap rate is crucial for companies seeking to optimize their financial strategies and manage their risk exposure.
Comparing 10-Year Interest Rate Swap Rates Across Markets
When analyzing the 10-year interest rate swap rate, it is essential to consider the differences in rates across various markets. The 10-year interest rate swap rate can vary significantly between the US, Europe, and Asia, reflecting the unique economic and financial conditions of each region. For instance, the 10-year interest rate swap rate in the US is often influenced by the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions, while in Europe, it is shaped by the European Central Bank’s actions. In Asia, the 10-year interest rate swap rate is often affected by the region’s rapid economic growth and the actions of central banks such as the Bank of Japan. Understanding these differences is crucial for investors and financial institutions seeking to optimize their investments and manage their risk exposure. By comparing and contrasting the 10-year interest rate swap rates across markets, market participants can gain valuable insights into the global economy and financial markets. For example, a lower 10-year interest rate swap rate in the US compared to Europe may indicate a more accommodative monetary policy in the US, while a higher rate in Asia may reflect the region’s rapid economic growth. By analyzing these differences, investors can make more informed investment decisions and optimize their portfolios. Furthermore, the 10-year interest rate swap rate serves as a benchmark for long-term interest rates, influencing the cost of borrowing and the value of investments. As such, understanding the differences in 10-year interest rate swap rates across markets is crucial for companies seeking to manage their financial risk and optimize their investments.
The Relationship Between Interest Rate Swaps and Bond Yields
The 10-year interest rate swap rate has a significant impact on bond yields, and understanding the relationship between the two is crucial for investors and financial institutions. In essence, the 10-year interest rate swap rate serves as a benchmark for long-term interest rates, influencing the cost of borrowing and the value of investments. When the 10-year interest rate swap rate increases, bond yields tend to rise, making borrowing more expensive and reducing the value of existing bonds. Conversely, a decrease in the 10-year interest rate swap rate leads to lower bond yields, making borrowing cheaper and increasing the value of existing bonds. This relationship is critical for investors seeking to optimize their portfolios and manage their risk exposure. For instance, a company issuing bonds may use interest rate swaps to hedge against changes in bond yields, thereby reducing its exposure to interest rate risk. Similarly, investors may use interest rate swaps to speculate on changes in bond yields, potentially earning profits from fluctuations in the market. Furthermore, the 10-year interest rate swap rate can also influence the credit spreads of corporate bonds, with changes in the swap rate affecting the perceived creditworthiness of issuers. As such, understanding the relationship between interest rate swaps and bond yields is essential for navigating the complex world of fixed-income investments.
Risks and Challenges Associated with Interest Rate Swaps
While interest rate swaps can be an effective tool for managing financial risk, they are not without their risks and challenges. One of the primary risks associated with interest rate swaps is counterparty risk, which refers to the risk that the counterparty may default on their obligations. This risk can be mitigated by carefully selecting counterparties and implementing robust risk management practices. Another risk is liquidity risk, which arises when it becomes difficult to exit a swap position quickly and at a fair price. This risk can be managed by maintaining a diversified portfolio of swaps and regularly monitoring market conditions. Operational risk is also a concern, as it can arise from inadequate systems, processes, and personnel. To mitigate this risk, it is essential to implement robust operational procedures and ensure that personnel are adequately trained. Additionally, interest rate swaps can also be affected by changes in market conditions, such as shifts in the 10-year interest rate swap rate, which can impact the value of the swap. To manage this risk, it is essential to regularly monitor market conditions and adjust the swap position accordingly. By understanding these risks and challenges, market participants can take steps to mitigate them and optimize their use of interest rate swaps. For instance, companies can implement robust risk management practices, diversify their swap portfolios, and regularly monitor market conditions to minimize their exposure to risk. By doing so, they can effectively manage their financial risk and achieve their business objectives.
The Future of Interest Rate Swaps in a Changing Market
The interest rate swap market is undergoing significant changes, driven by regulatory reforms, technological advancements, and shifting market dynamics. One of the key trends shaping the market is the increasing adoption of central clearinghouses, which aim to reduce counterparty risk and improve market transparency. Additionally, the rise of fintech and digital platforms is transforming the way interest rate swaps are traded, cleared, and settled. These developments have the potential to increase efficiency, reduce costs, and improve risk management for market participants. Furthermore, the ongoing evolution of monetary policy and the impact of macroeconomic factors, such as inflation and economic growth, are also influencing the 10-year interest rate swap rate and the broader interest rate swap market. As the market continues to evolve, it is essential for investors, financial institutions, and corporations to stay informed about these trends and developments, and to adapt their strategies accordingly. By doing so, they can effectively navigate the complexities of interest rate swaps and optimize their use of these financial instruments. For instance, companies can leverage digital platforms to streamline their swap operations, while investors can take advantage of central clearinghouses to reduce their counterparty risk exposure. As the market continues to evolve, one thing is clear: a deep understanding of the 10-year interest rate swap rate and its role in managing financial risk will be crucial for success in the years to come.
Conclusion: Navigating the Complexities of Interest Rate Swaps
In conclusion, navigating the complex world of interest rate swaps requires a deep understanding of the 10-year interest rate swap rate and its role in managing financial risk. By grasping the factors that influence the 10-year interest rate swap rate, including economic indicators, monetary policy, and market sentiment, investors, financial institutions, and corporations can make informed decisions about their use of interest rate swaps. Additionally, understanding the impact of interest rate swaps on corporate finance, the relationship between interest rate swaps and bond yields, and the risks and challenges associated with these financial instruments is crucial for effective risk management. As the interest rate swap market continues to evolve, it is essential to stay informed about the trends and developments shaping the market. By doing so, market participants can optimize their use of interest rate swaps and navigate the complexities of these financial instruments. Ultimately, a thorough understanding of the 10-year interest rate swap rate and its role in managing financial risk is critical for success in today’s fast-paced financial markets.

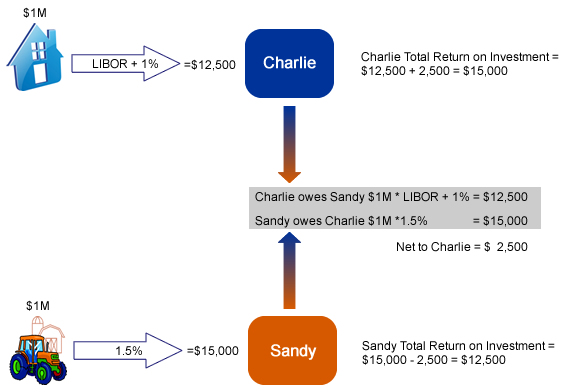
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_How_to_Value_Interest_Rate_Swaps_Sep_2020-01-4b6f55263e5a41b091bded09d63da811.jpg)
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/interest-rate-swap-4194467-1-d72db15d28f64e9b801fe940e5999c51.jpg)