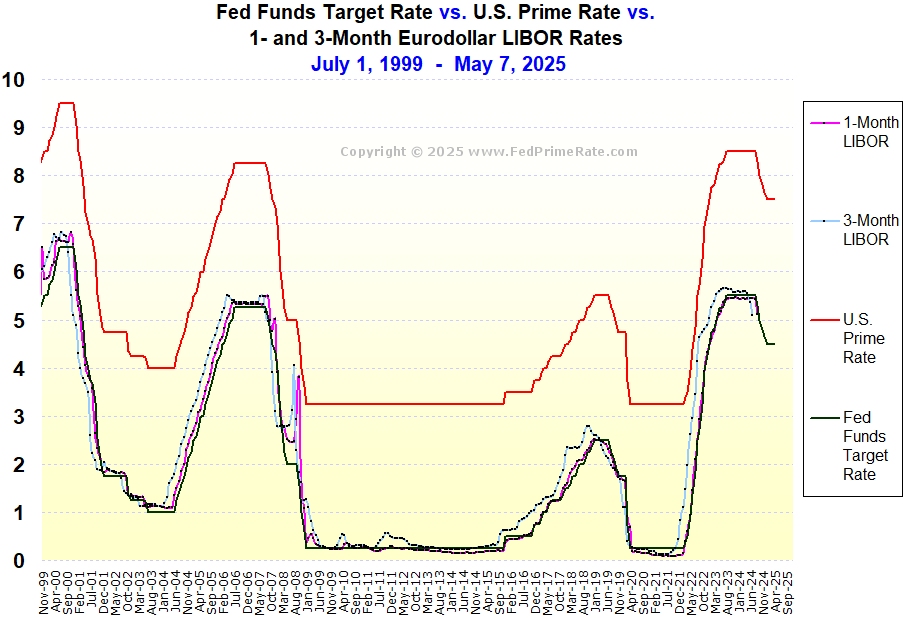
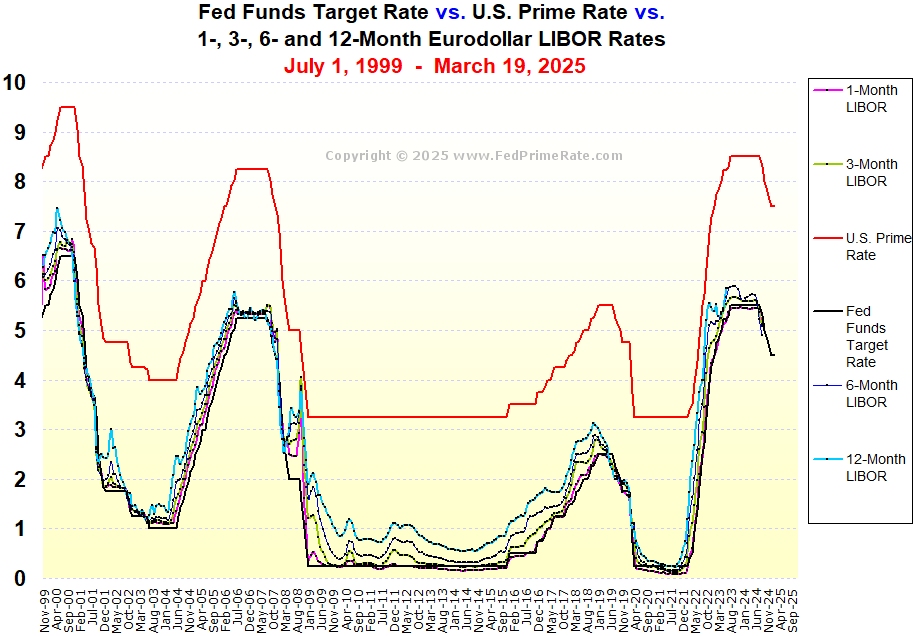
Understanding Historical Trends in Interbank Lending Rates
Interbank lending rates are vital indicators within the global financial system. These rates reflect the cost at which banks lend money to one another. They influence various aspects of the economy. One of the most well-known interbank lending rates was LIBOR. LIBOR served as a benchmark for trillions of dollars in financial products. Understanding its historical behavior offers valuable insights into market dynamics. This article explores these fluctuations over time. It offers a historical perspective. While not explicitly presenting a “1 year libor historical chart” at the outset, the information provides a view of the data contained within such a chart.
