Navigating the Complex World of SOFR Swap Rates
In the financial markets, the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR) has emerged as a crucial benchmark rate, playing a vital role in determining the cost of borrowing and lending. As a result, understanding short-term interest rate swaps, particularly the 1-month SOFR swap rate, is essential for making informed investment decisions. The significance of SOFR lies in its ability to provide a more accurate representation of the market’s overnight borrowing costs, making it a reliable indicator of market conditions. In this article, we will delve into the world of SOFR swap rates, exploring the mechanics, applications, and benefits of the 1-month SOFR swap rate, as well as its potential future developments.
What is a 1-Month SOFR Swap Rate and How Does it Work?
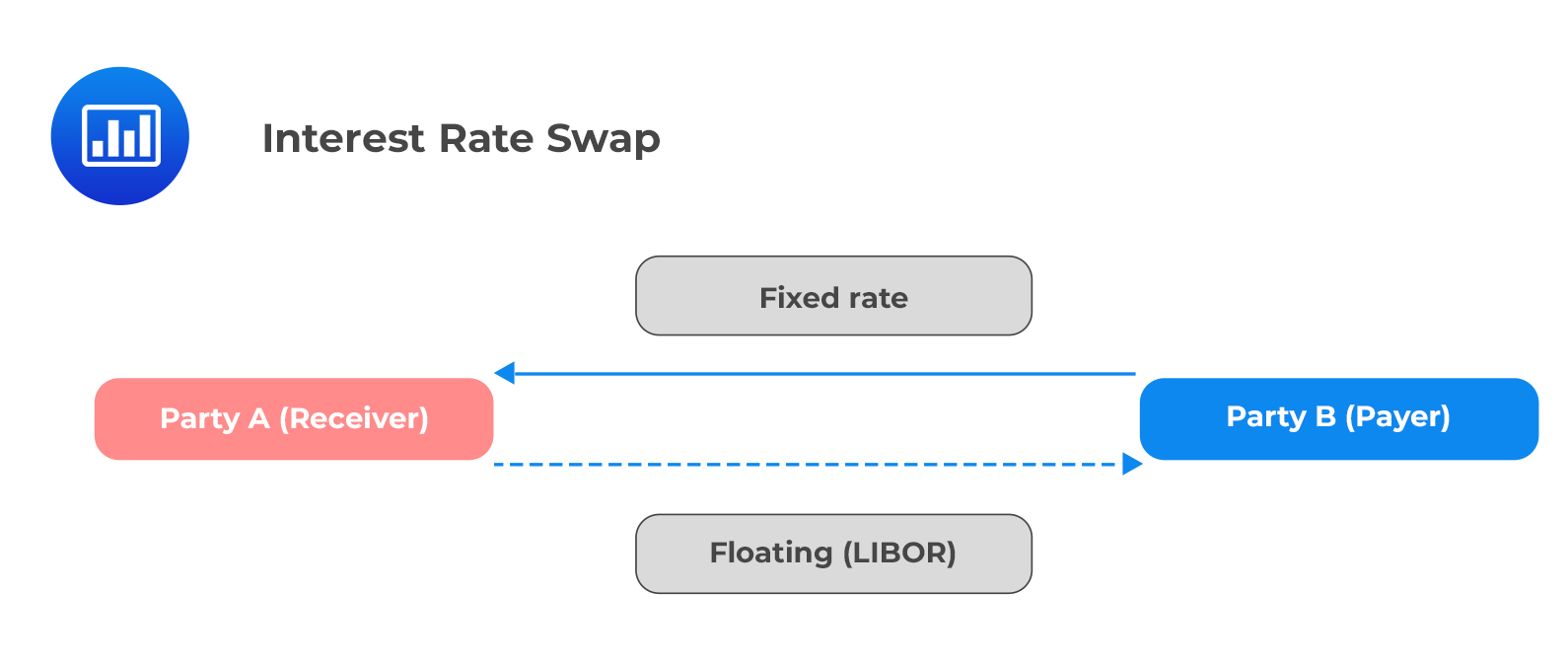
A 1-month SOFR swap rate is a type of short-term interest rate swap that allows parties to exchange fixed and floating interest payments based on the Secured Overnight Financing Rate (SOFR). This financial instrument is essential for hedging and risk management, as it enables companies to mitigate the risks associated with fluctuations in short-term interest rates. The 1-month SOFR swap rate is calculated as the fixed rate that equates the present value of the fixed leg with the present value of the floating leg, based on the SOFR index. In practice, this means that one party agrees to pay a fixed rate, while the other party pays a floating rate based on the SOFR, typically plus a spread. By understanding how 1-month SOFR swap rates work, companies can better navigate the complexities of short-term interest rate markets and make more informed investment decisions.
How to Calculate a 1-Month SOFR Swap Rate: A Step-by-Step Guide
Calculating a 1-month SOFR swap rate involves a series of steps that require a deep understanding of financial markets and mathematical concepts. To help readers navigate this complex process, we will provide a step-by-step guide on how to calculate a 1-month SOFR swap rate.