The significance of interbank lending rates extends beyond the banking sector. They impact interest rates for consumers and businesses. Monitoring these rates provides a gauge of overall financial health. It helps in understanding risk appetite within the market. The data, similar to that found in a “1 year libor historical chart,” reveals patterns. These patterns reflect economic cycles and major events. This article aims to dissect those patterns. It provides a clear understanding of their underlying causes. By examining the past, we can better understand the present. We can also anticipate potential future trends. The “1 year libor historical chart” encapsulates a wealth of information. It offers insights into market sentiment and economic performance.
This exploration into the past offers a crucial foundation. It allows us to grasp the complexities of today’s financial landscape. Interbank lending rates played a central role. The information presented helps to contextualize the data typically seen in a “1 year libor historical chart.” This understanding is essential for making informed financial decisions. It is also crucial for navigating the ever-changing global economy. The following sections delve deeper. They analyze the factors influencing these rates. They also examine their impact on various sectors.
Factors Influencing Lending Rate Volatility Over Time
Interbank lending rates are susceptible to a myriad of economic and political influences, causing fluctuations that resonate throughout the financial landscape. Understanding these factors is crucial for interpreting a 1 year libor historical chart and anticipating future trends. These rates, reflecting the cost at which banks lend to one another, act as a barometer of overall economic health.
Economic recessions typically lead to lower interbank lending rates as central banks often implement accommodative monetary policies to stimulate borrowing and investment. Conversely, periods of strong economic growth may see rates rise as demand for capital increases and central banks act to prevent inflation. Financial crises, characterized by uncertainty and a lack of trust, can trigger sharp spikes in these rates as banks become hesitant to lend to each other. Changes in monetary policy, such as adjustments to the federal funds rate or reserve requirements, directly impact the cost of funds for banks, thereby influencing interbank lending rates. Geopolitical events, ranging from trade wars to political instability, can also introduce volatility into financial markets, affecting lending rates as investors assess and react to perceived risks. Analyzing a 1 year libor historical chart often reveals patterns that correlate with these major events.
Moreover, inflation expectations play a significant role. If lenders anticipate higher inflation in the future, they will demand higher interest rates to compensate for the erosion of their purchasing power. Government fiscal policies, such as increased borrowing or spending, can also exert upward pressure on lending rates. Furthermore, regulatory changes impacting the banking sector can influence the availability of credit and, consequently, interbank lending rates. Examining a 1 year libor historical chart in conjunction with an understanding of these underlying factors provides a more comprehensive view of market dynamics. This comprehensive understanding is key to navigating the complexities of the modern financial system and identifying opportunities amidst the inherent volatility. Scrutinizing a 1 year libor historical chart allows individuals and institutions to gain valuable insights.
How to Interpret a Lending Rate History Graph
Understanding a historical chart of interbank lending rates requires familiarity with its basic components. Typically, such a chart plots time on the x-axis (horizontal) and the interest rate on the y-axis (vertical). The x-axis represents the period under review, which could range from months to decades. The y-axis shows the corresponding interbank lending rate, usually expressed as a percentage.
Analyzing the chart involves identifying trends and patterns. A rising line indicates increasing interbank lending rates, suggesting higher borrowing costs among banks. Conversely, a falling line signifies decreasing rates, implying cheaper borrowing. Sharp peaks and troughs often correspond to significant economic or political events. For instance, a rapid increase might reflect a period of economic instability or tightening monetary policy. A steep decline could indicate an economic slowdown or easing of monetary policy. Recognizing these patterns within a 1 year libor historical chart can offer valuable insights into market dynamics.