Step 1: Determine the SOFR Index
The first step in calculating a 1-month SOFR swap rate is to determine the SOFR index, which is based on the secured overnight financing rate. This rate is published daily by the New York Federal Reserve and reflects the cost of borrowing cash overnight, collateralized by U.S. Treasury securities.
Step 2: Determine the Fixed Leg
The fixed leg of the swap is the series of fixed interest payments made by one party to the other. To calculate the fixed leg, you need to determine the fixed rate, which is typically quoted as a spread over the SOFR index.
Step 3: Determine the Floating Leg
The floating leg of the swap is the series of floating interest payments made by the other party. To calculate the floating leg, you need to determine the SOFR rate plus a spread, which is typically quoted as a basis point spread over the SOFR index.
Step 4: Calculate the Present Value of the Fixed Leg
Using the fixed rate and the relevant discount factors, calculate the present value of the fixed leg. This involves discounting the fixed interest payments to their present value using the relevant yield curve.
Step 5: Calculate the Present Value of the Floating Leg
Using the SOFR rate and the relevant discount factors, calculate the present value of the floating leg. This involves discounting the floating interest payments to their present value using the relevant yield curve.
Step 6: Equate the Present Values
The final step is to equate the present value of the fixed leg with the present value of the floating leg. This involves solving for the fixed rate that makes the present values of both legs equal.
By following these steps, you can calculate a 1-month SOFR swap rate, which is essential for hedging and risk management in financial markets. Remember to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in SOFR swap rates to ensure accurate calculations and informed investment decisions.
Understanding the Factors that Influence 1-Month SOFR Swap Rates
The 1-month SOFR swap rate is influenced by a complex array of factors, including market conditions, economic indicators, and regulatory changes. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed investment decisions and navigating the complexities of short-term interest rate markets.
Market Conditions
The 1-month SOFR swap rate is heavily influenced by market conditions, such as supply and demand imbalances, liquidity, and volatility. For example, during times of high market stress, the 1-month SOFR swap rate may increase as investors seek safer assets, leading to a decrease in liquidity and an increase in borrowing costs.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators, such as GDP growth, inflation, and employment rates, also play a significant role in shaping the 1-month SOFR swap rate. For instance, a strong economy with low unemployment and rising inflation may lead to higher interest rates, which in turn can increase the 1-month SOFR swap rate.
Regulatory Changes
Regulatory changes, such as those implemented by the Federal Reserve, can also impact the 1-month SOFR swap rate. For example, changes to monetary policy, such as interest rate hikes or quantitative easing, can influence the 1-month SOFR swap rate by affecting the availability of credit and the overall direction of interest rates.
Other Factors
Other factors that can influence the 1-month SOFR swap rate include geopolitical events, natural disasters, and changes in investor sentiment. These factors can lead to sudden and unexpected changes in the 1-month SOFR swap rate, making it essential for investors to stay informed and adapt to changing market conditions.
In conclusion, the 1-month SOFR swap rate is influenced by a complex array of factors, including market conditions, economic indicators, and regulatory changes. By understanding these factors, investors can better navigate the complexities of short-term interest rate markets and make more informed investment decisions.
The Benefits of Using 1-Month SOFR Swap Rates in Financial Markets
The 1-month SOFR swap rate has become an essential tool in financial markets, offering a range of benefits to investors, hedgers, and speculators alike. By understanding the advantages of using 1-month SOFR swap rates, market participants can optimize their investment strategies and navigate the complexities of short-term interest rate markets.
Improved Risk Management
One of the primary benefits of using 1-month SOFR swap rates is improved risk management. By hedging against potential interest rate fluctuations, investors can reduce their exposure to market volatility and protect their investments from unexpected changes in interest rates.
Enhanced Liquidity
The 1-month SOFR swap rate also enhances liquidity in financial markets, providing investors with a deeper and more efficient market for short-term interest rate swaps. This increased liquidity enables market participants to enter and exit positions more easily, reducing transaction costs and improving overall market efficiency.
Increased Transparency
Another key benefit of using 1-month SOFR swap rates is increased transparency. By providing a standardized and widely accepted benchmark rate, the 1-month SOFR swap rate enables investors to compare and evaluate different investment opportunities more effectively, making it easier to make informed investment decisions.
Better Pricing and Valuation
The 1-month SOFR swap rate also facilitates better pricing and valuation of financial instruments, such as derivatives and securities. By providing a reliable and consistent benchmark rate, the 1-month SOFR swap rate enables investors to more accurately price and value their investments, reducing the risk of mispricing and improving overall market stability.
In summary, the 1-month SOFR swap rate offers a range of benefits to investors and market participants, including improved risk management, enhanced liquidity, increased transparency, and better pricing and valuation. By understanding these advantages, investors can optimize their investment strategies and navigate the complexities of short-term interest rate markets with confidence.
Real-World Applications of 1-Month SOFR Swap Rates
The 1-month SOFR swap rate has a wide range of real-world applications in financial markets, including hedging, speculation, and arbitrage. By understanding these applications, investors and market participants can better utilize the 1-month SOFR swap rate to achieve their investment objectives.