The ability to interpret a 1 year libor historical chart can be highly beneficial. It is important to remember that the chart does not exist in isolation. External factors, such as inflation figures, unemployment rates, and geopolitical developments, should all be considered. The 1 year libor historical chart offers a visual representation of complex financial data, making it more accessible. By carefully studying the trends and patterns, one can better grasp the historical forces shaping the global financial landscape. While specific dates and values aren’t explicitly stated here, the principles of interpretation remain consistent across various timeframes and lending rates. One of the best ways to monitor the overall financial health of lending is to carefully observe the 1 year libor historical chart.
The Role of Lending Rates in Global Markets
Interbank lending rates exert a considerable influence on the global financial system. These rates, reflecting the cost at which banks lend to one another, act as a foundational element influencing a wide spectrum of financial activities. The subtle movements in these rates can create a ripple effect, extending their impact far beyond the confines of the interbank market. While this article explores historical trends and doesn’t explicitly offer a “1 year libor historical chart”, understanding the principles discussed helps in interpreting such data.
A primary area affected by interbank lending rates is consumer interest rates. When banks face higher borrowing costs in the interbank market, they often pass these costs on to consumers through increased interest rates on loans, credit cards, and other forms of credit. Conversely, lower interbank lending rates can translate to more affordable borrowing options for individuals. Mortgage rates are also closely tied to interbank lending rates. Fluctuations in these rates can impact the affordability of homeownership, influencing both the housing market and broader economic activity. The dynamics of a “1 year libor historical chart” would showcase how these rates have shaped mortgage trends over time.
Corporate borrowing costs are similarly sensitive to interbank lending rate changes. Companies rely on borrowing to finance investments, expansions, and day-to-day operations. Higher interbank lending rates increase the cost of borrowing for corporations, potentially leading to reduced investment and slower economic growth. Conversely, lower rates can stimulate business activity by making borrowing more accessible and affordable. The insights gleaned from analyzing something akin to a “1 year libor historical chart” allows businesses to anticipate and adapt to potential shifts in the financial landscape. The significance of interbank lending rates underscores their crucial role in shaping the global financial environment. Although we’re not looking at a “1 year libor historical chart” directly, we are learning how such information is critical for understanding financial health.
Analyzing Peaks and Troughs in Benchmark Interest Rate Data
Throughout history, interbank lending rates have experienced periods of both significant highs and profound lows. Analyzing these fluctuations provides valuable insights into the health and stability of the global financial system. Understanding the underlying causes of these peaks and troughs is crucial for comprehending their consequences on the broader economy. A close look at a 1 year libor historical chart reveals these cyclical patterns.
Periods of elevated interbank lending rates are often associated with economic uncertainty or financial stress. Heightened risk aversion among lending institutions can drive up borrowing costs, reflecting concerns about the creditworthiness of counterparties. These periods may coincide with economic downturns, geopolitical instability, or regulatory changes that impact the supply and demand for funds in the interbank market. When lending becomes more expensive between banks, this increase can be visualized using a 1 year libor historical chart, and often translates to higher costs for consumers and businesses seeking loans.
Conversely, periods of low interbank lending rates typically occur during times of economic expansion or when central banks implement accommodative monetary policies. When economic conditions are favorable and confidence is high, lending institutions are more willing to extend credit at lower rates. Furthermore, central bank interventions, such as lowering policy interest rates or injecting liquidity into the financial system, can also contribute to a decline in interbank lending rates. The visual representation of these low periods, as shown in a 1 year libor historical chart, can indicate a period of easier access to capital and potentially increased economic activity. Examining a 1 year libor historical chart allows stakeholders to understand these changes.
Understanding the Transition Away from Legacy Benchmarks
The financial landscape is undergoing a significant transformation with the phasing out of established interbank lending benchmarks. This shift is driven by a desire for increased transparency and robustness in these crucial rates. Concerns about the integrity and reliability of older benchmarks have prompted the development and adoption of alternative reference rates. This evolution is reshaping how financial contracts are priced and managed globally, impacting a wide range of financial instruments and transactions. The transition away from legacy benchmarks represents a fundamental change in the structure of financial markets. This article helps understand the historical context, though it doesn’t directly display a 1 year libor historical chart.
One of the primary drivers behind this transition is the need for benchmarks that are less susceptible to manipulation and more reflective of actual market transactions. Newer benchmarks are often based on a broader range of data sources and incorporate more robust methodologies. This helps to ensure greater accuracy and reliability. The move towards more secure lending rate benchmarks aims to foster greater confidence in the financial system and reduce the risk of future crises. It is important to understand the history which can be glimpsed by reviewing a 1 year libor historical chart.
The implications of this transition are far-reaching, affecting everything from derivatives contracts to mortgage rates. Financial institutions and market participants are actively working to adapt to the new environment. This involves updating systems, revising contracts, and developing new risk management strategies. While the transition presents challenges, it also offers opportunities to enhance the efficiency and stability of financial markets. Viewing a 1 year libor historical chart allows one to grasp the magnitude of changes over time and the context for the current transition. The ongoing shift underscores the dynamic nature of the financial system and the importance of continuous adaptation to new realities. Those tracking 1 year libor historical chart data will find these trends invaluable in understanding market shifts.
Predicting Future Trends in Interbank Lending
Forecasting the future of interbank lending rates presents a complex challenge, influenced by a myriad of interconnected global factors. Predicting precise movements is inherently difficult, yet understanding the forces at play can offer valuable insights. Examining current economic conditions and considering expert forecasts becomes essential for anyone watching financial markets. While a precise “1 year libor historical chart” cannot predict future values, the chart illustrates that historical patterns rarely repeat exactly. Analyzing these patterns provides context.
Several key elements shape the trajectory of interbank lending rates. Prevailing economic conditions, including growth rates, inflation levels, and employment figures, exert considerable influence. Central bank policies, particularly decisions regarding benchmark interest rates and quantitative easing, also play a pivotal role. Geopolitical events, trade tensions, and regulatory changes can introduce volatility and uncertainty. Expert forecasts, derived from economic models and market analysis, offer valuable perspectives, but they should be viewed with caution, acknowledging the inherent limitations of predictive models. Monitoring a “1 year libor historical chart” provides a foundation for understanding these predictions.
Given the uncertainties, a prudent approach involves considering a range of potential scenarios. Stress testing financial models under various assumptions allows for the assessment of potential risks and opportunities. Staying informed about global economic developments, monitoring central bank communications, and consulting with financial professionals are crucial steps. The legacy of benchmarks, such as that displayed in a “1 year libor historical chart,” shows the importance of adaptability. The financial landscape is constantly evolving, and a flexible, informed approach is paramount for navigating the complexities of interbank lending in the years to come. A “1 year libor historical chart” acts as a reminder of past volatility and the need for careful planning.
The Ongoing Importance of Monitoring Lending Rates
Monitoring interbank lending rates remains crucial for individuals, businesses, and investors alike. These rates serve as vital indicators of the overall health and stability of the financial system, influencing a wide array of financial decisions. Understanding their fluctuations can provide valuable insights into the direction of the economy and potential risks or opportunities.
Interbank lending rates, including benchmarks which one might observe in a 1 year libor historical chart, have a direct bearing on borrowing costs across various sectors. For individuals, these rates can impact mortgage rates, credit card interest rates, and personal loan rates. Businesses rely on interbank lending rates to determine the cost of financing investments, expansions, and day-to-day operations. Investors also keenly watch these rates as they can influence bond yields, stock valuations, and overall market sentiment. Analyzing a 1 year libor historical chart and similar data helps stakeholders make informed choices.
In essence, interbank lending rates act as a barometer of economic conditions. By staying informed about their movements and understanding the factors that drive them, individuals, businesses, and investors can better navigate the financial landscape. The ability to interpret a 1 year libor historical chart, or any similar representation of lending rate trends, is a valuable skill in today’s complex financial world, enabling more strategic and informed financial planning and risk management.