Hedging
One of the primary applications of the 1-month SOFR swap rate is hedging. Companies and investors can use the 1-month SOFR swap rate to hedge against potential interest rate fluctuations, reducing their exposure to market volatility and protecting their investments from unexpected changes in interest rates.
Speculation
The 1-month SOFR swap rate also provides opportunities for speculation. Investors can use the 1-month SOFR swap rate to speculate on future interest rate movements, taking positions that reflect their market views and potentially earning profits from correct predictions.
Arbitrage
Another application of the 1-month SOFR swap rate is arbitrage. By identifying mispricings in the market, investors can use the 1-month SOFR swap rate to exploit these opportunities, earning profits from the differences in prices between two or more markets.
Portfolio Management
The 1-month SOFR swap rate can also be used in portfolio management, enabling investors to optimize their investment portfolios and achieve their desired risk-return profiles. By incorporating the 1-month SOFR swap rate into their investment strategies, investors can better manage their exposure to interest rate risk and improve overall portfolio performance.
Example: A company with a floating-rate loan can use the 1-month SOFR swap rate to hedge against potential interest rate increases, reducing its exposure to market volatility and protecting its cash flows.
In conclusion, the 1-month SOFR swap rate has a wide range of real-world applications in financial markets, including hedging, speculation, arbitrage, and portfolio management. By understanding these applications, investors and market participants can better utilize the 1-month SOFR swap rate to achieve their investment objectives and navigate the complexities of short-term interest rate markets.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Working with 1-Month SOFR Swap Rates
When working with 1-month SOFR swap rates, it is essential to avoid common mistakes that can lead to inaccurate calculations, mispriced trades, and potential losses. By understanding these pitfalls, investors and market participants can minimize their risk exposure and optimize their investment strategies.
Incorrectly Calculating the 1-Month SOFR Swap Rate
One common mistake is incorrectly calculating the 1-month SOFR swap rate. This can occur due to errors in inputting data, misunderstanding the formula, or failing to account for compounding. To avoid this mistake, it is crucial to carefully follow the step-by-step guide for calculating the 1-month SOFR swap rate and to double-check calculations.
Failing to Account for Market Conditions
Another mistake is failing to account for market conditions that can impact the 1-month SOFR swap rate. This includes ignoring changes in economic indicators, regulatory updates, and shifts in market sentiment. To avoid this mistake, investors should stay up-to-date with market developments and adjust their investment strategies accordingly.
Overlooking Counterparty Risk
Counterparty risk is another common pitfall when working with 1-month SOFR swap rates. This occurs when investors fail to assess the creditworthiness of their counterparties, leading to potential defaults or non-payment. To avoid this mistake, investors should conduct thorough due diligence on their counterparties and implement robust risk management strategies.
Misinterpreting the 1-Month SOFR Swap Rate
Misinterpreting the 1-month SOFR swap rate is another common mistake. This can occur when investors misunderstand the implications of the rate or fail to consider its limitations. To avoid this mistake, investors should have a deep understanding of the 1-month SOFR swap rate and its applications in hedging and risk management.
By avoiding these common mistakes, investors and market participants can optimize their use of 1-month SOFR swap rates and achieve their investment objectives. It is essential to stay vigilant, conduct thorough research, and implement robust risk management strategies to minimize the risk of errors and maximize returns.
Staying Ahead of the Curve: The Future of 1-Month SOFR Swap Rates
The use of 1-month SOFR swap rates is expected to continue to evolve in response to technological advancements, regulatory changes, and shifting market conditions. As the financial landscape continues to adapt to the post-LIBOR era, the importance of understanding 1-month SOFR swap rates will only increase.
Technological Advancements
The increasing adoption of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and blockchain technology is likely to revolutionize the way 1-month SOFR swap rates are calculated, traded, and managed. These advancements will enable faster, more accurate, and more efficient processing of complex financial data, leading to improved risk management and increased transparency.
Regulatory Changes
Regulatory bodies are expected to continue to refine and update their guidelines for the use of 1-month SOFR swap rates, ensuring that financial institutions and market participants are adequately prepared for the transition away from LIBOR. These changes will likely lead to increased standardization and consistency in the calculation and application of 1-month SOFR swap rates.
Market Developments
The ongoing evolution of financial markets will also impact the use of 1-month SOFR swap rates. As market conditions change, the demand for 1-month SOFR swap rates is likely to increase, driving innovation and growth in the development of new financial products and services.
Increased Adoption
The use of 1-month SOFR swap rates is expected to become more widespread, as financial institutions and market participants increasingly recognize the benefits of this alternative reference rate. This increased adoption will lead to improved liquidity, reduced counterparty risk, and enhanced risk management capabilities.
In conclusion, the future of 1-month SOFR swap rates looks bright, with technological advancements, regulatory changes, and market developments all contributing to their increased adoption and importance in financial markets. By staying ahead of the curve and understanding the evolving landscape of 1-month SOFR swap rates, investors and market participants can position themselves for success in the years to come.